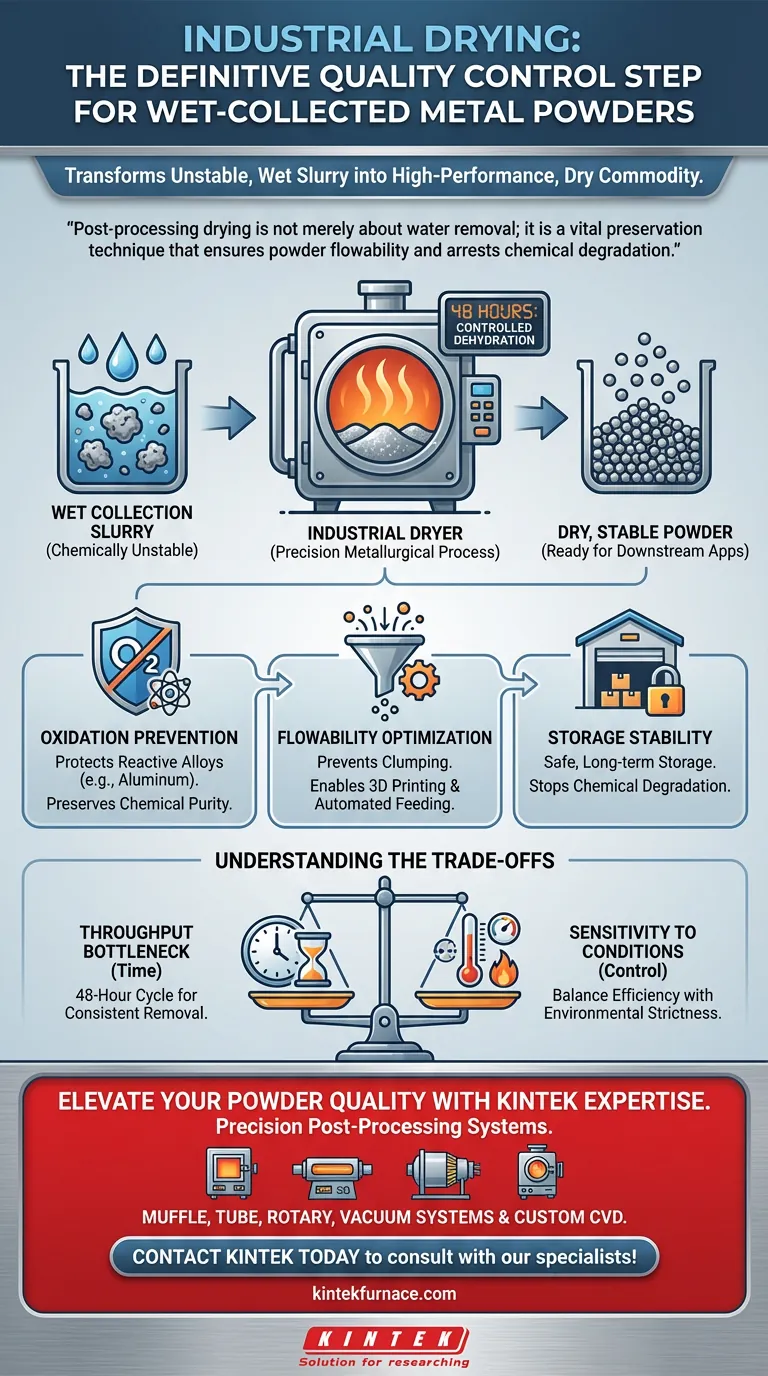
Industrial drying equipment serves as the definitive quality control step for metal powders produced via wet collection methods. Because these powders are collected in water tanks, the particles retain a significant amount of surface moisture that renders them chemically unstable and mechanically unusable. Industrial dryers execute a controlled dehydration process—often extending up to 48 hours—to stabilize the material and prepare it for downstream applications.
Post-processing drying is not merely about water removal; it is a vital preservation technique that ensures powder flowability and arrests chemical degradation. Without this controlled dehydration, reactive metals like aluminum alloys will oxidize, compromising the material's integrity before it can be used.

The Critical Role of Dehydration
Addressing Surface Moisture
When metal powders are harvested from water tanks, moisture adheres tightly to the particle surface. Industrial drying equipment is designed to systematically remove this surface moisture. This transforms the raw, wet slurry into a dry, stable commodity.
