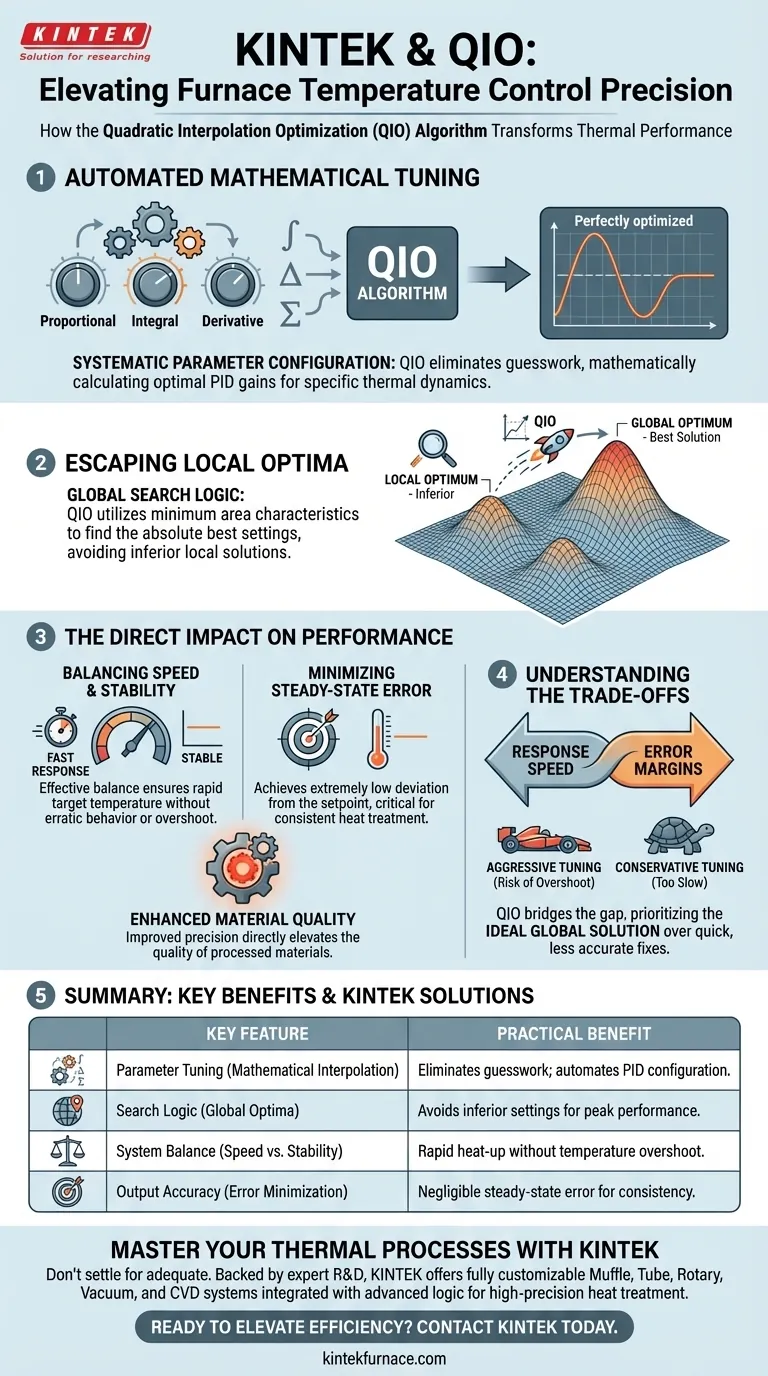
The Quadratic Interpolation Optimization (QIO) algorithm elevates control precision by mathematically automating the tuning process. It specifically targets the optimal configuration of controller parameters, such as proportional, integral, and derivative gains. By analyzing the minimum area characteristics of known performance points, it identifies the absolute best settings rather than settling for adequate ones, preventing the system from getting stuck in local optima.
QIO transforms temperature control by mathematically solving for the ideal balance between speed and stability, ensuring the highest quality heat treatment for processed materials.

