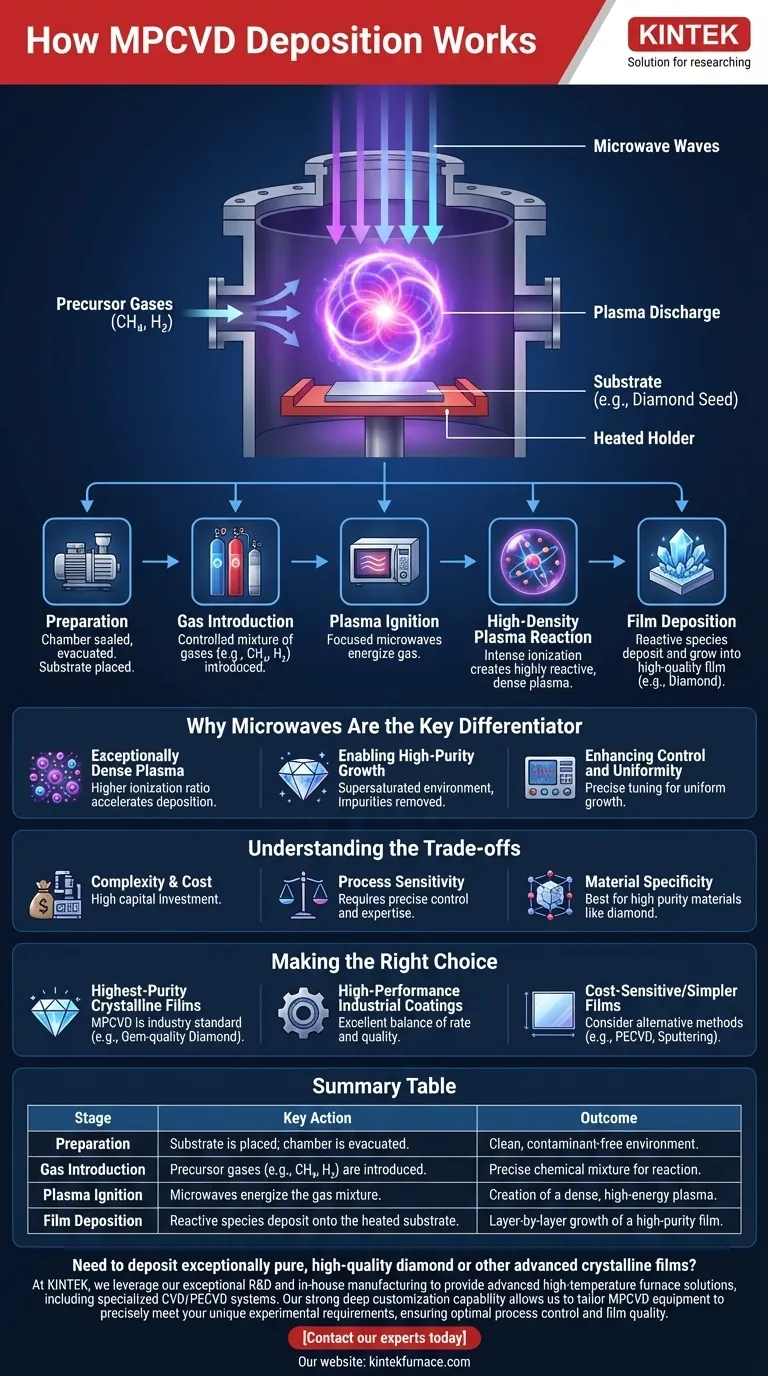
At its core, Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) is a process that uses focused microwave energy to ionize a gas mixture into a dense, highly reactive plasma. This plasma then chemically reacts and deposits a high-quality, solid film, such as synthetic diamond, onto a prepared substrate within a vacuum chamber.
MPCVD's true advantage lies not just in using a plasma, but in using microwaves to generate a uniquely dense and energetic plasma. This high level of ionization creates the ideal chemical environment for depositing exceptionally pure, high-quality films that other methods struggle to achieve.
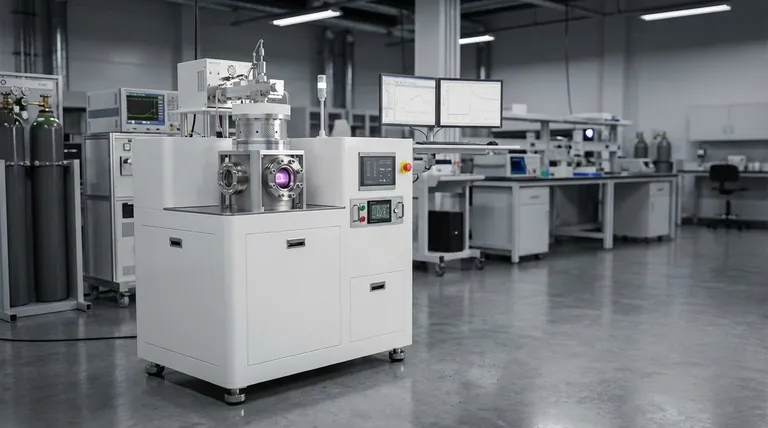

The MPCVD Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand why MPCVD is so effective, it's helpful to break down the process into its fundamental stages. Each step is precisely controlled to achieve the final material properties.
