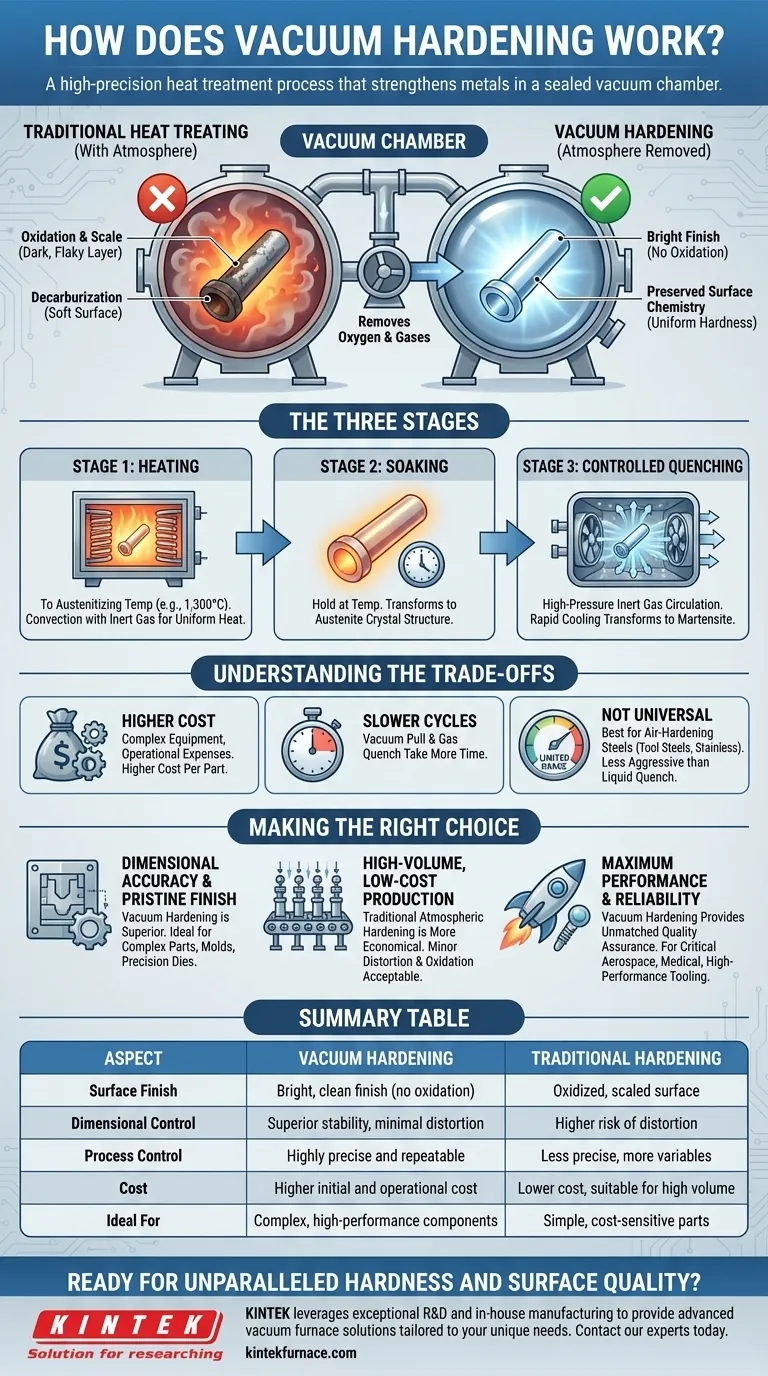
Vacuum hardening is a high-precision heat treatment process that strengthens metals by heating and rapidly cooling them inside a vacuum chamber. By removing oxygen and other atmospheric gases, the process prevents surface reactions like oxidation and discoloration. This allows for the creation of components with exceptional hardness and a clean, bright finish directly from the furnace.
