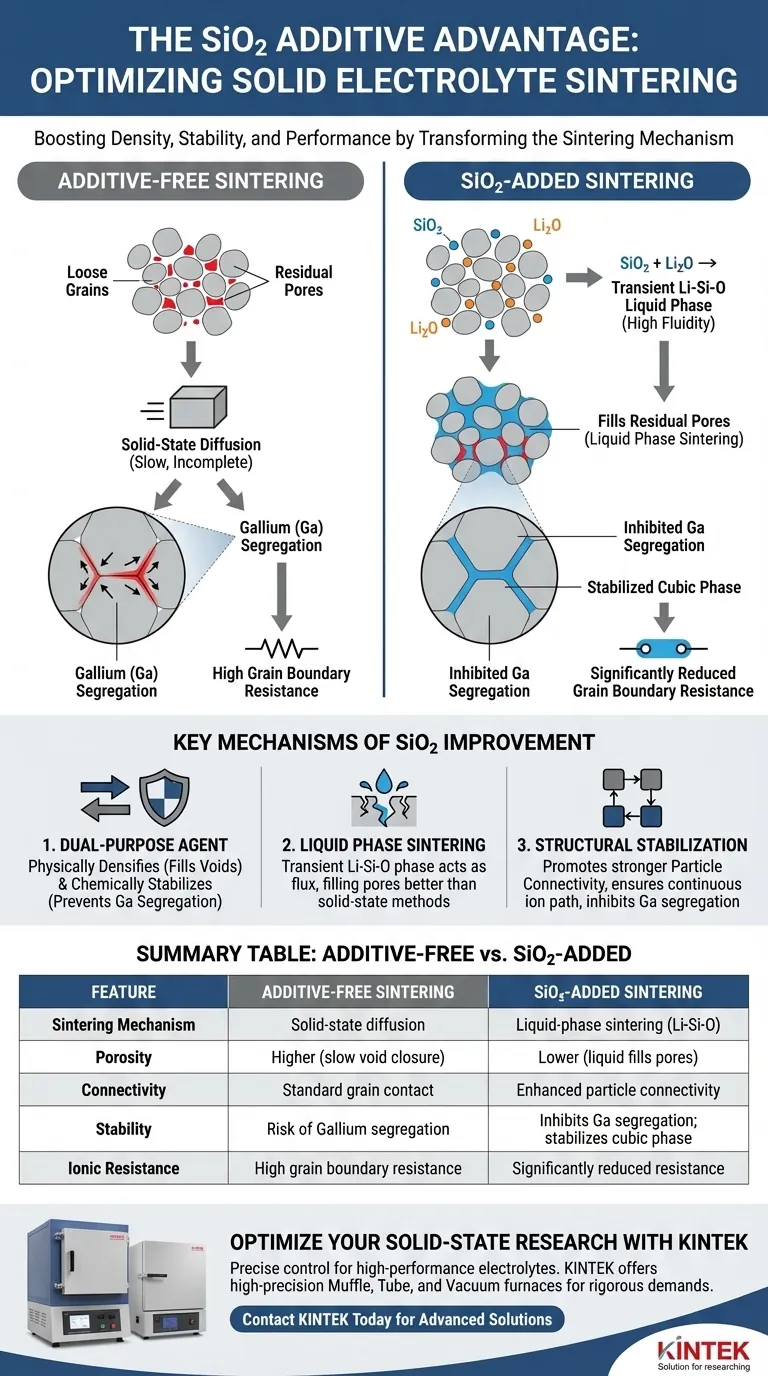
The introduction of Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) fundamentally alters the sintering mechanism by reacting with Lithium Oxide (Li2O) to create a transient liquid phase. This Li–Si–O phase exhibits high fluidity at sintering temperatures, allowing it to penetrate and fill residual pores between grain boundaries more effectively than additive-free or pure solid-state methods.
By facilitating a liquid-phase reaction, SiO2 acts as a dual-purpose agent: it physically densifies the material by filling voids and chemically stabilizes the structure by preventing Gallium segregation.

The Mechanism of Liquid Phase Sintering
Formation of the Transient Phase
In standard additive-free sintering, densification relies heavily on solid-state diffusion, which can be slow and leave voids.
When SiO2 is introduced, it reacts with Li2O. This reaction generates a transient Li–Si–O liquid phase.
