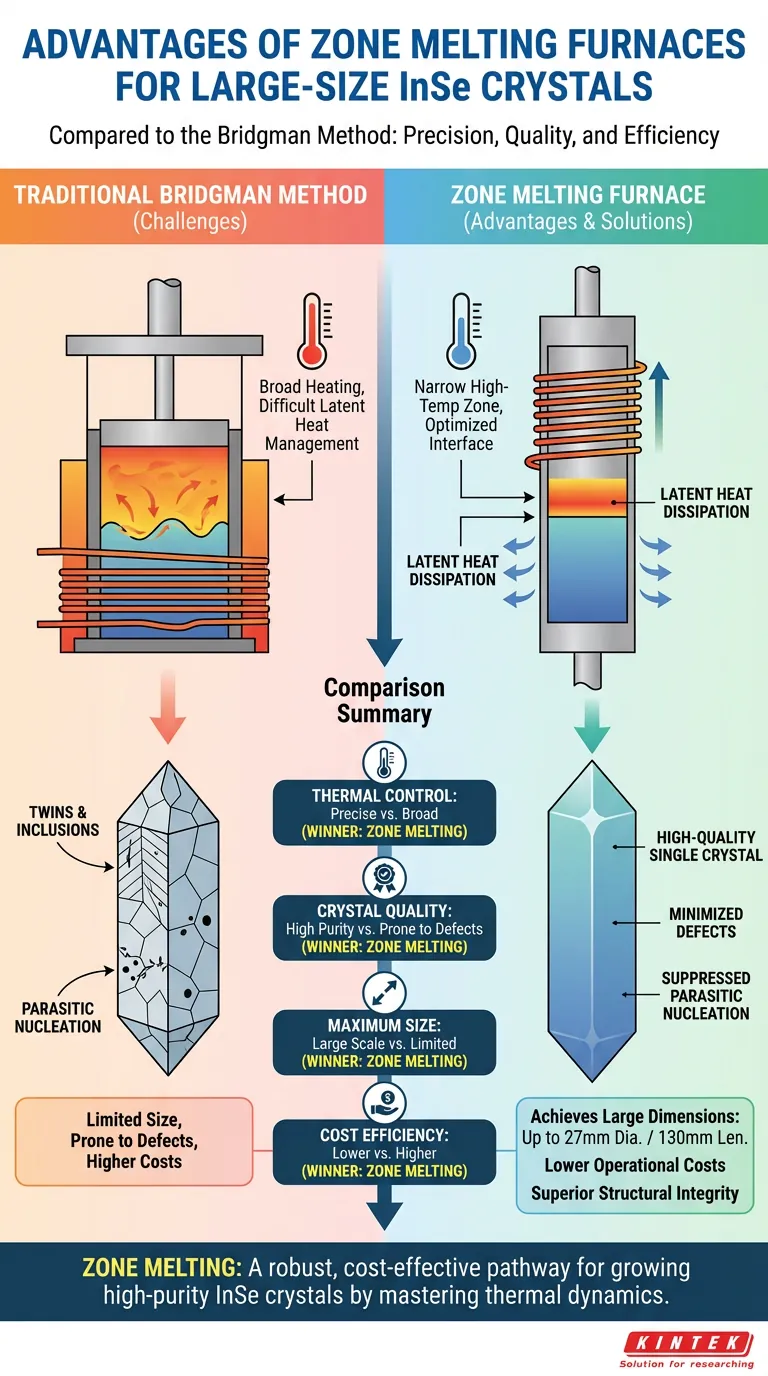
The zone melting furnace offers distinct advantages in thermal management and cost efficiency when compared to the Bridgman method for preparing Indium Selenide (InSe) crystals. By utilizing a narrow high-temperature zone, this method optimizes the solid-liquid interface, resulting in significantly lower operational costs and the ability to produce large-size ingots with superior structural integrity.
Core Takeaway The shift from Bridgman to zone melting represents a move toward precise thermal dynamics. By effectively managing latent heat, zone melting suppresses the formation of common defects like twins and inclusions, enabling the growth of high-quality crystals up to 27 mm in diameter.

Enhancing Crystal Quality Through Thermal Control
Optimizing the Solid-Liquid Interface
The primary technical advantage of the zone melting furnace is its ability to improve the optimization of the solid-liquid interface.