The core value of vacuum hardening is not just achieving hardness, but achieving it with unparalleled control. By eliminating atmospheric contamination, the process delivers superior dimensional stability and surface integrity, making it ideal for high-performance and complex components.

The Core Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Interference
Traditional heat treating occurs in the presence of air, which leads to undesirable chemical reactions on the metal's surface at high temperatures. Vacuum hardening fundamentally solves this problem by removing the atmosphere itself.
How a Vacuum Prevents Oxidation
The most visible benefit is the prevention of oxidation. Without oxygen, the formation of scale—a dark, flaky layer of iron oxide—is completely avoided. This results in a "bright" metallic surface that doesn't require subsequent cleaning or machining to remove a damaged outer layer.
Preserving Surface Chemistry
Beyond aesthetics, the vacuum preserves the carbon content of the steel's surface. In atmospheric furnaces, a reaction called decarburization can occur, where carbon leaches out of the surface, leaving it softer than the core. A vacuum environment ensures the carbon stays where it belongs, guaranteeing uniform hardness throughout the component.
The Three Stages of Vacuum Hardening
The process is meticulously controlled from start to finish within a single, sealed chamber, typically following three distinct phases.
Stage 1: Heating to Austenitizing Temperature
The components are heated to a specific critical temperature, often up to 1,300°C (2,372°F). This heating is typically done via convection, using a small amount of inert gas (like nitrogen) to circulate heat evenly. The precise computer control ensures the entire part reaches the target temperature uniformly.
Stage 2: Soaking for Transformation
Once at the target temperature, the material is "soaked" or held for a predetermined period. This allows the steel's internal crystal structure to fully transform into a state known as austenite, which is essential for achieving maximum hardness upon cooling.
Stage 3: Controlled Quenching
To lock in the hardness, the components must be cooled rapidly. In a vacuum furnace, this is achieved by back-filling the chamber with high-pressure inert gas. The gas is circulated at high velocity by powerful fans, rapidly extracting heat and forcing the austenite to transform into martensite, the hard, strong crystal structure desired.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum hardening offers significant advantages, it is not the universal solution for all applications. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines that represent a significant capital investment. The process itself, including the time to pull a vacuum and the use of high-purity inert gases, leads to a higher cost per part compared to traditional atmospheric hardening.
Slower Cycle Times
Pulling a vacuum before heating and using gas for quenching can be slower than open-air or salt bath processes. This makes it less suitable for extremely high-volume, low-cost parts where speed is the primary economic driver.
Not a Universal Quenching Method
The rate of cooling achieved with gas quenching, while fast, is not as extreme as a liquid quench (oil or water). Therefore, vacuum hardening is best suited for air-hardening steels (like tool steels) and certain stainless steels. Low-alloy steels that require a very aggressive quench to achieve full hardness may not be suitable candidates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct hardening process depends entirely on the technical requirements and economic constraints of your component.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy and a pristine surface finish: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice for complex parts, injection molds, and precision dies where post-treatment machining is costly or impossible.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: For simple components where minor distortion and surface oxidation are acceptable (and can be cleaned post-treatment), traditional atmospheric hardening remains more economical.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability: For critical components in aerospace, medical, or high-performance tooling, the clean, repeatable, and precisely controlled nature of vacuum hardening provides unmatched quality assurance.
By understanding these trade-offs, you can confidently choose the process that delivers the required performance for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Hardening | Traditional Hardening |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Bright, clean finish (no oxidation) | Oxidized, scaled surface |
| Dimensional Control | Superior stability, minimal distortion | Higher risk of distortion |
| Process Control | Highly precise and repeatable | Less precise, more variables |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational cost | Lower cost, suitable for high volume |
| Ideal For | Complex, high-performance components | Simple, cost-sensitive parts |
Ready to achieve unparalleled hardness and surface quality for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your vacuum hardening process delivers the precise dimensional stability and clean finish your high-performance applications demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hardening solutions can enhance your product's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















