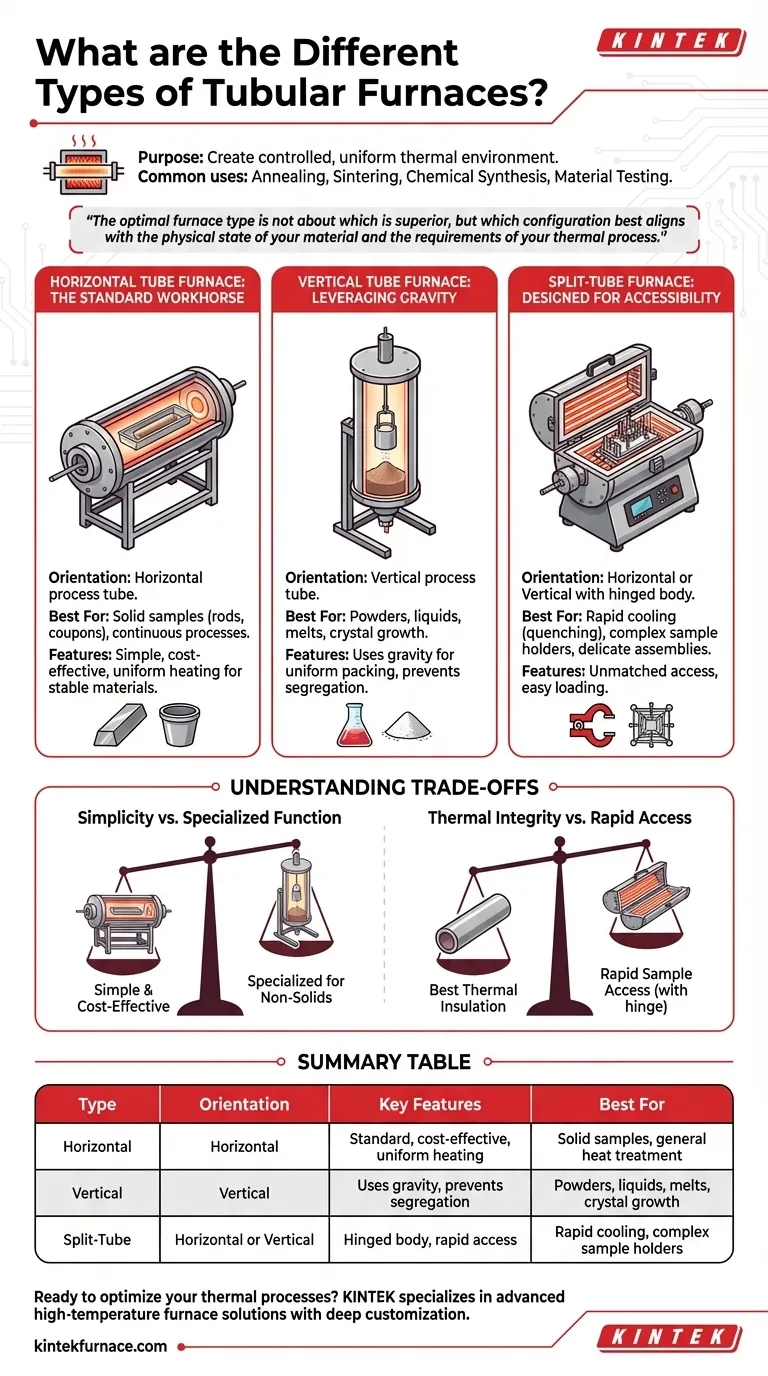
In essence, tubular furnaces are categorized by their physical orientation and construction. The three primary types are horizontal, vertical, and split-tube furnaces. Each design is engineered to solve specific challenges related to how a material is held, heated, and accessed, making the choice of furnace type a critical decision based on your specific process needs.
The optimal furnace type is not about which is superior, but which configuration—horizontal, vertical, or split-tube—best aligns with the physical state of your material and the requirements of your thermal process.

The Purpose of a Tubular Furnace
A tubular furnace is a high-temperature electric heating device that creates a precisely controlled thermal environment within a cylindrical cavity. Its core function is to achieve and maintain a uniform temperature zone for processing materials.
Why It's a Critical Tool
The primary advantage of a tubular furnace is its ability to create a contained, stable, and often atmospheric-controlled environment. This is essential for a wide range of scientific and industrial applications.
Common uses include annealing, sintering, chemical synthesis, material testing, and heat treatment of metals and ceramics. They are staples in research labs, academic institutions, and small-batch manufacturing.
A Breakdown of Furnace Types
The classification of a tubular furnace is defined by the orientation of its process tube and whether the furnace body can be opened.
The Horizontal Tube Furnace: The Standard Workhorse
This is the most common configuration, where the process tube is situated horizontally. It is the default choice for a vast number of general-purpose applications.
Horizontal furnaces are ideal for processing solid samples, such as rods, coupons, or crucibles containing stable materials. They are also well-suited for continuous processes where materials are pushed or pulled through the tube.
The Vertical Tube Furnace: Leveraging Gravity
In this design, the process tube is oriented vertically. This seemingly simple change is critical for specific types of materials and processes.
Vertical furnaces are essential when working with powders, liquids, or melts that would be difficult to contain or would react unevenly in a horizontal orientation. Gravity helps ensure uniform packing and prevents segregation, making them ideal for certain crystal growth methods and material synthesis.
The Split-Tube Furnace: Designed for Accessibility
A split-tube furnace features a hinged body that allows it to be opened lengthwise. This design can be applied to both horizontal and vertical orientations.
Its main benefit is unmatched sample access. This is crucial for processes requiring very rapid cooling (quenching), as the furnace can be opened to expose the sample to ambient temperatures. It also simplifies the loading of delicate or complex sample assemblies that cannot be easily slid into a solid tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing simplicity, cost, and process-specific needs. No single type is universally superior.
Simplicity vs. Specialized Function
A standard horizontal furnace is often the simplest and most cost-effective option. Its straightforward design makes it a robust tool for countless applications.
Vertical furnaces introduce more complexity in mounting and sample handling but are indispensable for processes involving non-solid materials where gravity is a key factor.
Thermal Integrity vs. Rapid Access
A solid, single-piece furnace body generally offers the best thermal insulation and temperature uniformity because it is a continuous, sealed cylinder.
A split-tube furnace introduces a physical seam. While modern designs minimize heat loss, the hinge mechanism adds mechanical complexity and cost in exchange for the immense benefit of rapid sample access and easy loading.
How to Select the Right Furnace
Your final choice should be dictated entirely by the demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment of solid materials: A horizontal tube furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is working with powders, melts, or specific crystal growth methods: A vertical tube furnace is necessary to properly manage the material.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample cooling or using complex sample holders: A split-tube furnace provides unmatched accessibility that justifies its design.
Understanding these fundamental designs empowers you to align your equipment precisely with your scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Type | Orientation | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Horizontal | Standard design, cost-effective, uniform heating | Solid samples, general heat treatment, continuous processes |
| Vertical | Vertical | Uses gravity, prevents segregation, uniform packing | Powders, liquids, melts, crystal growth |
| Split-Tube | Horizontal or Vertical | Hinged body, rapid access, easy loading | Rapid cooling, complex sample holders, delicate assemblies |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today for expert guidance and tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















