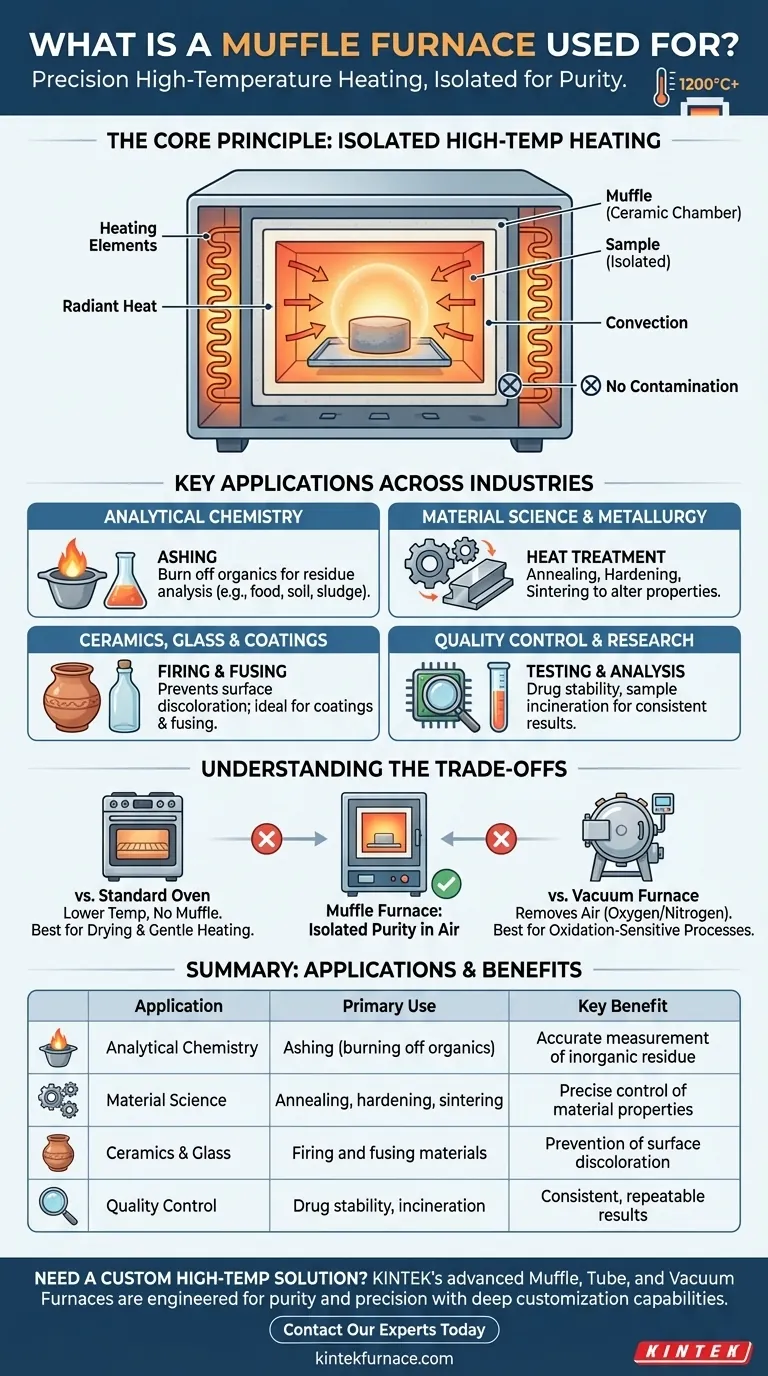
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for a wide range of material processing and testing applications. Its primary function is to heat a material to a precise, elevated temperature—often up to 1200°C (2192°F) or higher—while keeping it completely isolated from the heating source and any harmful byproducts of combustion. This ensures the sample remains pure and the process is highly controlled.
The core value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to get extremely hot, but its ability to do so within a controlled, isolated chamber. This "muffle" prevents contamination, ensuring that the results of a test or process are due to the heat alone, not a chemical reaction with the heating element or fuel exhaust.
