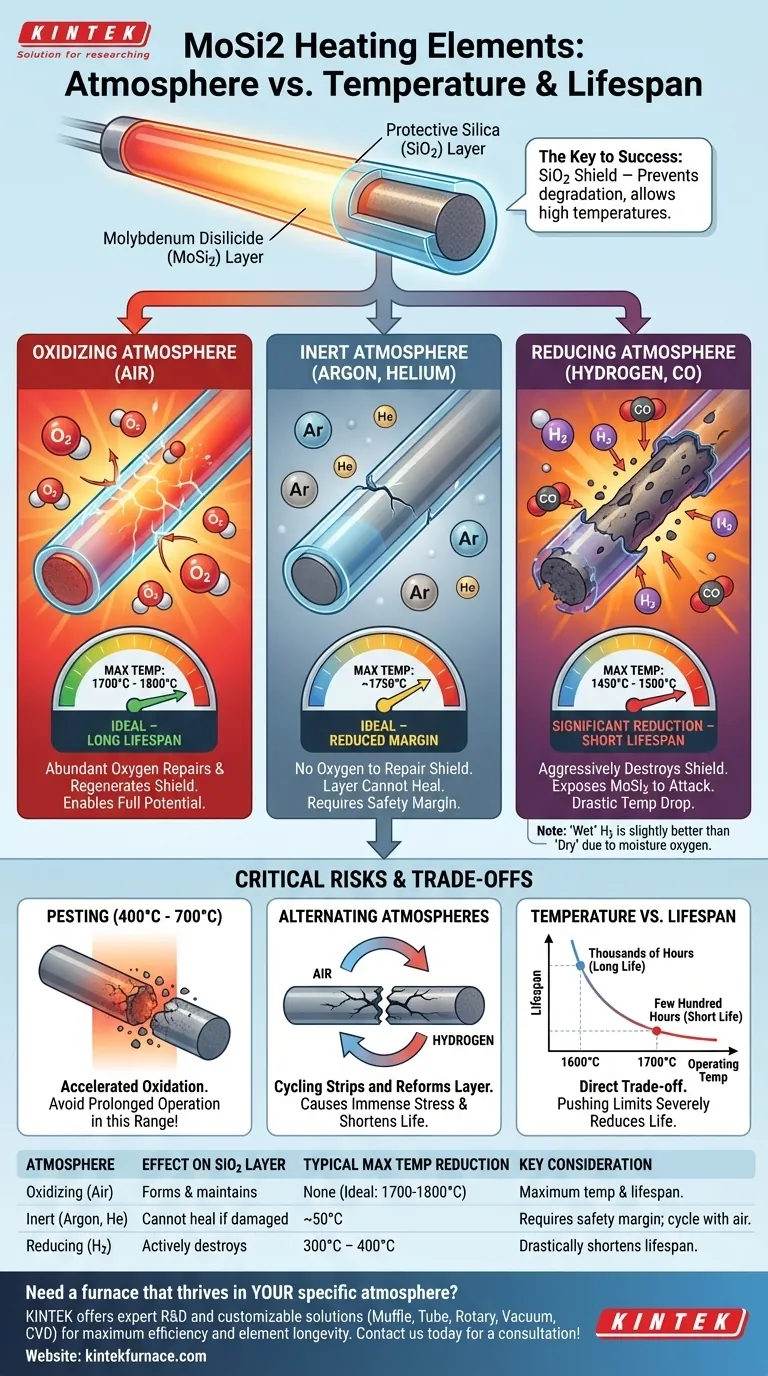
The operating atmosphere is the single most critical factor determining the maximum temperature and lifespan of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements. While these elements are capable of extreme heat, their performance is fundamentally tied to the chemical environment they operate in. For example, an 1800-type element rated for 1800°C in air must be de-rated to 1450°C in a dry hydrogen atmosphere to prevent rapid failure.
The ability of a MoSi2 element to reach and sustain high temperatures depends entirely on the formation of a protective quartz glass (silica) layer on its surface. An oxidizing atmosphere like air creates and maintains this layer, while other atmospheres either fail to support it or actively destroy it, forcing a reduction in maximum operating temperature.

