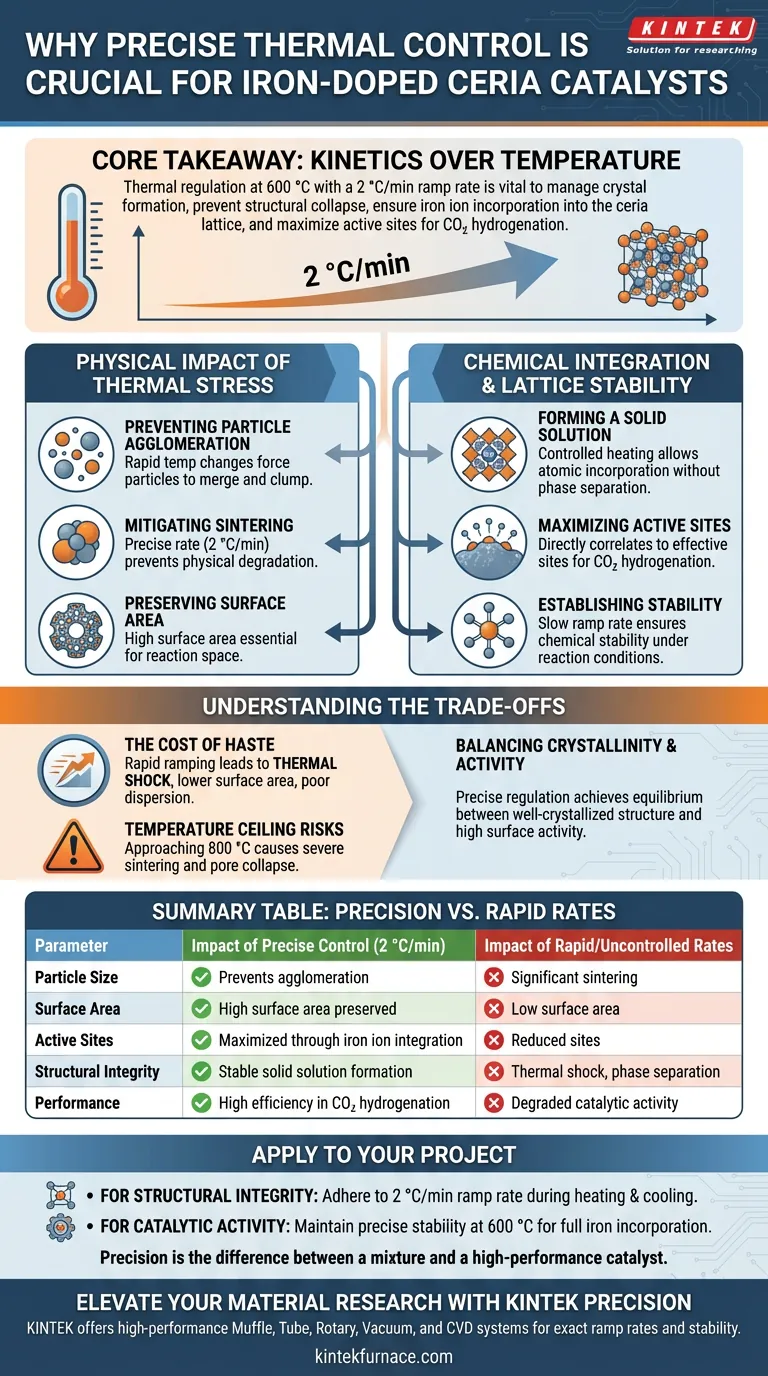
Precise control of heating and cooling rates is the defining factor in determining the structural integrity and chemical potency of iron-doped ceria catalysts. During the final calcination stage at 600 °C, utilizing a slow, governed rate—specifically 2 °C/min—is necessary to mitigate thermal stress. Without this regulation, the material is prone to excessive sintering and agglomeration, which compromises the physical architecture required for effective catalysis.
Core Takeaway Thermal regulation is not merely about reaching a target temperature; it is about managing the kinetics of crystal formation to prevent structural collapse. By strictly controlling the ramp rate, you ensure the successful incorporation of iron ions into the ceria lattice, creating a stable solid solution that maximizes active sites for carbon dioxide hydrogenation.

