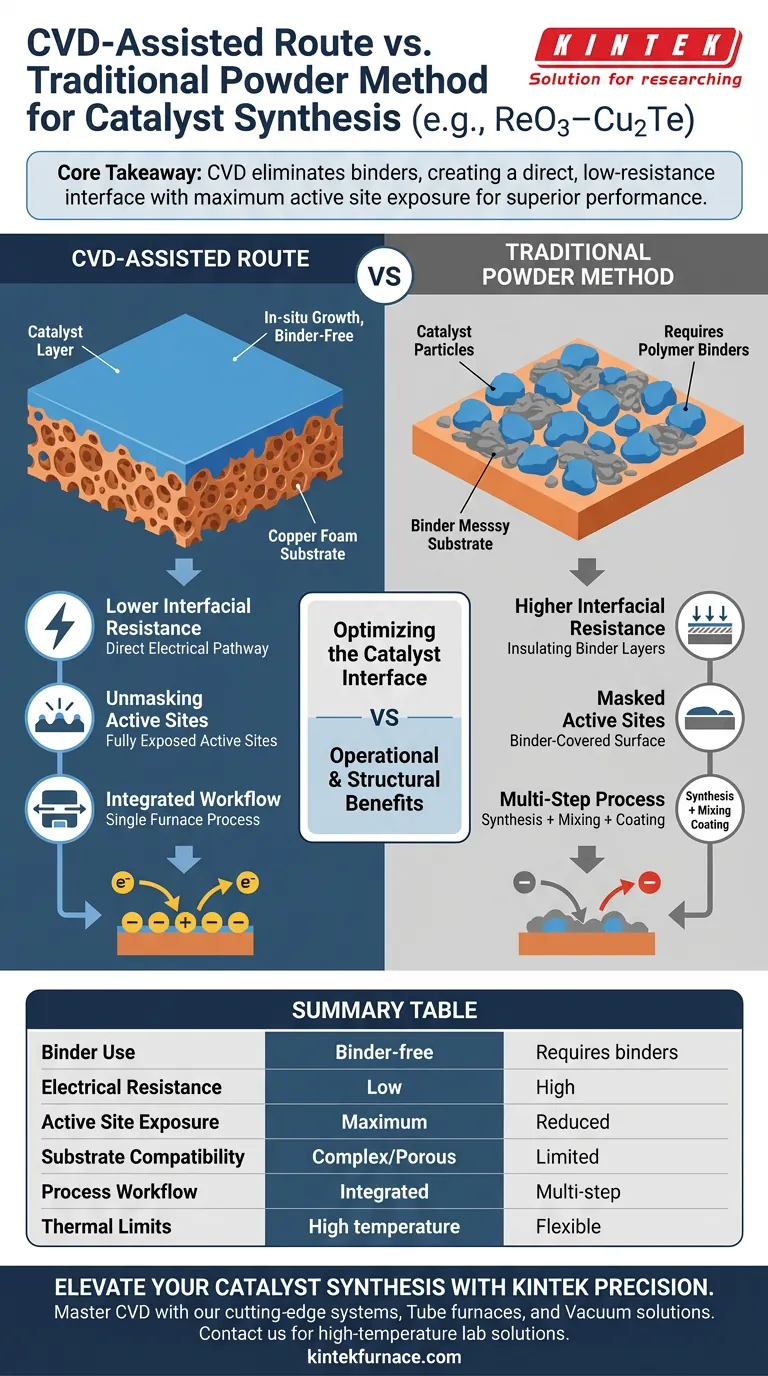
The primary advantage of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) assisted route is its ability to facilitate the in-situ growth of catalyst materials directly onto conductive substrates, such as copper foam. Unlike traditional methods, this approach completely eliminates the need for polymer binders to adhere the catalyst to the electrode.
Core Takeaway: Traditional powder methods rely on binders that inadvertently insulate the catalyst and block activity. The CVD route solves this by creating a direct, binder-free interface, which significantly lowers resistance and maximizes the exposure of active sites for superior electrochemical performance.

Optimizing the Catalyst Interface
The most critical difference between the CVD route and the powder method lies in how the catalyst interacts with the current collector.
Elimination of Binders
In the traditional powder method, synthesizing the material is only half the battle. To create a functional electrode, you must mix the catalyst powder with a binder to make it stick to the substrate.