Preparation: The Chamber and Substrate
The process begins by placing a substrate, often a small "seed" of the material to be grown, onto a holder inside a reaction chamber. The chamber is then sealed and evacuated to a very low pressure, removing any atmospheric contaminants that could compromise the purity of the film.
Gas Introduction
Once the vacuum is established, a carefully controlled mixture of precursor gases is introduced into the chamber. For diamond growth, this mixture is typically composed of a carbon source (like methane, CH₄) and a much larger volume of hydrogen (H₂).
Plasma Ignition: The Role of Microwaves
Microwave energy, similar to that in a household microwave but far more powerful and focused, is directed into the chamber. This energy excites the gas mixture, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a glowing ball of plasma.
The High-Density Plasma Reaction
The intense electromagnetic field generated by the microwaves causes free electrons to oscillate violently. These electrons collide with gas molecules, causing a cascade of further ionization. This creates a high-density plasma where over 10% of the gas can be ionized—a significantly higher ratio than in many other plasma deposition techniques.
Film Deposition and Growth
Within this energetic plasma, the precursor gases break down into their constituent atoms and reactive radicals (like atomic hydrogen and carbon species). These species then deposit onto the heated substrate, assembling into the desired crystalline structure, layer by layer. The high concentration of atomic hydrogen also serves to etch away any non-diamond carbon, ensuring a high-purity final product.
Why Microwaves Are the Key Differentiator
While other methods use plasma, the use of microwaves in MPCVD provides distinct advantages that are critical for growing materials like high-quality diamond.
Creating an Exceptionally Dense Plasma
Microwaves are extremely efficient at coupling energy into the gas at specific pressures, creating a far denser and more ionized plasma than methods like direct current (DC) or radio frequency (RF) plasma. This high density directly accelerates the deposition rate.
Enabling High-Purity Growth
The unique chemistry within the microwave plasma is ideal for diamond deposition. It creates a supersaturated environment of the specific carbon and hydrogen atomic groups needed for growth while simultaneously removing impurities and defects from the growing film.
Enhancing Control and Uniformity
The power and frequency of the microwaves can be precisely controlled, allowing for fine-tuning of the plasma's density, temperature, and shape. This gives operators exceptional control over the film's growth rate and ensures a uniform deposition across the substrate's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the challenges associated with MPCVD.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
MPCVD systems involve sophisticated and expensive components, including high-power microwave generators, precisely engineered resonant cavities, and robust vacuum systems. This represents a significant capital investment.
Process Sensitivity
The exceptional quality of MPCVD films is a direct result of precise process control. The final outcome is highly sensitive to small variations in gas pressure, gas mixture ratios, substrate temperature, and microwave power. Achieving consistent results requires significant process expertise.
Material Specificity
MPCVD is a highly specialized process that excels at producing a narrow range of high-purity materials, with diamond being the most prominent example. It may not be the most efficient or cost-effective method for depositing simpler or amorphous films.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique depends entirely on the desired outcome. MPCVD is a powerful tool, but its application must align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing the highest-purity crystalline films, like gem-quality diamond: MPCVD is the undisputed industry-standard method due to its ability to create a clean, highly ionized plasma environment.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance industrial coatings (e.g., hard, low-friction films): MPCVD offers an excellent balance of deposition rate and superior film quality that justifies its complexity for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive or large-area deposition of simpler films: You may want to evaluate alternative methods like conventional PECVD or sputtering, which can be more economical for less demanding materials.
Ultimately, selecting MPCVD is a decision to prioritize exceptional material quality and purity through precise plasma control.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Substrate is placed; chamber is evacuated. | Clean, contaminant-free environment. |
| Gas Introduction | Precursor gases (e.g., CH₄, H₂) are introduced. | Precise chemical mixture for reaction. |
| Plasma Ignition | Microwaves energize the gas mixture. | Creation of a dense, high-energy plasma. |
| Film Deposition | Reactive species deposit onto the heated substrate. | Layer-by-layer growth of a high-purity film. |
Need to deposit exceptionally pure, high-quality diamond or other advanced crystalline films?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including specialized CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to tailor MPCVD equipment to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal process control and film quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a customized MPCVD solution can advance your research or production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the two main methods of synthetic diamond production? Discover HPHT vs. CVD for Lab-Grown Gems
- How is MPCVD used in manufacturing polycrystalline diamond optical components? Achieve Superior Optical Performance
- What are the key advantages of MPCVD in diamond synthesis? Achieve High-Purity, Scalable Diamond Production
- What is the relationship between diamond growth rate and quality in the MPCVD method? Balancing Speed and Purity for Your Application
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth



