Unlike the Bridgman method, which often struggles with interface stability, zone melting allows for finer control over the growth front. This stability is critical for maintaining a consistent crystal structure throughout the ingot.
Managing Latent Heat
Effective dissipation of heat is essential for preventing structural anomalies during crystallization.
The zone melting process excels at conducting the latent heat of crystallization away from the growth interface. By managing the movement of a narrow high-temperature zone, the system prevents heat buildup that could otherwise destabilize the crystal structure.
Structural Integrity and Defect Reduction
Minimizing Parasitic Nucleation
One of the most persistent challenges in crystal growth is the occurrence of parasitic nucleation, where unwanted crystals form alongside the main ingot.
Zone melting significantly minimizes parasitic nucleation, ensuring that the growth is dominated by a single, high-quality crystal orientation rather than a poly-crystalline mass.
Reducing Twins and Inclusions
InSe crystals are prone to specific defects such as twins (structural boundaries) and inclusions (impurities trapped inside the lattice).
The zone melting technique effectively suppresses these defects. The controlled thermal gradient allows impurities to remain in the molten zone rather than incorporating into the solid crystal, resulting in higher purity.
Operational Efficiency and Scalability
Achieving Larger Dimensions
The improved control offered by this method translates directly into larger attainable crystal sizes.
Using a zone melting furnace, it is possible to grow high-quality crystal ingots with substantial dimensions, specifically up to 27 mm in diameter and 130 mm in length.
Lowering Operational Costs
Beyond quality, the zone melting furnace provides a distinct economic advantage.
The reference indicates that this method results in lower operational costs compared to the traditional Bridgman method. This efficiency makes it a more viable option for producing large-scale InSe crystals.
Understanding Process Dependencies
The Necessity of Zone Management
While the advantages are clear, they rely entirely on the precise execution of the technique.
The benefits described—defect reduction and heat conduction—are contingent upon successfully managing the movement of the narrow high-temperature zone. Failure to strictly control this narrow zone would negate the thermal advantages over the Bridgman method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding between zone melting and the Bridgman method for InSe preparation, consider your specific priorities regarding cost and defect tolerance.
- If your primary focus is reducing defects: The zone melting furnace is superior for minimizing inclusions, twins, and parasitic nucleation through better interface optimization.
- If your primary focus is cost efficiency: This method offers lower operational costs while still achieving large-scale dimensions (up to 130 mm length).
Zone melting provides a robust, cost-effective pathway to growing large, high-purity InSe crystals by mastering the thermal dynamics of the growth interface.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Zone Melting Method | Bridgman Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Control | Narrow zone for precise interface stability | Broad heating, harder to manage latent heat |
| Crystal Quality | Low defects (minimal twins/inclusions) | Prone to parasitic nucleation and impurities |
| Maximum Size | Up to 27 mm diameter / 130 mm length | Limited by interface stability issues |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs | Higher complexity and overhead |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Maximize your laboratory's potential with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet your specific research or production requirements.
Whether you are growing large-size InSe crystals or conducting advanced heat treatments, our equipment ensures the precision and durability your work demands.
Ready to optimize your crystal growth process? Contact us today to consult with our technical team and find the perfect furnace for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Min Jin, Xuechao LIU. Growth and Characterization of Large-size InSe Crystal from Non-stoichiometric Solution <i>via</i> a Zone Melting Method. DOI: 10.15541/jim20230524
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- What role does a tubular furnace play in converting precursors into microwave-absorbing Fe-CN@CoCN? Expert Insights
- Why is it necessary to maintain a vacuum inside the tube? To Enable Controlled Electron Flow
- What is the heating rate of a tube furnace? Balancing Speed with Safety for Your Lab
- What functions does a tube atmosphere furnace perform for high-entropy alloy catalysts? Essential Reduction & Control
- What type of processing environment do high-temperature tube and muffle furnaces provide? Master Thermal Precision
- What process environment does a drop-tube furnace system provide? Expert Simulated Waste Incineration Research
- Why are high-temperature tube furnaces used for TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 alloys? Essential Benefits for Material Science
- What problems existed with early tube furnace designs? Discover the Flaws That Hindered Performance



















