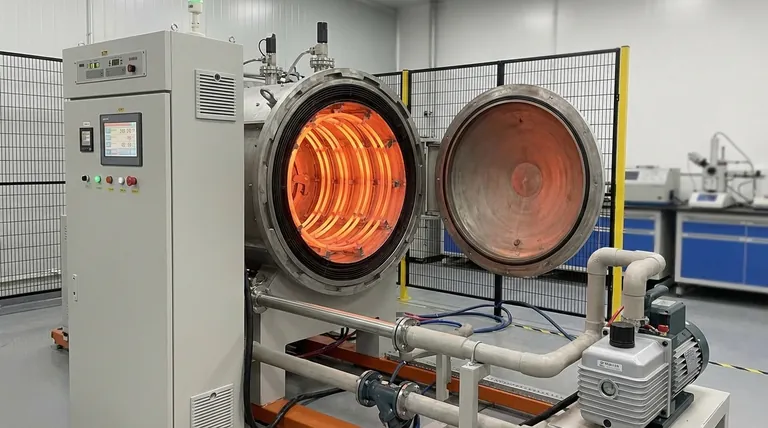
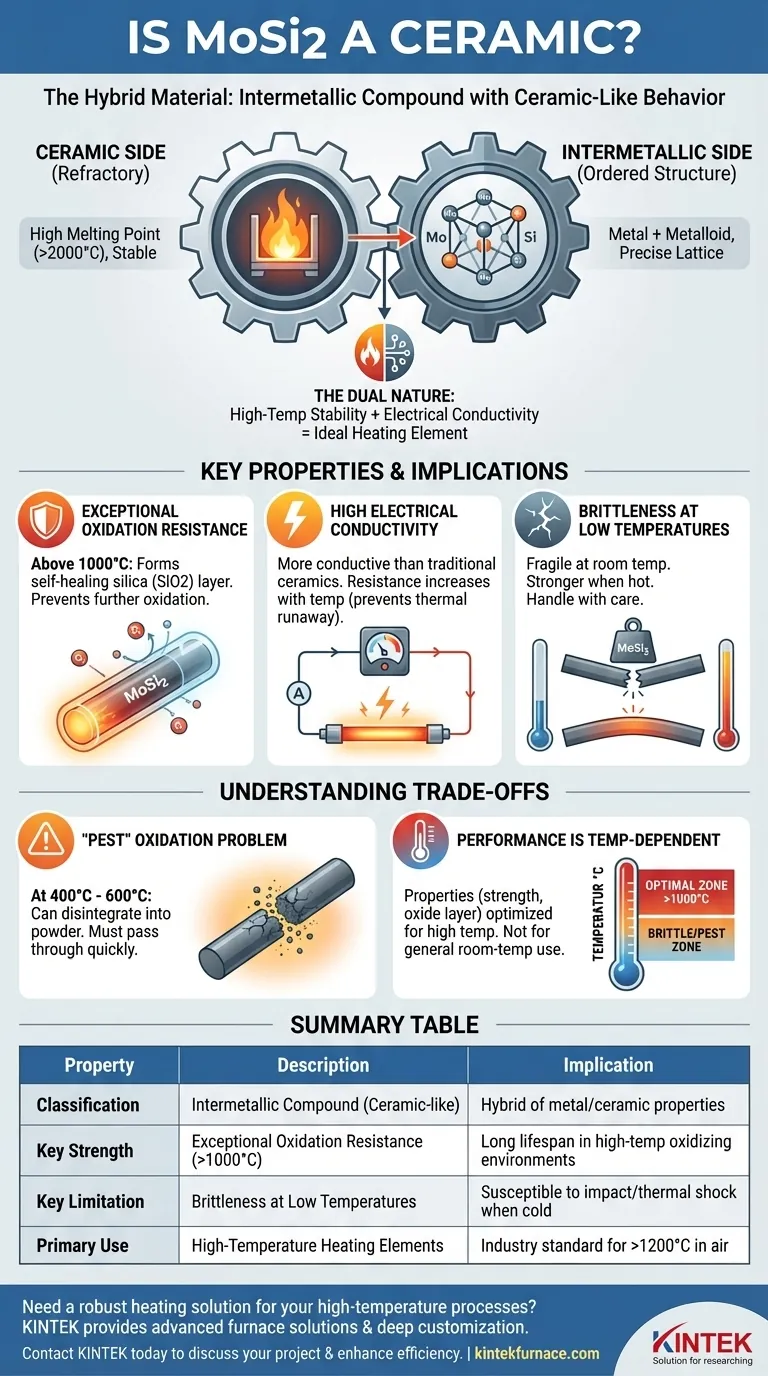
Yes, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is classified as a refractory ceramic. However, this simple classification doesn't capture the full picture. It is more precisely an intermetallic compound that possesses ceramic-like properties, particularly at high temperatures, giving it a unique position in materials science.
