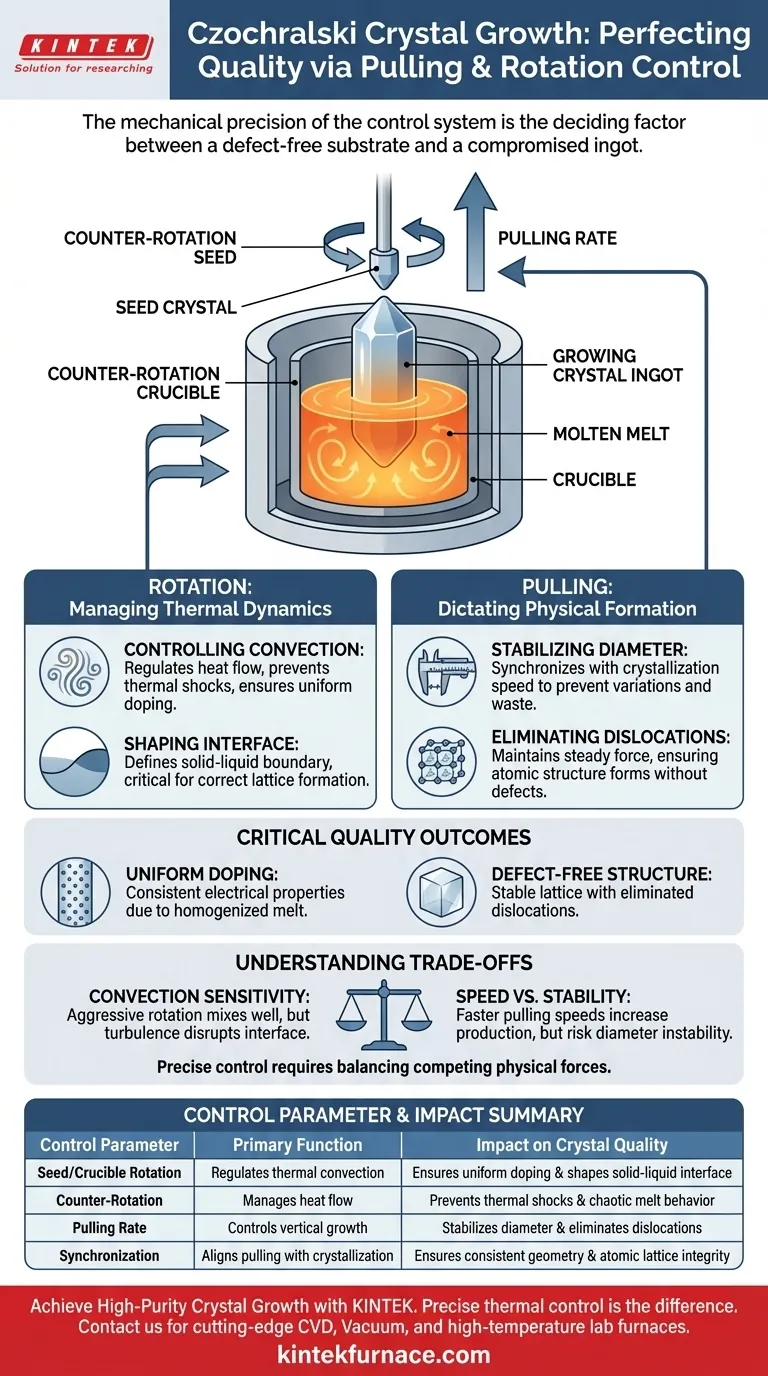
The quality of a Czochralski-grown crystal depends fundamentally on the precise manipulation of pulling rates and rotation speeds. This mechanical control system directly dictates the thermal environment within the melt, determining the structural and chemical integrity of the final product.
By fine-tuning the counter-rotation of the seed and crucible alongside the vertical pulling rate, the control system manages internal thermal convection and the solid-liquid interface. This precision is required to eliminate dislocations, ensure uniform doping, and maintain a consistent crystal diameter.

Regulating Thermal Dynamics via Rotation
The rotation mechanism is not merely for mixing; it is the primary tool for shaping the thermal environment of the melt.
Controlling Internal Thermal Convection
The control system manages the counter-rotation of the seed crystal and the crucible. This specific physical movement regulates the flow of heat within the molten material.
