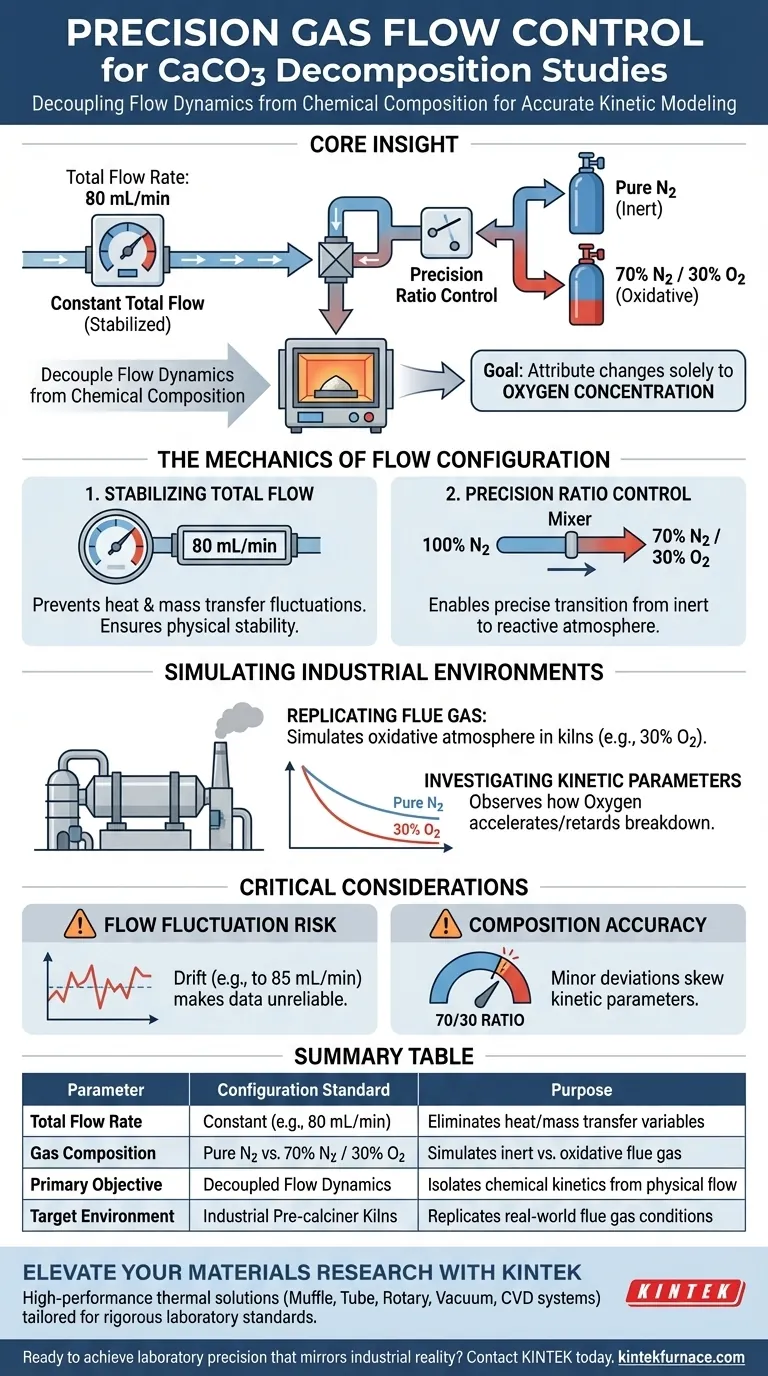
To configure a precision gas flow control system for studying calcium carbonate decomposition, researchers must simultaneously stabilize the total flow rate while varying the specific gas composition. This typically involves locking the total volumetric flow at a constant value, such as 80 mL/min, while precisely alternating the intake ratio between inert gases (like pure Nitrogen) and oxidative mixtures (such as 70% Nitrogen and 30% Oxygen).
Core Insight: The primary goal of this configuration is to decouple flow dynamics from chemical composition. By keeping the total flow constant, researchers can attribute changes in decomposition kinetics solely to the oxygen concentration, effectively simulating the real-world conditions of industrial pre-calciner kilns.

The Mechanics of Flow Configuration
To accurately study decomposition, the system must control two distinct variables: the total volume of gas passing over the sample and the specific makeup of that gas.
Stabilizing Total Flow Rate
The foundation of the experiment is a constant total flow rate, typically set to 80 mL/min.
