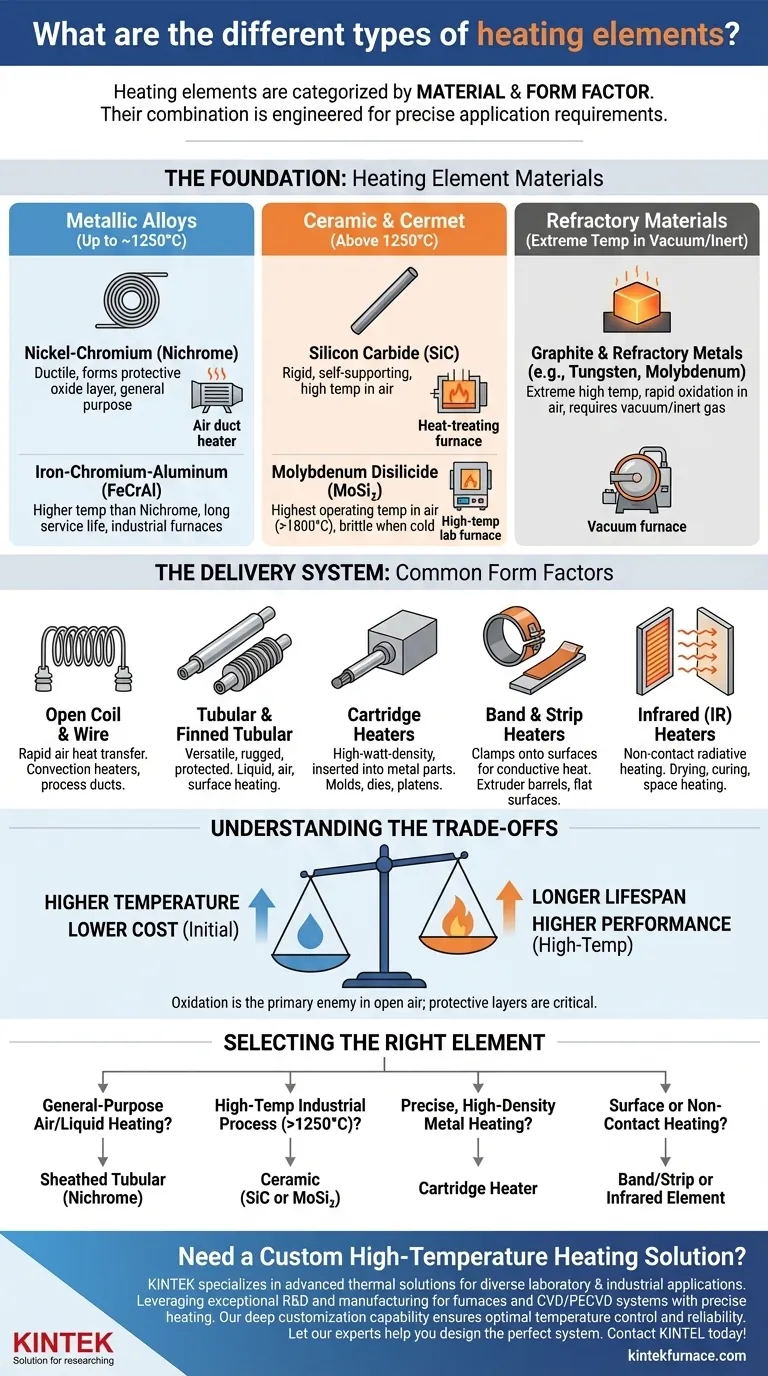
Heating elements are primarily categorized in two ways: by the material they are made from and by their physical form factor. Common materials include metal alloys like nickel-chromium (Nichrome) and ceramics like silicon carbide, while common forms include simple wires, protected tubular elements, and specialized cartridge heaters. The specific combination of material and form is engineered to meet precise application requirements.
The core principle to understand is that an element's material determines its maximum temperature and resistance to oxidation, while its physical shape dictates how that heat is delivered to a target system—be it air, liquid, or a solid surface.
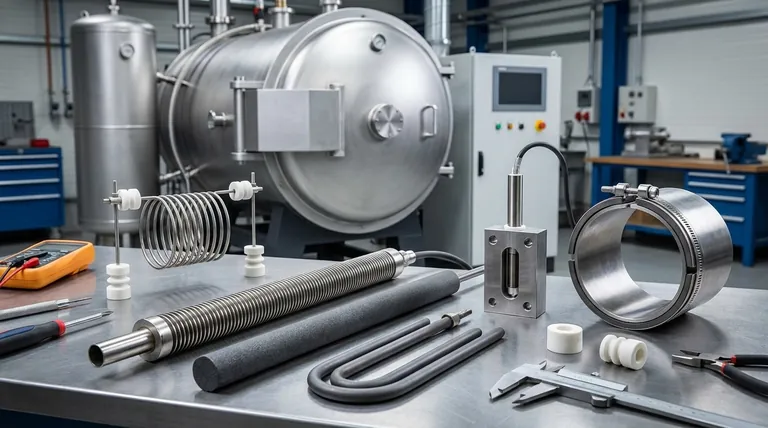

The Foundation: Heating Element Materials
The material is the heart of any heating element. Its properties define the operational limits, lifespan, and efficiency of the entire heating system. Materials are chosen based on their electrical resistance, ability to withstand high temperatures, and resistance to environmental degradation.
Metallic Alloys (The Workhorses)
Metallic alloys are the most common materials used for general-purpose heating up to around 1250°C (2280°F).
- Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome): This is a widely used alloy known for its ductility and ability to form a stable, protective layer of chromium oxide when heated, which prevents further oxidation and element failure.
- Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl): Often sold under trade names like Kanthal, this alloy can operate at higher temperatures than Nichrome. It also forms a protective oxide layer (aluminum oxide) that contributes to a long service life.
Ceramic & Cermet Composites (The High-Temperature Specialists)
When temperatures exceed the limits of metallic alloys, ceramic-based materials are required.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): These elements are rigid, self-supporting rods or tubes capable of operating in air at very high temperatures. They are common in industrial furnaces for heat treating and glass processing.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): MoSi₂ elements offer the highest operating temperatures in air, often exceeding 1800°C (3270°F). They are brittle at room temperature but become pliable at high heat, forming a protective silica glass layer.
Refractory Materials (The Extreme Environment Experts)
For the most extreme temperatures, particularly in vacuum or inert atmospheres, pure refractory metals and graphite are used.
- Graphite: An excellent high-temperature material, but it will rapidly oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen. It is therefore restricted to vacuum furnaces or those filled with a protective, non-reactive gas.
- Refractory Metals: Metals like tungsten and molybdenum have extremely high melting points but also suffer from high oxidation rates, limiting their use to oxygen-free environments.
The Delivery System: Common Form Factors
The physical shape, or form factor, of a heating element is designed to transfer heat efficiently into a specific substance or space.
Open Coil & Wire Elements
This is the simplest form, consisting of a bare resistance wire often supported by ceramic insulators. It allows for direct and rapid heat transfer to air, making it common in convection heaters and industrial process air ducts.
Tubular & Finned Tubular Heaters
These are highly versatile and rugged. The resistance coil is encased in a metal sheath (like stainless steel or Incoloy) and insulated from the sheath with compacted magnesium oxide powder. This protects the element from moisture and mechanical damage, making it suitable for heating liquids, air, and surfaces. Fins can be added to increase the surface area for better air heating.
Cartridge Heaters
A cartridge heater is a tube-shaped, heavy-duty element designed for high-watt-density heating. It is inserted into drilled holes in metal parts, such as dies, platens, and molds, to provide concentrated, conductive heat from within.
Band & Strip Heaters
These elements are designed to clamp directly onto a surface. Band heaters are circular and used to heat cylindrical parts like the barrels of plastic extruders. Strip heaters are flat and used to heat flat surfaces via conduction.
Infrared (IR) Heaters
Infrared elements transfer heat primarily through electromagnetic radiation rather than conduction or convection. They are ideal for non-contact heating, such as drying paint, curing coatings, or heating people in large open spaces, as they heat the target object directly without needing to heat the air in between.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing competing factors. An ideal choice for one application can be a catastrophic failure in another.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
As a general rule, the hotter you run an element, the shorter its lifespan will be. All materials degrade over time, and high temperatures accelerate this process. Running an element even 50°C below its maximum rated temperature can dramatically increase its service life.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between cost and temperature capability. A simple Nichrome wire is inexpensive, but it cannot perform in the high-temperature environments where a Molybdenum Disilicide element excels. The initial cost must be weighed against the operational requirements and expected lifespan.
The Critical Role of Oxidation
For most elements operating in open air, oxidation is the primary enemy. The protective oxide layers formed by Nichrome and FeCrAl alloys are what allow them to survive. Any disruption to this layer leads to rapid failure. This is also why materials like graphite and tungsten are strictly limited to vacuum or inert gas applications.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your ideal heating element is the one that safely and efficiently meets the specific thermal demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose air or liquid heating: A sheathed tubular element made with a Nichrome alloy offers the best balance of cost, durability, and safety.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processes (>1250°C): You must use specialized materials like Silicon Carbide or Molybdenum Disilicide in a form suited for your furnace.
- If your primary focus is precise, high-density heating of a metal block or mold: A cartridge heater is the purpose-built solution designed for insertion and conductive heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is heating a surface or non-contact drying: Choose a band or strip heater for direct contact, or an infrared element for efficient non-contact radiative heating.
Matching the right material and form factor to your application is the key to designing an efficient and reliable heating system.
Summary Table:
| Category | Material/Form Factor | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) | Good ductility, forms protective oxide layer, up to ~1250°C | General-purpose air/liquid heating, convection heaters |
| Metallic Alloys | Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) | Higher temp than Nichrome, long service life | Industrial furnaces, high-temp process heating |
| Ceramics | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Rigid, self-supporting, very high temp in air | Industrial furnaces for heat treating, glass processing |
| Ceramics | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Highest operating temp in air (>1800°C), brittle at room temp | Extreme high-temperature industrial furnaces |
| Refractory | Graphite / Tungsten / Molybdenum | Extreme high temp, but oxidizes rapidly; requires vacuum/inert gas | Vacuum furnaces, high-temp research |
| Form Factor | Tubular / Finned Tubular | Sheathed, rugged, versatile, protected from environment | Liquid/air/surface heating, industrial processes |
| Form Factor | Cartridge Heater | Tube-shaped, high-watt-density, inserted into metal | Heating molds, platens, dies via conduction |
| Form Factor | Band / Strip Heater | Clamps onto surfaces for direct conductive heating | Extruder barrels, surface heating |
| Form Factor | Infrared (IR) Heater | Non-contact heating via electromagnetic radiation | Drying paints, curing coatings, space heating |
Need a Custom High-Temperature Heating Solution?
Selecting the right heating element is critical for the performance and longevity of your equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal solutions for diverse laboratory and industrial applications.
Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, we provide a comprehensive product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—all designed with precision heating at their core.
Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely engineer heating systems to meet your unique experimental or process requirements, ensuring optimal temperature control, efficiency, and reliability.
Let our experts help you design the perfect heating system. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















