One of the most fundamental functions of a muffle furnace is to determine the inorganic ash content of a material. By heating a sample at high temperatures, the furnace burns away all organic matter, leaving behind only the non-combustible inorganic residue (ash) for weighing and further analysis.
The true value of a muffle furnace lies in its ability to provide an extremely hot, yet perfectly controlled and contamination-free, environment. This allows you to either break a material down to analyze its core components or build a new material up through thermal processing.

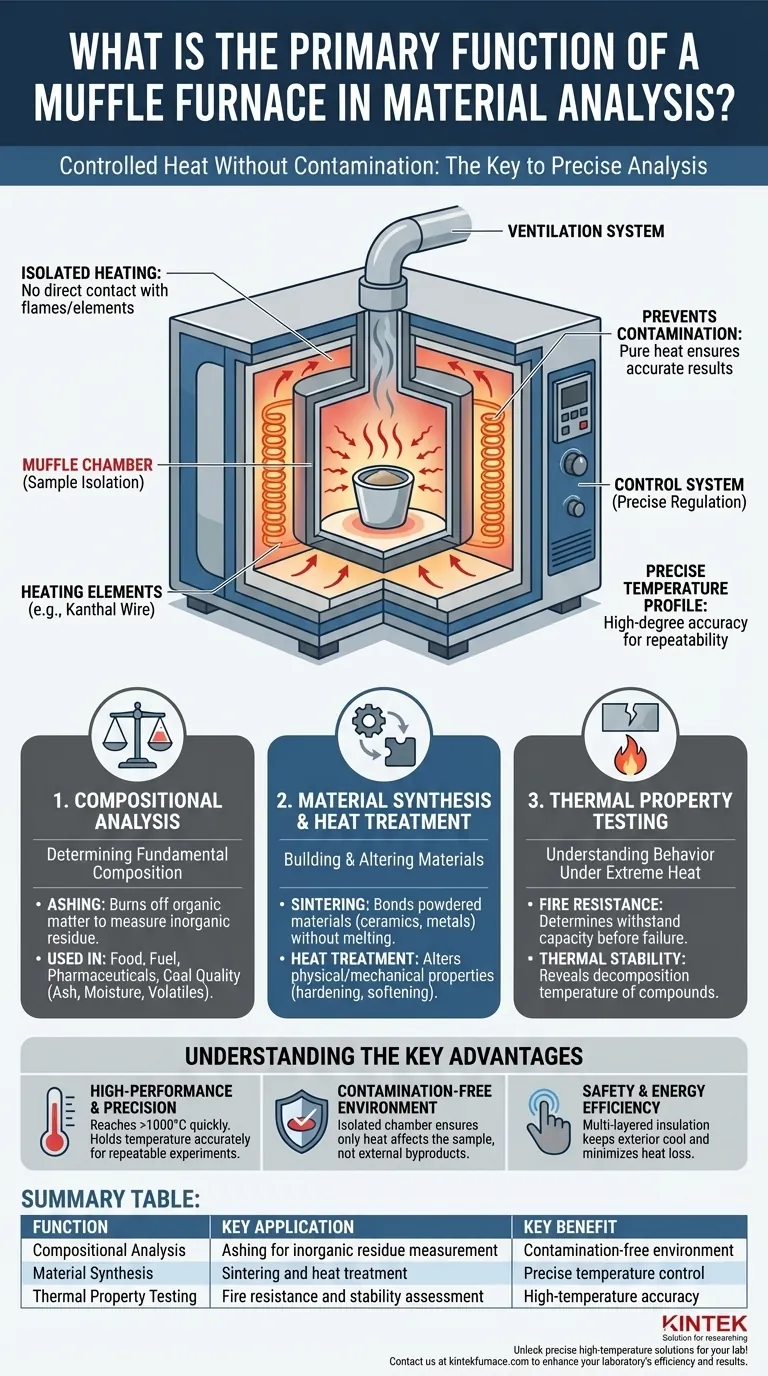
The Principle: Controlled Heat Without Contamination
A muffle furnace is not simply an oven. Its design is centered on isolating the sample from the source of heat, which is the key to its function in precise material analysis.
What is the "Muffle"?
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that holds the sample. This chamber is sealed off from the heating elements.
This design prevents any direct contact between the sample and the flames or electrical elements. It ensures the sample is heated purely through convection and radiation.
The primary benefit is preventing contamination. In direct-heating furnaces, byproducts of combustion or material from the heating elements could corrupt the sample, invalidating analytical results.
Core Components of the System
A muffle furnace operates as a complete system. Its key parts include the heating elements (like Kanthal wire) that generate the high temperatures and the insulated outer casing for safety and efficiency.
A critical component is the control system, which uses temperature sensors to precisely regulate and maintain the desired temperature profile for an experiment.
Many furnaces also include ventilation systems to safely expel any fumes or gases produced as the material is heated.
Key Applications in Material Analysis
The ability to provide clean, controlled heat makes the muffle furnace indispensable across various scientific and industrial fields. Its applications can be grouped into three main categories.
1. Compositional Analysis
This is the most common use. By subjecting a sample to high heat, you can determine its fundamental composition.
The primary example is ashing, where organic materials in food, fuel, or pharmaceuticals are burned off to measure the remaining inorganic content.
In fields like coal quality testing, it is used to determine not just ash content but also moisture levels and volatile content, which are critical indicators of fuel quality.
2. Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
Muffle furnaces are not just for breaking things down; they are also for building things up.
Sintering is a key process where powdered materials, like ceramics or metals, are heated to bond together and form a solid, dense object without melting.
They are also essential for heat treatment of metals and other materials to alter their physical and mechanical properties, such as hardening or softening them.
3. Thermal Property Testing
Understanding how a material behaves under extreme heat is crucial for engineering and safety.
Muffle furnaces are used for fire resistance testing to see how long a material can withstand high temperatures before failing.
They also help determine the thermal stability of chemical compounds, revealing the temperature at which they begin to decompose.
Understanding the Key Advantages
Using a muffle furnace offers distinct advantages over other heating methods, which is why it remains a laboratory staple. These benefits stem directly from its core design.
High-Performance and Precision
Muffle furnaces are engineered to reach very high temperatures (often over 1000°C) quickly and, more importantly, to hold that temperature with a high degree of accuracy.
This precision is essential for repeatable experiments and for processes that require a specific temperature profile.
Contamination-Free Environment
As mentioned, the isolated muffle chamber is the furnace's defining advantage. It guarantees that the only changes occurring in the sample are due to the heat being applied, not from external contaminants.
Safety and Energy Efficiency
Modern furnaces are built with advanced, multi-layered insulation. This not only makes them safer to operate by keeping the exterior cool but also improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific function of the muffle furnace depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is determining composition: Your goal is to use the furnace's clean, high heat to burn away organic components and accurately measure the inorganic residue.
- If your primary focus is creating or modifying materials: You will leverage the furnace's precise temperature control for processes like sintering or heat treatment to achieve desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is testing material durability: You will use the furnace to simulate extreme thermal conditions and observe how your material withstands high-temperature stress.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a versatile and fundamental tool for anyone needing to understand, create, or test materials at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Compositional Analysis | Ashing for inorganic residue measurement | Contamination-free environment |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering and heat treatment | Precise temperature control |
| Thermal Property Testing | Fire resistance and stability assessment | High-temperature accuracy |
Unlock precise high-temperature solutions for your lab with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures they meet your unique experimental needs for accurate material analysis and synthesis. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