The Physical Impact of Thermal Stress
Preventing Particle Agglomeration
Rapid changes in temperature introduce significant thermal stress to the catalyst material. This stress forces particles to merge and clump together, a process known as agglomeration.
Mitigating Sintering
When particles agglomerate, the material undergoes sintering, effectively fusing distinct particles into larger masses. Implementing a precise heating and cooling rate, such as 2 °C/min, keeps this physical degradation in check.
Preserving Surface Area
The direct consequence of preventing sintering is the preservation of the catalyst's specific surface area. A high surface area is non-negotiable for catalytic performance, as it provides the physical space necessary for chemical reactions to occur.
Chemical Integration and Lattice Stability
Forming a Solid Solution
For iron-doped ceria to function correctly, the iron ions must be integrated into the ceria crystal structure, forming a solid solution. Controlled heating provides the necessary thermodynamic environment for this atomic incorporation to occur without inducing phase separation.
Maximizing Active Sites
The formation of this solid solution directly correlates to the number of active sites available on the catalyst. These sites are specifically tuned for carbon dioxide hydrogenation reactions, rendering the catalyst effective for its intended application.
Establishing Stability
A slow ramp rate ensures that the interaction between the iron and the ceria lattice is chemically stable. This prevents the active components from degrading or separating during subsequent use under reaction conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Haste
Accelerating the heating rate to save processing time is a common but fatal error in catalyst preparation. Rapid ramping leads to "thermal shock," which invariably results in lower surface area and poor dispersion of the active iron species.
Temperature Ceiling Risks
While the target temperature for this specific process is 600 °C, exceeding this limit can be detrimental. As seen in general catalyst preparation principles, temperatures approaching 800 °C often lead to severe sintering, pore structure collapse, and a reduction in surface oxygen vacancies.
Balancing Crystallinity and Activity
The goal of thermal treatment is to find the equilibrium between a well-crystallized structure and high surface activity. Precise temperature regulation is the only mechanism that allows you to achieve both simultaneously, rather than sacrificing one for the other.
How to Apply This to Your Project
To ensure optimal performance of your iron-doped ceria catalysts, apply the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Strictly adhere to a ramp rate of 2 °C/min during both heating and cooling to minimize thermal stress and prevent particle agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Activity: maintain precise temperature stability at 600 °C to guarantee the full incorporation of iron ions into the ceria lattice for maximum hydrogenation efficiency.
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between a mixture of oxides and a high-performance catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Impact of Precise Control (2 °C/min) | Impact of Rapid/Uncontrolled Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Prevents agglomeration; maintains fine particles | Significant sintering and particle clumping |
| Surface Area | High surface area preserved for reactions | Low surface area due to structural collapse |
| Active Sites | Maximized through iron ion integration | Reduced sites due to poor phase dispersion |
| Structural Integrity | Stable solid solution formation | Thermal shock and phase separation |
| Performance | High efficiency in CO2 hydrogenation | Degraded catalytic activity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let thermal stress compromise your catalyst's potential. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to deliver the exact ramp rates your research demands. Whether you need a standard setup or a customized lab furnace for unique doping processes, we provide the stability and control necessary to maximize your active sites.
Contact KINTEK Today for a Tailored Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Albert Gili, Reinhard Schomäcker. One-pot synthesis of iron-doped ceria catalysts for tandem carbon dioxide hydrogenation. DOI: 10.1039/d4cy00439f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Laboratory Drying Oven for Re2O7/Al2O3 Catalysts? Ensure High Dispersion & Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in forage palm and agave biomass processing? Optimize Stabilization Today
- How does a gas mass flow control system (MFC) prevent copper foil adhesion? Mastering Atmospheric Purity
- What is the primary function of adding bentonite and cement as binders? Optimize Iron Ore Briquette Strength
- What is the significance of an in-situ high-temperature heating stage? Unlock Real-Time Crystal Structure Insights
- What role does Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) play in determining the calcination parameters for manganese phosphate?
- How does extending the duration of high-temperature constant phase affect iron grain growth? Maximize Zinc Extraction
- Why is high raw material purity essential for magnesium alloy research? Ensure Precise Thermodynamic Data Quality



