Filling Residual Pores
Because this liquid phase has high fluidity at sintering temperatures, it acts as a flux.
It effectively flows into and fills the residual pores situated between grain boundaries. This leads to a denser final electrolyte compared to methods that do not utilize this liquid-phase mechanism.
Structural and Chemical Stabilization
Promoting Particle Connectivity
The presence of the liquid phase does more than just fill holes; it acts as a bridge between grains.
The addition of Silicon (Si) promotes stronger particle connectivity. This ensures a continuous path for ion conduction, which is critical for electrolyte performance.
Inhibiting Gallium Segregation
A common issue in doped solid electrolytes (specifically those using Gallium) is the tendency for dopants to separate from the main structure.
Additives containing Si stabilize the cubic phase structure by inhibiting the segregation of Gallium (Ga) at the grain boundaries.
Reducing Grain Boundary Resistance
The combination of physical densification and chemical stabilization yields a specific performance metric.
By preventing Ga segregation and improving connectivity, the introduction of SiO2 significantly reduces grain boundary resistance.
Understanding the Interactions (Trade-offs)
Dependence on Liquid Phase Dynamics
While beneficial, this process marks a shift from solid-state sintering to liquid-phase sintering.
The success of this method relies entirely on the formation and behavior of the transient Li–Si–O phase. Unlike solid-state methods, the microstructure is determined by how this liquid phase distributes and eventually solidifies.
The Limitation of "Ga Doping Alone"
The primary reference highlights a specific comparison to using Gallium doping without Silicon.
The trade-off of omitting SiO2 is a higher likelihood of Ga segregation. Without the stabilizing effect of Si, the cubic phase is less stable, leading to higher resistance at the grain boundaries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of SiO2 is not merely an additive step; it is a strategy to overcome the physical limitations of solid-state diffusion.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Density: Utilize SiO2 to leverage the high fluidity of the Li–Si–O liquid phase to fill residual pores that solid-state sintering cannot close.
- If your primary focus is Minimizing Resistance: Employ SiO2 to inhibit Gallium segregation, ensuring the grain boundaries remain conductive and the cubic phase remains stable.
The introduction of SiO2 provides a corrective mechanism that simultaneously resolves physical porosity and chemical instability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Additive-Free Sintering | SiO2-Added Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering Mechanism | Solid-state diffusion | Liquid-phase sintering (Li–Si–O) |
| Porosity | Higher (slow void closure) | Lower (liquid fills residual pores) |
| Connectivity | Standard grain contact | Enhanced particle connectivity |
| Stability | Risk of Gallium segregation | Inhibits Ga segregation; stabilizes cubic phase |
| Ionic Resistance | High grain boundary resistance | Significantly reduced resistance |
Optimize Your Solid-State Battery Research with KINTEK
Precise control over sintering dynamics is the key to high-performance electrolytes. At KINTEK, we understand the complexities of liquid-phase reactions and structural stabilization. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces specifically designed to handle the rigorous demands of solid-state electrolyte processing.
Whether you need to eliminate Gallium segregation or maximize material density, our customizable high-temp systems deliver the thermal uniformity your lab requires. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our advanced laboratory solutions can bring your material innovations to life.
Visual Guide
References
- Seung Hoon Chun, Sangbaek Park. Synergistic Engineering of Template‐Guided Densification and Dopant‐Induced Pore Filling for Pressureless Sintering of Li<sub>7</sub>La<sub>3</sub>Zr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>12</sub> Solid Electrolyte at 1000 °C. DOI: 10.1002/sstr.202500297
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is induced heat generated in a conductive material exposed to a magnetic field? Master Rapid, Contactless Heating
- What gas is used in a graphite furnace? A Guide to Argon vs. Nitrogen for Optimal Analysis
- What function does a water quenching tank serve in Ni-Ti alloy heat treatment? Lock in Superelasticity & Shape Memory
- Why is a fluidized bed reactor considered ideal for the co-gasification of biomass and non-biomass waste?
- What is the function of a drying oven in the post-treatment process of Ni and Zn-doped MgO nanoparticles?
- What are the technological advantages of using a Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) system? Precision for Semiconductors
- What is a sintering furnace used for? Fuse Powders into Dense, High-Performance Parts
- What problem does a fluidized bed address in ceramic molds? Ensure Uniform Shells for High-Temp Casting



