By adjusting these speeds, the system controls internal thermal convection. This ensures that heat is distributed logically rather than chaotically, preventing thermal shocks that could damage the growing crystal.
Shaping the Solid-Liquid Interface
The interaction between the rotating seed and the crucible defines the shape of the solid-liquid interface. This is the boundary where the melt transforms into the crystal lattice.
Precise control of this boundary is critical. If the interface shape fluctuates due to irregular rotation, the crystal structure cannot form correctly.
The Impact of Pulling Rate
While rotation manages the melt environment, the pulling system dictates the physical formation of the ingot.
Stabilizing Crystal Diameter
The system must maintain a stable single crystal diameter throughout the growth process.
This is achieved by synchronizing the pulling rate with the crystallization speed. If the pulling is too fast or too slow relative to growth, the diameter will vary, leading to wasted material or structural instability.
Eliminating Dislocations
One of the most critical functions of the pulling system is the elimination of dislocations.
Dislocations are structural defects in the crystal lattice. By maintaining a steady, precise pulling force, the system ensures the atomic structure forms without interruptions or misalignments.
Critical Quality Outcomes
The ultimate goal of the control system is to produce a crystal that meets strict industrial specifications.
Ensuring Uniform Doping
For a semiconductor crystal to be useful, it must have consistent electrical properties. This requires uniform doping—the even distribution of dopant atoms throughout the silicon.
The rotation control system ensures the melt is homogenized. This prevents "hot spots" of dopant concentration, resulting in a crystal with uniform resistivity and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precise control requires balancing competing physical forces.
The Sensitivity of Convection
Aggressive rotation can improve mixing, but excessive speed may create turbulent convection.
Turbulence can disrupt the solid-liquid interface, introducing the very defects the system is designed to prevent.
Speed vs. Stability
Increasing the pulling rate improves production speed but risks the stability of the diameter.
Prioritizing speed over precision often results in crystals with higher dislocation densities or irregular geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Optimizing the pulling and rotation parameters requires aligning mechanical inputs with your specific output goals.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize stability in the pulling rate to ensure the elimination of dislocations and a stable lattice structure.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Consistency: Prioritize optimizing the counter-rotation speeds to govern thermal convection and ensure uniform doping distribution.
Ultimately, the mechanical precision of the control system is the deciding factor between a highly conductive, defect-free substrate and a compromised ingot.
Summary Table:
| Control Parameter | Primary Function | Impact on Crystal Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Seed/Crucible Rotation | Regulates thermal convection | Ensures uniform doping and shapes the solid-liquid interface |
| Counter-Rotation | Manages heat flow | Prevents thermal shocks and prevents chaotic melt behavior |
| Pulling Rate | Controls vertical growth | Stabilizes crystal diameter and eliminates structural dislocations |
| Synchronization | Aligns pulling with crystallization | Ensures consistent geometry and atomic lattice integrity |
Achieve High-Purity Crystal Growth with KINTEK
Precise control of thermal dynamics is the difference between a flawed ingot and a high-performance substrate. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers cutting-edge systems including CVD, Vacuum, and customizable high-temperature lab furnaces designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you are aiming for zero-dislocation structural integrity or uniform electrical doping, our equipment provides the stability and precision your research requires. Contact us today to explore our customizable solutions and enhance your lab’s efficiency!
Visual Guide
References
- Tuncay Dikici, Serdar Yıldırım. Structural and Nanomechanical Properties of Silicon Single Crystals Grown by the Czochralski Method. DOI: 10.21205/deufmd.2025277915
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What critical environmental conditions does a high-temperature recrystallization annealing furnace provide? Maximize Steel Strength
- What is the purpose of using an industrial-grade oven for segmented drying? Optimize Electrode Integrity & Adhesion
- How does a forced-air drying oven contribute to asphalt degradation? Accelerate Material Salt Erosion Simulation
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for precursors on carbon paper? Maximize Material Performance
- What are the advantages of using microwave drying equipment for organic gels? Preserve Pore Structures Effectively
- How does a vacuum pressure infiltration system contribute to Diamond/Cu composite green bodies? Achieve 60% Density
- What role does Sodium Chloride (NaCl) play as a thermal buffer? Optimizing Si/Mg2SiO4 Composite Synthesis
- Why is precise control of heating and cooling rates necessary for iron-doped ceria? Optimize Your Catalyst Performance



