How Atmospheres Dictate Performance
The performance of a MoSi2 element is not about the material melting, but about protecting it from chemical degradation. This protection comes from a thin, self-healing layer that forms on its surface at high temperatures.
The Protective Silica (SiO2) Layer
When a MoSi2 element heats up in the presence of oxygen, a thin, non-porous layer of silica (SiO2), or quartz glass, forms on its surface. This layer is the key to the element's success; it acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation and chemical attack on the core MoSi2 material.
Oxidizing Atmospheres (Air)
This is the ideal environment for MoSi2 elements. The abundant oxygen in the air constantly repairs and regenerates the protective silica layer, allowing the elements to operate safely at their maximum rated temperatures (1700°C or 1800°C) for extended periods.
Inert Atmospheres (Argon, Helium)
Inert gases like Argon or Helium do not chemically react with the element. However, they also do not provide the oxygen needed to form or repair the protective silica layer. If the layer is damaged, it cannot heal, making the element vulnerable. This is why the maximum temperature is slightly reduced, typically by 50°C, to provide a safety margin.
Reducing Atmospheres (Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide)
These environments are the most aggressive. Reducing gases actively strip oxygen from the silica layer, chemically destroying it and exposing the underlying MoSi2 to attack. This forces a significant reduction in operating temperature—often by 300-400°C—to slow down this destructive process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Operating outside of an ideal air atmosphere introduces significant risks that must be managed by controlling the temperature and understanding the underlying chemical reactions.
The Low-Temperature Threat: "Pesting"
MoSi2 elements have a critical vulnerability in the 400°C to 700°C range. Prolonged operation in this temperature window leads to a phenomenon called pesting, which is a form of accelerated oxidation that can cause the element to disintegrate. Furnaces should be designed to pass through this temperature range as quickly as possible.
The Impact of Moisture
Interestingly, a "wet" hydrogen atmosphere allows for a slightly higher operating temperature than a "dry" one. The water vapor (H2O) contains oxygen, which can partially offset the reducing effect of the hydrogen and help maintain a minimal protective layer on the element's surface.
Damage from Alternating Atmospheres
Switching a furnace between oxidizing (air) and reducing (hydrogen) atmospheres is extremely detrimental. This cycle repeatedly strips away and attempts to reform the protective layer, causing immense stress and drastically shortening the element's lifespan.
Maximum Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
It is crucial to understand that an element's maximum rated temperature is not its recommended continuous operating temperature. There is a direct trade-off between operating temperature and service life.
The Inverse Relationship
Pushing an element to its absolute temperature limit will severely reduce its lifespan. Operating just 100-200°C below the maximum can extend its life from a few hundred hours to several thousand hours.
A Practical Example
An element might run continuously for thousands of hours at 1600°C in air. The same element operating at 1700°C might only last for a few hundred hours before requiring replacement. This demonstrates the steep cost in lifespan for a marginal gain in temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process requirements dictate the necessary trade-offs in temperature and element life.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and longest life: You must operate in an air atmosphere. This is the only environment that supports the element's full potential.
- If your process requires an inert atmosphere (e.g., Argon): De-rate the element's maximum temperature by at least 50°C and consider periodically cycling the furnace with air at a high temperature to regenerate the protective layer.
- If you must use a reducing atmosphere (e.g., Hydrogen): You must strictly adhere to the much lower temperature limits for that gas and accept a significantly shorter element lifespan as an unavoidable cost of the process.
Ultimately, mastering your high-temperature process begins with respecting the chemistry between your heating elements and the atmosphere inside your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Effect on Protective Silica Layer | Typical Max Temperature Reduction vs. Air | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing (Air) | Forms & maintains the protective layer | None (Ideal: 1700°C - 1800°C) | Enables maximum temperature and lifespan |
| Inert (Argon, Helium) | Layer cannot heal if damaged | ~50°C | Requires safety margin; periodic air cycling can help |
| Reducing (Hydrogen) | Actively destroys the protective layer | 300°C - 400°C | Drastically shortens lifespan; 'wet' hydrogen is slightly better |
Need a furnace that thrives in your specific process atmosphere? The right heating element is critical for achieving your target temperature without premature failure. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique needs—including atmosphere control. Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for maximum efficiency and element longevity. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















