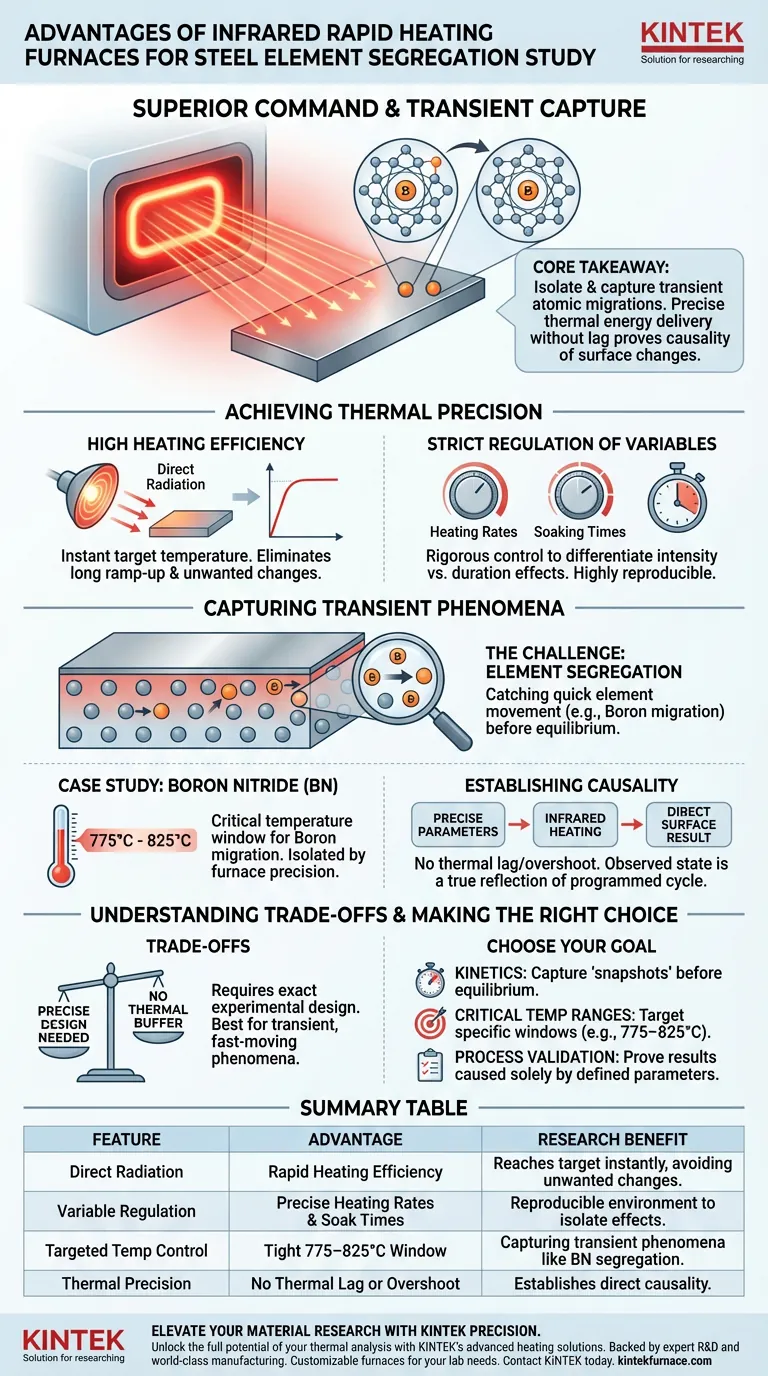
Infrared Rapid Heating Furnaces offer superior command over thermal processing compared to conventional heating methods. They provide exceptional heating efficiency and precise temperature regulation, allowing researchers to strictly dictate heating rates and soaking durations.
Core Takeaway The definitive advantage of this technology is the ability to isolate and capture transient atomic migrations. By delivering exact thermal energy without significant lag, researchers can prove that observed surface changes are the direct result of specific annealing parameters, rather than artifacts of uncontrolled heating.

