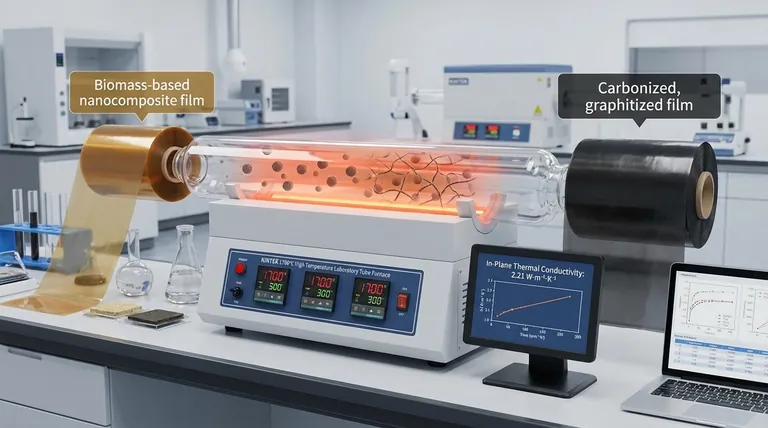
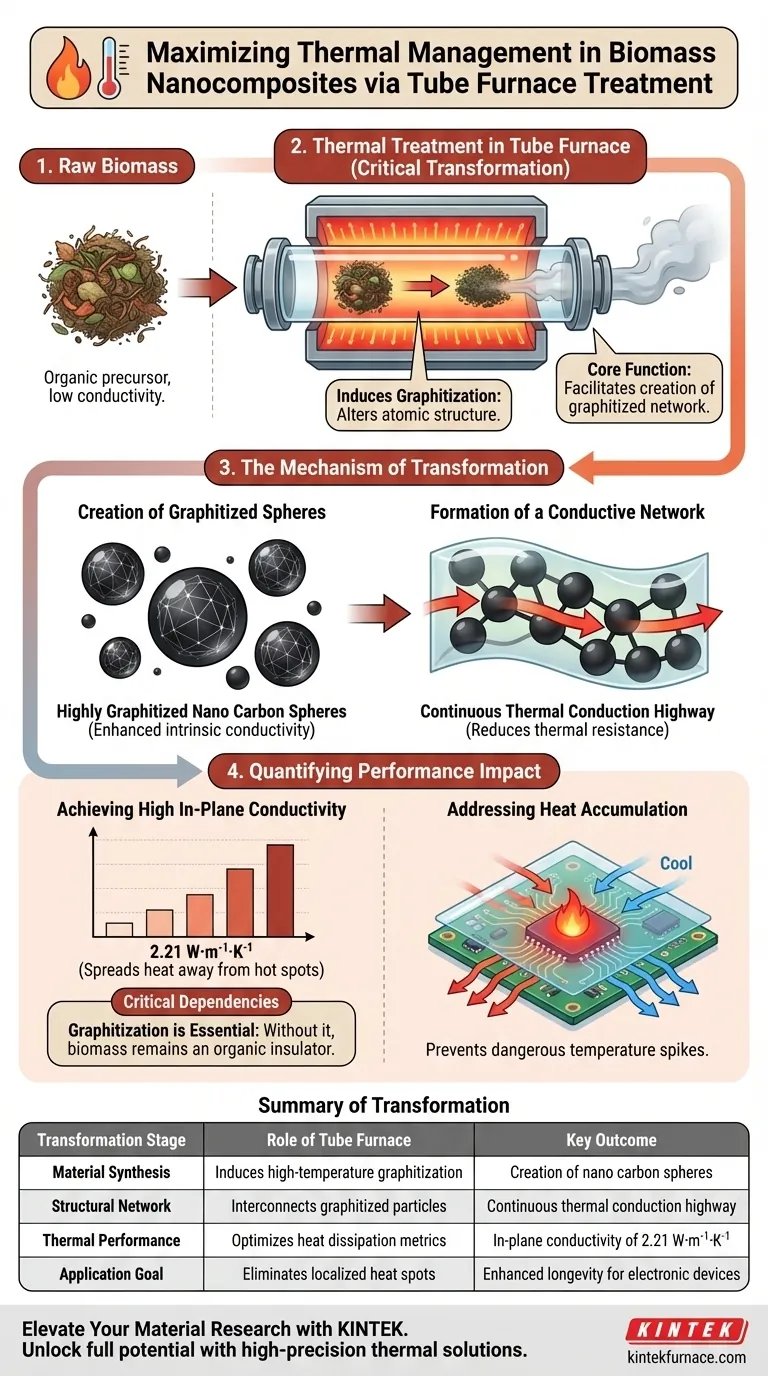
Thermal treatment in a tube furnace is the critical transformation step that converts raw biomass into highly conductive nano carbon spheres. This process does not merely dry or cure the material; it fundamentally alters its atomic structure through graphitization, which is the prerequisite for effective heat management.