The CVD process bypasses this step entirely. It grows the material directly onto the substrate (like copper foam), creating a robust physical connection without distinct adhesive layers.
Lower Interfacial Resistance
Binders are often electrically insulating or poorly conductive. When used to coat catalysts, they introduce unnecessary resistance between the catalyst and the current collector.
By removing the binder, the CVD route ensures a direct electrical pathway. This reduction in interfacial resistance improves charge transfer efficiency between the catalyst and the electrolyte.
Unmasking Active Sites
A significant downside of the powder method is that the binder can physically cover the surface of the catalyst particles. This "masking" effect renders potential active sites useless.
CVD facilitates the exposure of the pristine catalyst surface. This ensures that the maximum number of active sites are available for reactions, directly enhancing activity in applications like the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER).
Operational and Structural Benefits
Beyond the microscopic interface, the CVD route offers distinct advantages regarding process efficiency and material quality.
Integrated Workflow
A tube furnace CVD system can streamline the synthesis process by integrating annealing and growth into a single workflow.
This removes the need for intermediate sample transfers or complex high-vacuum equipment. It reduces operational complexity while enabling the production of high-purity coatings.
Coating Complex Geometries
The CVD process is a "non-line of sight" technique. This means the gas-phase precursors can penetrate and coat complex, irregular shapes.
This is particularly valuable when using porous substrates like copper foam. CVD ensures a uniform coating even on internal surfaces that traditional physical coating methods might miss.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an objective decision, you must recognize the constraints of the CVD approach compared to the powder method.
Thermal Constraints
CVD typically requires high temperatures to decompose precursors and grow crystals. This limits your choice of substrate to materials that can withstand these thermal conditions without degrading.
Equipment Dependency
While CVD eliminates the "binder mixing" step, it introduces a reliance on specialized equipment (furnaces and gas flow controllers). The powder method, conversely, is generally more flexible regarding the hardware required for the initial synthesis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between CVD and the powder method depends on your specific performance requirements and substrate limitations.
- If your primary focus is maximizing electrochemical activity: Prioritize the CVD route to ensure a binder-free interface, low resistance, and fully exposed active sites for reactions like HER.
- If your primary focus is substrate versatility: Consider the powder method if you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates or require a process that is less dependent on specialized furnace geometry.
By removing the binder barrier, the CVD route transforms the catalyst from a simple coating into an integrated component of the electrode system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD-Assisted Route | Traditional Powder Method |
|---|---|---|
| Binder Use | Binder-free (in-situ growth) | Requires polymer binders |
| Electrical Resistance | Low (direct contact) | High (insulating binder layers) |
| Active Site Exposure | Maximum (pristine surface) | Reduced (masked by adhesive) |
| Substrate Compatibility | Complex/Porous (e.g., copper foam) | Limited to surface coating |
| Process Workflow | Integrated annealing & growth | Multi-step synthesis & mixing |
| Thermal Limits | High temperature required | Generally more flexible |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Ready to transition from traditional powder methods to high-performance binder-free electrodes? KINTEK provides the cutting-edge tools you need to master the Chemical Vapor Deposition process. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of CVD systems, Tube furnaces, and Vacuum systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production requirements.
Don't let binders bottleneck your electrochemical performance. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our high-temperature lab solutions can help you achieve superior charge transfer and maximum active site exposure in your material research.
Visual Guide
References
- Aruna Vijayan, N. Sandhyarani. Efficient and sustainable hydrogen evolution reaction: enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of ReO<sub>3</sub>-incorporated Cu<sub>2</sub>Te catalysts. DOI: 10.1039/d4ya00023d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How durable are CVD coatings? Unlock Extreme Durability for Your Components
- What are the primary application areas of CVD technology? Unlock Advanced Thin-Film Solutions for Your Industry
- What are the characteristics and uses of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings? Enhance Durability and Efficiency in Your Applications
- Why is CVD considered a scalable process? Unlock High-Volume, Uniform Coatings for Your Industry
- Why is Sodium Chloride (NaCl) used in CVD of Vanadium-doped MoS2? Optimize Doping with Salt Flux
- How does chemical vapor deposition differ from physical vapor deposition (PVD)? Choose the Right Method for Your Application
- What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and its primary purpose? Build High-Performance Materials Atom by Atom
- What are the structural advantages of a customized AP-SCVD system? High-Throughput WO3 Thin Film Production



