The Necessity of Extended Cycles
Effective drying is rarely instantaneous. The process often requires controlled dehydration over extended periods, such as 48 hours. This duration ensures that moisture is evaporated completely and consistently throughout the bulk material, rather than just drying the outer layers.
Preventing Material Degradation
Mitigating Oxidation Risks
Water is a catalyst for corrosion, particularly for fine metal particles with high surface areas. If moisture is not removed promptly and thoroughly, the metal powder faces immediate risk of oxidation. This chemical reaction alters the properties of the powder, often making it unsuitable for high-performance applications.
Protecting Reactive Alloys
The stakes are highest when working with reactive metal powders, such as aluminum alloys. These materials degrade rapidly in the presence of water. Specialized drying protects the chemical purity of these alloys, ensuring they retain their specified mechanical properties for end-use.
Ensuring Processability
Guaranteeing Flowability
Moisture causes metal particles to stick together, leading to clumping. Thorough drying breaks these bonds to ensure flowability. Free-flowing powder is a strict requirement for handling, transport, and feeding into manufacturing equipment like 3D printers or presses.
Stabilizing for Storage
Wet or damp powder cannot be stored safely. By removing excess water, drying equipment stabilizes the powder for long-term storage. This prevents degradation during the time gap between production and final usage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Throughput Bottleneck
The primary trade-off of this process is time. A 48-hour drying cycle represents a significant pause in production throughput. Manufacturers must account for this latency in their supply chain planning to prevent bottlenecks.
Sensitivity to Conditions
Drying is a "controlled" process, not just the application of high heat. Applying excessive heat to speed up the process can alter the metal's microstructure or induce oxidation. Therefore, the equipment must balance efficiency with strict environmental controls to preserve particle integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your metal powder, align your drying strategy with your material requirements.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: Prioritize the full duration of the drying cycle to prevent oxidation, particularly when handling reactive materials like aluminum alloys.
- If your primary focus is handling efficiency: Ensure the equipment achieves total surface moisture removal to guarantee the flowability required for automated feeding systems.
By treating the drying phase as a precision metallurgical process rather than a simple utility, you secure the commercial value and performance of your metal powder.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Moisture Removal | Eliminates water from wet collection slurry | Stabilizes the raw material for processing |
| Oxidation Prevention | Protects reactive alloys (e.g., Aluminum) | Preserves chemical purity and integrity |
| Flowability Optimization | Prevents clumping and particle sticking | Enables automated feeding and 3D printing |
| Extended Dehydration | Controlled cycles (up to 48 hours) | Ensures deep, consistent moisture removal |
| Storage Stability | Removes catalysts for corrosion | Facilitates safe, long-term material storage |
Elevate Your Powder Quality with KINTEK Expertise
Don’t let moisture compromise your material integrity. At KINTEK, we understand that precision post-processing is the difference between a high-performance alloy and wasted material. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-temp Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems specifically designed for the delicate stabilization of reactive metal powders. Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable CVD system for unique production needs, our lab solutions ensure your powders achieve maximum flowability and zero oxidation.
Ready to optimize your drying cycle? Contact KINTEK today to consult with our specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- С. М. Фролов, T. V. Dudareva. Metal Powder Production by Atomization of Free-Falling Melt Streams Using Pulsed Gaseous Shock and Detonation Waves. DOI: 10.3390/jmmp9010020
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of bed powder in LLZO sintering? Optimize Lithium Stability and Phase Purity
- Why is achieving process pressure within defined time important? Boost Efficiency, Quality, and Safety
- What are the process advantages of using template synthesis for the preparation of zinc selenide (ZnSe)?
- How does optimizing fuel gas mass flow affect the thermal efficiency of an industrial furnace? Maximize Heat Retention
- What effect does water-quench cooling equipment have on the microstructure of Invar 36? Expert Analysis
- What conditions are required for grafting norbornene functional groups onto S-glass fiber surfaces? Expert Protocol
- Why is a laboratory electric blast drying oven necessary for determining the water absorption rate of mortar?
- Why is graphene oxide (GO) essential in microwave synthesis? Unlock Rapid Growth and Precise 2D Nanocomposite Control



















