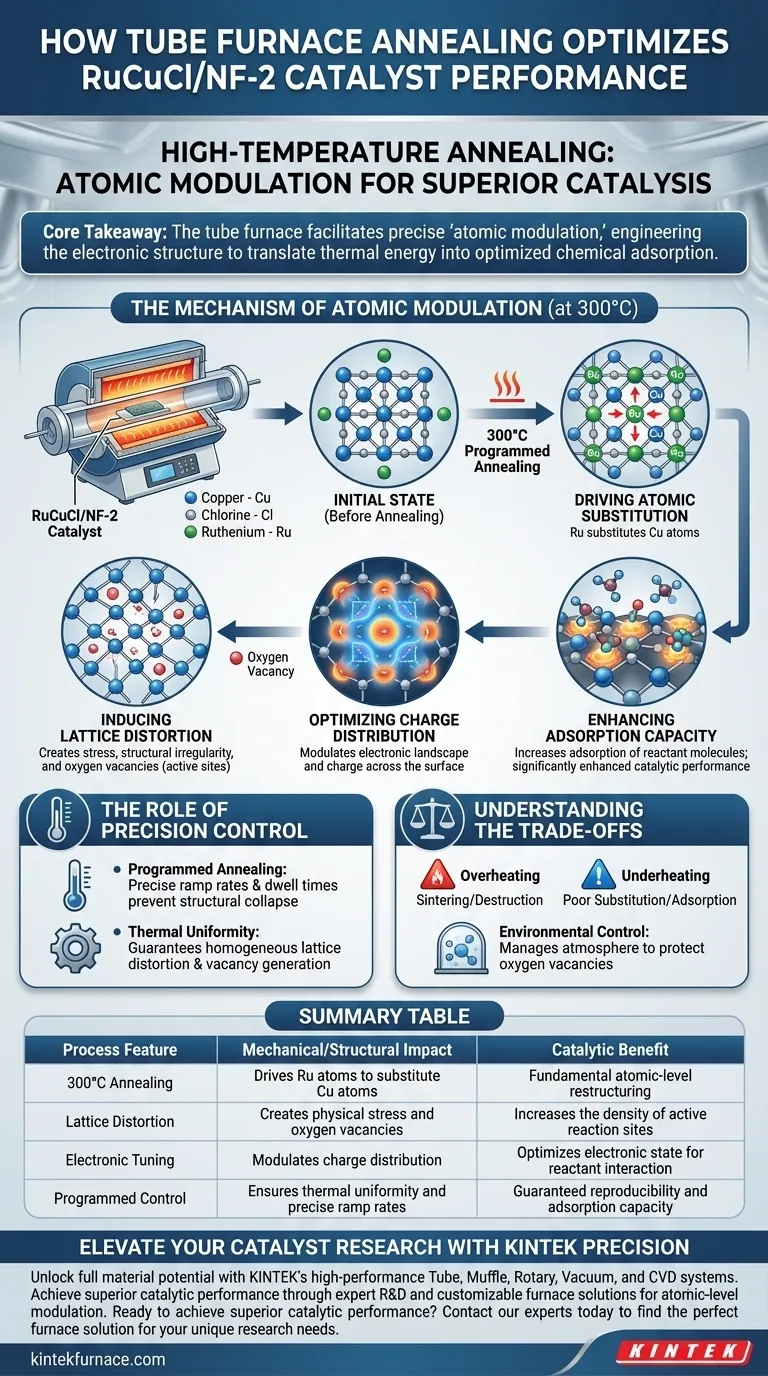
High-temperature annealing in a tube furnace fundamentally restructures the RuCuCl/NF-2 catalyst at the atomic level to unlock superior performance. Specifically, programmed annealing at 300°C drives the substitution of copper atoms by ruthenium atoms within the crystal lattice. This atomic exchange creates oxygen vacancies and lattice distortions that optimize charge distribution, making the material significantly more effective at adsorbing reactant molecules.
The Core Takeaway The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it facilitates a precise "atomic modulation." By driving ruthenium-copper substitution, the annealing process engineers the electronic structure of the catalyst, directly translating thermal energy into optimized chemical adsorption and enhanced catalytic activity.

The Mechanism of Atomic Modulation
Driving Atomic Substitution
The primary function of the annealing process, typically conducted at 300°C, is to provide the thermal energy necessary to alter the material's composition.
Under these precise thermal conditions, ruthenium (Ru) atoms substitute copper (Cu) atoms within the lattice structure. This is not a surface-level change but a fundamental shift in the bulk arrangement of the catalyst.