Achieving Thermal Precision
High Heating Efficiency
The fundamental benefit of an Infrared Rapid Heating Furnace is its efficiency. Unlike convection-based systems that rely on heating the air around a sample, infrared radiation transfers energy directly to the material.
This allows the system to reach target temperatures almost instantly. It eliminates long ramp-up periods where unwanted microstructural changes might occur.
Strict Regulation of Variables
The technology enables rigorous control over two critical variables: heating rates and soaking times. This precision is necessary to differentiate between effects caused by the duration of heat exposure versus the intensity of the temperature itself.
By controlling these factors, researchers can create a highly reproducible experimental environment.
Capturing Transient Phenomena
The Challenge of Element Segregation
Studying how elements separate and move within a material requires catching them in the act. In steel materials, elements like Boron migrate from the internal matrix to the surface during heating.
This migration is often transient, meaning it happens quickly and can be missed if the heating source is sluggish or imprecise.
Case Study: Boron Nitride (BN)
The primary reference highlights the specific study of Boron Nitride (BN) segregation. To understand how Boron moves, researchers must look at specific critical temperature windows.
The furnace allows for the isolation of the 775 to 825 degrees Celsius range. This is the critical window where Boron migration is most active and significant.
Establishing Causality
Because the furnace provides such tight control, researchers can confirm that surface products are the direct result of the specific parameters set.
There is no ambiguity regarding whether the segregation occurred during a slow cooling phase or an overshoot in temperature. The observed surface state is a true reflection of the programmed annealing cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Requirement for Precise Design
While the reference highlights the precision of the tool, this sensitivity implies a need for exact experimental design. Because the furnace reacts so quickly, there is no "thermal buffer" to smooth out errors in the heating profile.
Specificity of Application
The advantages described are most potent when studying transient or fast-moving phenomena. For steady-state processes where rapid heating rates are irrelevant, the advanced capabilities of an infrared system may exceed the necessities of the experiment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of an Infrared Rapid Heating Furnace, align your experimental goals with its strengths:
- If your primary focus is Kinetics: Utilize the rapid heating rates to capture "snapshots" of element migration before equilibrium is reached.
- If your primary focus is Critical Temperature Ranges: Use the precise regulation to target specific windows, such as the 775–825°C range for Boron, to isolate temperature-dependent behaviors.
- If your primary focus is Process Validation: Leverage the strict control of soaking times to prove that surface products are caused solely by your defined annealing parameters.
The Infrared Rapid Heating Furnace transforms the study of segregation from a general observation of final states into a precise analysis of atomic movement.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage | Research Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Radiation | Rapid heating efficiency | Reaches target temperature instantly, avoiding unwanted microstructural changes. |
| Variable Regulation | Precise heating rates & soak times | Creates a reproducible environment to isolate temperature vs. duration effects. |
| Targeted Temp Control | Tight 775–825°C window isolation | Crucial for capturing transient phenomena like Boron Nitride (BN) segregation. |
| Thermal Precision | No thermal lag or overshoot | Establishes direct causality between annealing parameters and surface products. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your thermal analysis with KINTEK’s advanced heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you are studying transient element segregation or complex kinetics, our furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Ensure every annealing cycle is a true reflection of your research parameters.
Ready to achieve superior thermal control? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Effect of BN Surface Segregation on Coatability in Hot-dip Galvanizing of B-added Steel. DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.isijint-2025-180
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is one of the primary functions of a muffle furnace in material analysis? Discover Its Role in Precise Ash Content Determination
- What are the main structural components of a box furnace? Essential Guide for Efficient Material Processing
- How should samples be placed inside the muffle furnace? Ensure Uniform Heating and Safety
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the significance of muffle furnaces in the ceramics industry? Unlock Precision and Purity for Superior Ceramics
- How does a high-temperature box furnace contribute to the accuracy of oxidation kinetics experiments? Achieve Precision
- What is the defining characteristic of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- Why is high-temperature calcination necessary for NiFe2O4? Optimize Spinel Formation with Industrial Muffle Furnaces



