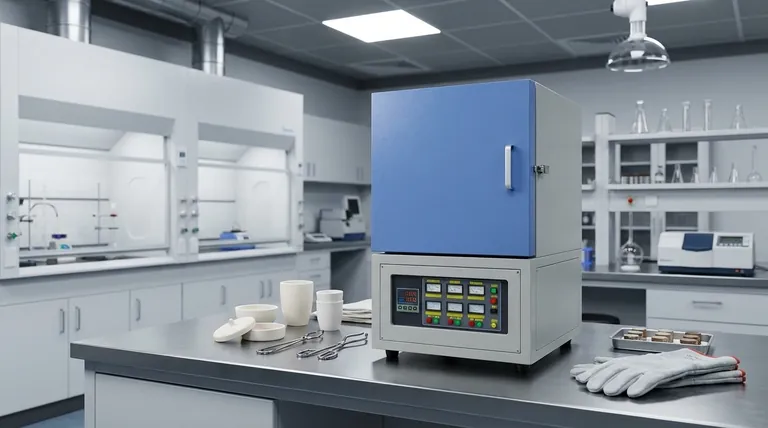

The Core Principle: Isolated High-Temperature Heating
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle" itself—an insulated internal chamber that contains the sample. Understanding this design reveals why it is the go-to instrument for so many critical applications.
What is a "Muffle"?
The muffle is a specialized box, often made of high-purity alumina or other ceramic materials, that sits inside the furnace. The heating elements heat the outside of this box.
The sample is placed inside the muffle, meaning it never comes into direct contact with the electric coils or gas flames that generate the heat. The heat is transferred through radiation and convection within this sealed chamber.
Preventing Process Contamination
This separation is critical for process purity. In a direct-fired furnace, byproducts from fuel combustion can react with the sample, altering its chemical composition.
Even in an electric furnace without a muffle, particles from the heating elements could flake off and contaminate the material. The muffle acts as a physical barrier, ensuring a clean heating environment.
Achieving Uniform & Precise Temperatures
By heating the entire muffle chamber, the furnace creates a highly uniform temperature zone. This ensures that the entire sample is heated evenly, which is crucial for repeatable material testing and consistent heat treatment processes.
Modern muffle furnaces use sophisticated controllers to precisely manage temperature ramps and holding times, offering a high degree of process control.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique combination of high heat and high purity makes muffle furnaces indispensable in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Analytical Chemistry & Environmental Testing
The most common application is ashing. This is the process of burning off all organic material in a sample at a controlled temperature to accurately measure the weight of the inorganic residue (ash).
This is fundamental for quality control in food science, polymer analysis, soil testing, and environmental sample assessment, such as determining the ash content in wastewater sludge.
Material Science & Metallurgy
Muffle furnaces are used for the heat treatment of metals to alter their physical and mechanical properties.
Key processes include annealing (softening a metal and relieving internal stresses), hardening (increasing strength), and sintering (fusing powdered materials together with heat, below their melting point).
Ceramics, Glass & Coatings
The high temperatures are ideal for firing ceramics and fusing glass. The controlled environment prevents discoloration or unwanted chemical reactions on the surface.
They are also used for applying enamel coatings to metals and for determining the proper firing temperatures for new ceramic formulations.
Research & Quality Control
In the pharmaceutical industry, furnaces are used for drug stability testing and quality control of inorganic ingredients. In biomedical fields, they can be used for the clean incineration of biological samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature job. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Muffle Furnace vs. Standard Oven
A standard laboratory oven typically operates at much lower temperatures and lacks the insulated muffle chamber. Ovens are for drying and gentle heating, while muffle furnaces are for high-temperature transformations like ashing or sintering.
Muffle Furnace vs. Vacuum Furnace
A muffle furnace excels at preventing contamination from the heating source. However, the sample is still heated in the presence of air (oxygen and nitrogen).
If a process is sensitive to oxidation or requires a completely inert environment, a vacuum furnace or a specialized controlled-atmosphere furnace is necessary. These instruments first remove the air and can backfill the chamber with a gas like argon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is removing organic material (ashing): The muffle furnace is the industry-standard tool for this exact purpose.
- If your primary focus is testing material durability at extreme heat: The muffle furnace provides a stable, repeatable, and clean environment for these tests.
- If your primary focus is altering metal properties in air (annealing, hardening): A muffle furnace offers the precise temperature control needed for metallurgical processes.
- If your primary focus is a process sensitive to oxygen: You must use a vacuum furnace or a controlled-atmosphere furnace, not a standard muffle furnace.
By understanding that a muffle furnace is designed for purity at high temperatures, you can confidently determine when it is the right instrument for your application.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing (burning off organic material) | Accurate measurement of inorganic residue |
| Material Science | Annealing, hardening, sintering of metals | Precise control of material properties |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing and fusing materials | Prevention of surface discoloration |
| Quality Control | Drug stability testing, sample incineration | Consistent, repeatable results |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your unique process?
KINTEK's advanced muffle furnaces are engineered for purity and precision. Whether your application requires ashing, heat treatment, or material testing, our Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum Furnaces are backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. We offer strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can provide the perfect high-temperature solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