Inducing Lattice Distortion
As ruthenium atoms replace copper, the difference in atomic size and properties causes physical stress within the crystal structure.
This results in lattice distortion, a deliberate structural irregularity. Simultaneously, this process generates a high concentration of oxygen vacancies (missing oxygen atoms in the lattice), which serve as highly active sites for chemical reactions.
Optimizing Charge Distribution
The physical changes—substitution, distortion, and vacancies—lead to an electronic transformation.
This atomic-level modulation of charge distribution alters how electrons move across the catalyst surface. By tuning the electronic landscape, the annealing process ensures that the active sites are electrically primed to interact with reactants.
Enhancing Adsorption Capacity
The ultimate goal of this structural and electronic engineering is to improve how the catalyst interacts with the outside world.
The optimized charge distribution increases the adsorption capacity of active sites for reactant molecules. Because the reactants can adhere more effectively to the catalyst surface, the overall catalytic performance is significantly enhanced.
The Role of Precision Control
The Necessity of Programmed Annealing
The transformation of RuCuCl/NF-2 relies on programmed annealing, where temperature ramp rates and dwell times are strictly controlled.
A tube furnace is essential here because it provides a precise thermal environment. The atomic substitution described above is thermodynamically sensitive; deviations in temperature could fail to drive the substitution or lead to unwanted structural collapse.
Thermal Uniformity
While the primary mechanism occurs at 300°C, the equipment must ensure this temperature is uniform across the sample.
As seen in similar catalytic processes, temperature variations can lead to inconsistent atomic diffusion. The tube furnace ensures that the thermal field is uniform, guaranteeing that the lattice distortion and vacancy generation occur homogeneously throughout the catalyst material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
The specific benefits of annealing RuCuCl/NF-2 are tied to a tight temperature window, typically around 300°C.
Overheating can lead to excessive sintering or the destruction of the delicate lattice distortions created during the substitution process. Conversely, underheating provides insufficient energy for the ruthenium atoms to effectively replace copper, resulting in a catalyst with poor adsorption capabilities.
Environmental Control
While the primary reference highlights thermal control, the tube furnace also dictates the atmospheric environment.
If the furnace atmosphere is not properly managed (e.g., unintended oxidation or reduction due to leaks), the specific chemistry of the oxygen vacancies can be altered. Maintaining the integrity of the annealing environment is just as critical as maintaining the temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your RuCuCl/NF-2 catalyst, consider the following approach:
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Active Sites: Ensure your furnace is calibrated to maintain exactly 300°C, as this is the critical threshold for driving the Ru-Cu substitution and generating oxygen vacancies.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Utilize the programmed annealing features of the tube furnace to standardize ramp rates, ensuring the lattice distortion is consistent across every batch.
Success depends on using the tube furnace not just as a heater, but as a precision tool to engineer the atomic geometry of your catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Mechanical/Structural Impact | Catalytic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 300°C Annealing | Drives Ru atoms to substitute Cu atoms in the lattice | Fundamental atomic-level restructuring |
| Lattice Distortion | Creates physical stress and oxygen vacancies | Increases the density of active reaction sites |
| Electronic Tuning | Modulates charge distribution across the surface | Optimizes electronic state for reactant interaction |
| Programmed Control | Ensures thermal uniformity and precise ramp rates | Guaranteed reproducibility and adsorption capacity |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your materials through superior thermal engineering. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of atomic-level modulation. Whether you are optimizing Ru-Cu substitution or engineering complex lattice distortions, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal uniformity and programmed control essential for your success.
Ready to achieve superior catalytic performance? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Tao Chen, Qiangchun Liu. RuCu Nanorod Arrays Synergistically Promote Efficient Water-Splitting. DOI: 10.3390/catal15010098
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What problems existed with early tube furnace designs? Discover the Flaws That Hindered Performance
- How does a PID temperature controller function in a tube furnace? Enhance Your Pyrolysis Precision
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in the carbonization of ionic liquid precursors? Master Thermal Control
- What is the role of high-temperature calcination in a tube furnace for H-Beta zeolite? Engineer Precision Catalysts
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Why is a Horizontal Tube Furnace used for the torrefaction of Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)? Boost Fuel Efficiency Now
- Why is it necessary to evacuate and seal quartz tubes for NiPS3 crystals? Master CVT Precision & Purity
- Why is a quartz tube furnace used for two-stage LiFePO4 coating? Master Oxidation Control and Conductivity



