Molybdenum Disilicide exists at the intersection of ceramics and metals. Understanding it as an intermetallic compound that behaves like a high-performance ceramic is the key to leveraging its exceptional properties for high-temperature applications.

What Defines MoSi2: A Hybrid Material
Molybdenum Disilicide's classification can be confusing because it doesn't fit neatly into a single category. Its identity is a blend of two distinct material types.
The Ceramic Side: Refractory Behavior
A refractory material is one that is physically and chemically stable at very high temperatures. MoSi2 excels in this regard, with a melting point over 2000°C.
This heat resistance is its most ceramic-like trait and the primary reason it is grouped with materials like alumina or silicon carbide for high-temperature use.
The Intermetallic Side: Ordered Structure
Technically, MoSi2 is an intermetallic compound. This means it is a specific, ordered chemical compound of a metal (Molybdenum) and a metalloid (Silicon).
Unlike a simple metal alloy, its atoms are arranged in a precise, repeating crystal lattice. This ordered structure is responsible for both its high strength at elevated temperatures and its significant brittleness at lower temperatures.
Why This Dual Nature Matters
This hybrid classification is crucial for its application. Engineers choose MoSi2 when they need the high-temperature stability of a ceramic but also require a degree of electrical conductivity that most traditional ceramics cannot provide.
It is not an electrical insulator. This property is precisely what allows it to function as a resistive heating element, where electricity is passed through it to generate heat.
Key Properties and Their Implications
The unique nature of MoSi2 gives rise to a set of properties that make it ideal for extreme environments, especially those involving heat and oxygen.
Exceptional Oxidation Resistance
This is the most critical property of MoSi2. At temperatures above 1000°C, it reacts with oxygen to form a thin, protective surface layer of pure silica (SiO2).
This glassy layer is self-healing, non-porous, and prevents the underlying material from further oxidation, allowing MoSi2 components to operate for long periods in air at extreme temperatures.
High Electrical Conductivity
While not as conductive as a pure metal like copper, MoSi2 has significantly higher electrical conductivity than traditional ceramics.
Its resistance increases with temperature, which is a desirable characteristic for a heating element as it helps regulate power and prevent thermal runaway.
Brittleness at Low Temperatures
Like many advanced ceramics and intermetallics, MoSi2 is extremely brittle and fragile at room temperature.
This makes manufacturing and handling a challenge. It is strong and more ductile when hot, but any impact or thermal shock when it's cold can lead to catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and the specialized nature of MoSi2 comes with clear limitations that must be respected in its design and application.
The "Pest" Oxidation Problem
While it has excellent resistance to oxidation at very high temperatures, MoSi2 suffers from a phenomenon known as "pest" oxidation at moderate temperatures (typically 400°C to 600°C).
In this range, it can disintegrate into a powder. For this reason, heating elements made from MoSi2 are designed to move through this temperature range as quickly as possible.
Performance Is Temperature-Dependent
The material's best properties only manifest at high temperatures. Its brittleness, strength, and even its protective oxide layer are all highly dependent on the operating temperature.
It is a specialized material engineered for hot, oxidizing environments and is not a suitable choice for general-purpose structural components, especially at or near room temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting MoSi2 requires a clear understanding of its strengths and weaknesses relative to your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating elements in air: MoSi2 is an industry-standard choice, offering unparalleled performance and lifespan above 1200°C.
- If you need a structural component for room-temperature use: MoSi2 is almost always the wrong choice due to its extreme brittleness.
- If you are designing for a vacuum or reducing atmosphere: The protective silica layer will not form, making MoSi2 a poor choice compared to refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten.
By treating Molybdenum Disilicide as the specialized, high-performance hybrid it is, you can unlock its remarkable capabilities in the demanding environments it was designed for.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Intermetallic Compound (Ceramic-like) | Hybrid of metal and ceramic properties |
| Key Strength | Exceptional Oxidation Resistance (>1000°C) | Long lifespan in high-temperature, oxidizing environments |
| Key Limitation | Brittleness at Low Temperatures | Susceptible to damage from impact or thermal shock when cold |
| Primary Use | High-Temperature Heating Elements | Industry standard for applications above 1200°C in air |
Need a robust heating solution for your high-temperature processes?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether your application requires the specific capabilities of a MoSi2 heating element or another advanced material, our experts can help you select or custom-engineer the perfect furnace system. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