Maintaining this constant rate is critical because fluctuations in flow volume can alter heat transfer rates and mass transport around the sample.
By locking this variable, you ensure that physical changes in the gas stream do not interfere with the chemical data being collected.
Precision Ratio Control
Once the total flow is stabilized, the system is configured to mix gases to exact specifications.
Common configurations switch between pure Nitrogen (N2) and specific mixtures, such as 70% N2 and 30% O2.
This ability to dial in specific ratios allows the system to transition from an inert environment to a reactive one without disrupting the overall flow velocity.
Simulating Industrial Environments
The specific gas ratios used in these systems are not arbitrary; they are designed to replicate the harsh environments found in manufacturing.
Replicating Flue Gas
The configuration specifically aims to simulate actual flue gas environments.
In industrial settings, calcium carbonate is processed in pre-calciner kilns where the atmosphere is rarely pure.
By introducing controlled amounts of Oxygen (e.g., 30%), the system mimics the oxidative atmosphere inside these kilns, providing data that is relevant to large-scale processing.
Investigating Kinetic Parameters
The ultimate output of this configuration is the measurement of kinetic parameters.
Researchers use this setup to observe how the presence of oxygen accelerates or retards the breakdown of calcium carbonate.
Because the flow is precise, any change in the decomposition rate can be scientifically attributed to the atmospheric chemistry rather than experimental error.
Critical Considerations for Experimental Integrity
While precision flow control provides high-quality data, it requires rigorous adherence to calibration standards to avoid common pitfalls.
The Risk of Flow Fluctuation
If the total flow rate drifts (e.g., moving from 80 mL/min to 85 mL/min) when the gas composition changes, the kinetic data becomes unreliable.
The system must be robust enough to handle the switching of gas sources without causing pressure spikes or drops.
Balancing Composition Accuracy
Simulating a specific atmosphere requires that the 70/30 ratio be exact.
Even minor deviations in oxygen concentration can significantly skew the kinetic parameters, leading to incorrect conclusions about how the material behaves in an industrial kiln.
Applying This to Your Research
When setting up your flow control parameters, your configuration should be dictated by your specific end goal.
- If your primary focus is Fundamental Kinetics: Prioritize the stability of the pure Nitrogen stream to establish a reliable baseline decomposition rate before introducing variables.
- If your primary focus is Industrial Simulation: Ensure your gas mixture precisely matches the oxygen concentration of the target flue gas environment (e.g., the 30% O2 mix) to generate applicable process data.
Precise control of the atmosphere is the only way to bridge the gap between laboratory theory and industrial reality.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Configuration Standard | Purpose in Decomposition Study |
|---|---|---|
| Total Flow Rate | Constant (e.g., 80 mL/min) | Eliminates heat/mass transfer variables |
| Gas Composition | Pure N2 vs. 70% N2 / 30% O2 | Simulates inert vs. oxidative flue gas |
| Primary Objective | Decoupled Flow Dynamics | Isolates chemical kinetics from physical flow |
| Target Environment | Industrial Pre-calciner Kilns | Replicates real-world flue gas conditions |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision gas flow is critical for accurate kinetic modeling, but it is only as effective as the furnace it operates within. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable thermal solutions designed for rigorous laboratory standards.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are studying fundamental kinetics or simulating industrial flue gas environments, our high-temp furnaces are tailored to your unique specifications.
Ready to achieve laboratory precision that mirrors industrial reality?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Dingxiang Zhuang, Bin Sun. Thermal Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate at Multiple Heating Rates in Different Atmospheres Using the Techniques of TG, DTG, and DSC. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15020108
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a standard Quartz Crystal Sensor required during germanium evaporation for nanocrystal fabrication?
- How are quartz tubes used in laboratory applications? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Processes
- How is a dual-color infrared thermometer used to evaluate (Hf─Zr─Ti)C ceramic coatings? Precision Thermal Monitoring
- What are the technical advantages of using high-purity quartz tubes? Optimize Heat and Purity in Combustion Analysis
- What is the wear resistance of alumina ceramics compared to manganese steel and high-chromium cast iron? Discover the Superior Choice for Abrasive Environments
- What is the purpose of configuring a hot gas filter within a Catalytic Hydropyrolysis (CHP) process? Ensure Reactor Life
- What is the role of a mechanical vacuum pump in the preparation of FeAl alloys? Achieve 10⁻² Pa for Pure Synthesis
- What is the significance of using ceramic or quartz sample boats for solid fuels? Ensure Precise Thermal Analysis



