How QIO Optimizes Control
Mathematical Tuning of Parameters
Precision in electric furnaces relies heavily on the correct tuning of controller parameters.
QIO replaces manual guesswork by using mathematical interpolation. It systematically calculates the optimal values for proportional, integral, and derivative gains to match the specific thermal dynamics of the furnace.
Escaping Local Optima
A major flaw in traditional search algorithms is their tendency to get stuck in local optima.
This happens when a standard algorithm finds a solution that looks good compared to its immediate neighbors, but is inferior to the true best solution (the global optimum).
QIO avoids this trap by using the minimum area characteristics of known points. This allows it to look beyond immediate improvements and locate the global optimal solution for the entire system.
The Direct Impact on Performance
Balancing Speed and Stability
Thermal control often involves a conflict between heating up quickly and maintaining a stable temperature.
QIO results in a parameter set that effectively balances fast response times with system stability. This ensures the furnace reaches its target temperature rapidly without erratic behavior.
Minimizing Steady-State Error
Once the target temperature is reached, maintaining it is critical.
The algorithm achieves extremely low steady-state error. This means the actual temperature deviates very little from the setpoint over time, which is essential for consistent processing.
Enhancing Material Quality
The ultimate goal of improved precision is the quality of the output.
By reducing temperature fluctuations and ensuring accurate heat application, QIO directly improves the quality of heat treatment for the processed materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Conflict of Objectives
While QIO is superior to traditional methods, it is navigating a difficult trade-off between response speed and error margins.
Aggressive tuning for speed can often lead to overshoot (exceeding the temperature), while conservative tuning for stability can be too slow.
The Necessity of Global Optimization
The primary "cost" of high precision is the need to find the global optimum.
Simple algorithms are faster to compute but less accurate. QIO bridges this gap, but it inherently prioritizes finding the ideal solution over the "quickest fix" offered by basic search methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Implementing QIO is about moving from "sufficient" control to "optimal" control.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: QIO reduces cycle times by enabling a fast response time without sacrificing stability.
- If your primary focus is Product Quality: QIO ensures the extremely low steady-state error required for high-precision heat treatment.
Precision is not just about hitting a number; it is about the stability of that number over time.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Optimization Mechanism | Practical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter Tuning | Mathematical Interpolation | Eliminates guesswork; automates PID configuration. |
| Search Logic | Global Optima Identification | Avoids inferior local settings for peak performance. |
| System Balance | Speed vs. Stability Tuning | Ensures rapid heat-up without temperature overshoot. |
| Output Accuracy | Error Area Minimization | Achieves negligible steady-state error for consistency. |
Master Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK Expertise
Don't settle for "adequate" temperature control when you can achieve mathematical perfection. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique high-temperature applications. Our furnaces are engineered to integrate advanced logic, ensuring you minimize steady-state error and maximize material quality.
Ready to elevate your laboratory’s efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to speak with our specialists and find the ideal high-performance furnace for your specific research needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Serdar Ekinci, Євген Зайцев. Efficient control strategy for electric furnace temperature regulation using quadratic interpolation optimization. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84085-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is MgO used as a hard template for waste PET to carbon conversion? Unlock 3D Porous Structures
- How does industrial-scale forging equipment influence the morphology of primary carbonitrides in H13 tool steel?
- What is the significance of industrial drying equipment for metal powders? Master Post-Processing & Quality Control
- Why are Cu2O and Ga2O3 targets preferred for CuGaO2 films? Achieving Precision in Delafossite Sputtering
- Why is staged temperature control required in industrial air drying ovens for carbon nanofibers? Key Safety Insights
- Why is Barium Titanate annealed after SPS? Restore Material Stoichiometry and Electrical Performance
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum drying oven for mineral powders? Optimize Polymer Bonding and Density
- What is the primary function of multi-stage oxidation ovens? Secure High-Strength Carbon Fiber Stabilization



