The core function of the tube furnace is to facilitate the creation of a graphitized network within the film. This network acts as a thermal highway, allowing the material to achieve high in-plane thermal conductivity (specifically 2.21 W·m⁻¹·K⁻¹) to solve heat accumulation problems in electronics.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Creation of Graphitized Spheres
The primary role of the tube furnace is to subject the biomass to specific thermal conditions that induce graphitization.
This process converts the organic precursor into highly graphitized nano carbon spheres. The high degree of graphitization is essential because it significantly enhances the intrinsic thermal conductivity of the individual particles.
Formation of a Conductive Network
High conductivity in individual particles is not enough; they must work together.
When these graphitized spheres are integrated into the nanocomposite film, they arrange to form a continuous thermal conduction network. This interconnected structure reduces thermal resistance, allowing heat to flow efficiently across the material.
Quantifying the Performance Impact
Achieving High In-Plane Conductivity
The result of this network formation is a substantial increase in the film's ability to transfer heat laterally.
The thermal treatment enables the composite to achieve an in-plane thermal conductivity of 2.21 W·m⁻¹·K⁻¹. This specific metric indicates how effectively the material can spread heat away from a localized hot spot.
Addressing Heat Accumulation
This performance capability directly addresses the challenge of heat accumulation in integrated electronic devices.
By rapidly spreading heat across the film's surface, the material prevents dangerous temperature spikes that can degrade electronic components.
Understanding the Critical Dependencies
The Necessity of Graphitization
It is important to understand that the thermal management properties are entirely dependent on the success of the graphitization process.
Without the specific thermal treatment provided by the tube furnace, the biomass would remain an organic insulator rather than becoming a thermal conductor. The efficiency of the final film is directly tied to the quality of the nano carbon spheres produced during this stage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of biomass-based nanocomposite films, consider how the thermal treatment aligns with your specific engineering objectives.
- If your primary focus is thermal dissipation: Prioritize the graphitization quality in the tube furnace, as this dictates the maximum potential conductivity (aiming for the 2.21 W·m⁻¹·K⁻¹ benchmark).
- If your primary focus is device longevity: Ensure the film is integrated specifically to leverage its in-plane conductivity, positioning it to spread heat away from sensitive integrated circuits.
The tube furnace is not just a heating element; it is the tool that engineers the material's ability to act as an effective thermal interface.
Summary Table:
| Transformation Stage | Role of Tube Furnace | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Induces high-temperature graphitization | Creation of nano carbon spheres |
| Structural Network | Interconnects graphitized particles | Continuous thermal conduction highway |
| Thermal Performance | Optimizes heat dissipation metrics | In-plane conductivity of 2.21 W·m⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Application Goal | Eliminates localized heat spots | Enhanced longevity for electronic devices |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your biomass-based nanocomposites with KINTEK’s high-precision thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to achieve the precise graphitization temperatures required for superior thermal management.
Whether you are aiming for high in-plane conductivity or custom thermal interfaces, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our equipment can drive your next material breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Junchao Ren, Qingfa Zhang. All‐Biomass Nanocomposite Films via Facile and Sustainable Design Procedure for Thermal Management and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202510372
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of using a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Dynamic, Uniform Heating for Powders
- What should be considered when purchasing a horizontal tube furnace? Key Factors for Your Thermal Process
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the preparation of barium ferrite? Achieve Optimal Magnetism
- What is the primary function of a vacuum quartz tube in CVT? Grow High-Purity Bi4I4 Crystals Successfully
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace in the preparation of WSe2 thin films? Master Precise Atomic Deposition
- What are the technical advantages of using a PID programmable controller in tube furnace control modules?
- What is the function of a tube reduction furnace? Enhance Ru@PG Catalysts with Ar/H2 Precision
- How is a laboratory tube furnace utilized to convert metal-organic precursors? Master Thin Film Pyrolysis Today



















