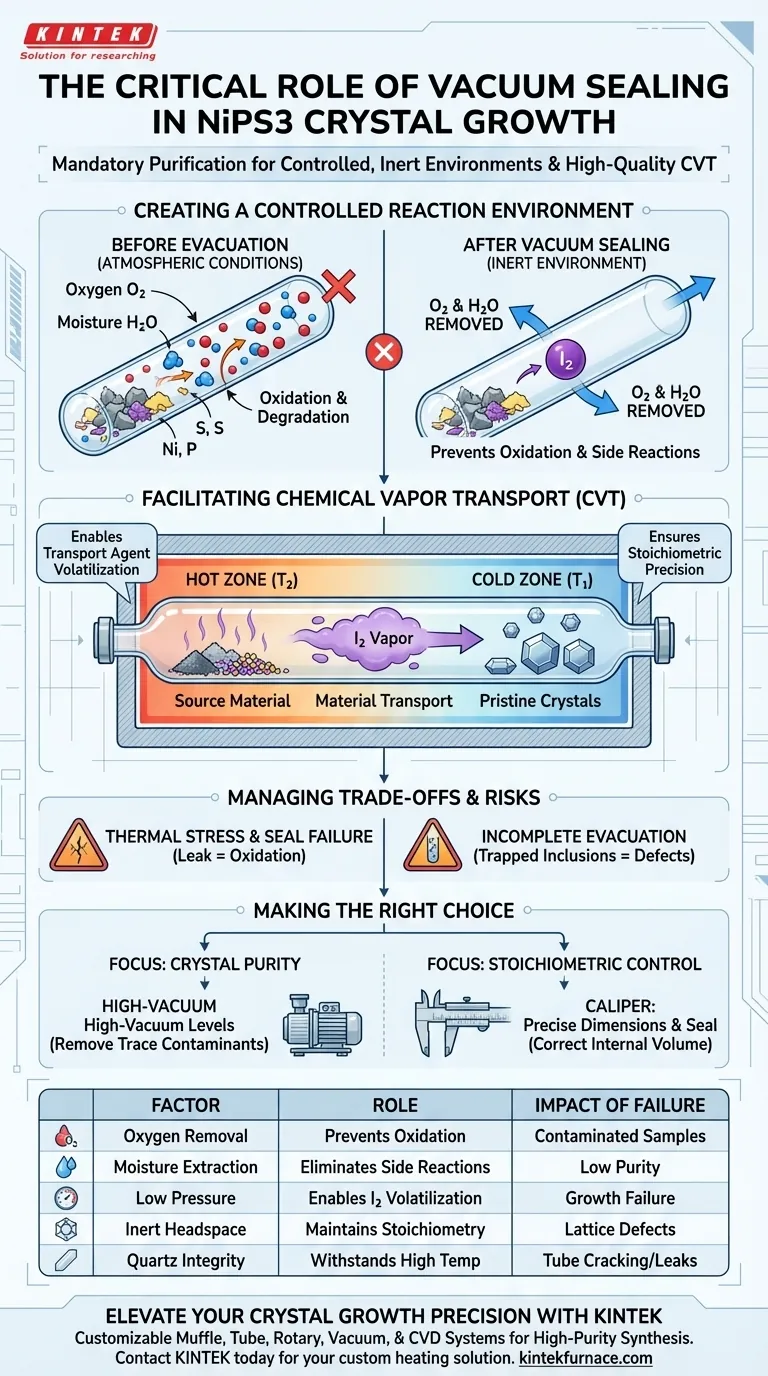
Evacuating and sealing quartz tubes is a mandatory purification step that creates a strictly controlled, inert environment for the growth of NiPS3 crystals. By removing atmospheric oxygen and moisture via a vacuum system, you prevent the degradation of raw materials and enable the precise chemical reactions required for high-quality Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT).
The vacuum sealing process serves two non-negotiable functions: it protects reactive precursors from oxidation and establishes the necessary pressure conditions for the transport agent to function. Without this step, the synthesis will inevitably result in contaminated samples or incorrect chemical stoichiometry.
Creating a Controlled Reaction Environment
To grow pristine NiPS3 van der Waals crystals, you must eliminate variables that compete with the desired reaction. The vacuum system is the primary tool for establishing this baseline.
Preventing Oxidation of Precursors
At the high temperatures required for crystal growth, raw materials become highly reactive.
If oxygen is present in the tube, it will react with the source materials (Nickel, Phosphorus, or Sulfur) before they can form the desired crystal lattice. Evacuation removes oxygen, ensuring the precursors react only with each other.
Eliminating Atmospheric Moisture
Moisture is equally detrimental to the CVT process.
Even trace amounts of water vapor trapped inside the quartz tube can disrupt the chemical balance. A high-vacuum seal ensures that moisture is fully extracted, preventing unintended side reactions that ruin crystal purity.
Facilitating Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT)
Beyond simple protection, the vacuum plays an active mechanical role in the transport process. The physics of CVT relies on specific pressure and volume conditions within the tube.
Enabling Transport Agent Volatilization
The growth of NiPS3 relies on a transport agent, typically iodine, to move material across a temperature gradient.
Evacuating the tube provides the necessary "headspace" and low-pressure environment for the iodine to volatilize (turn into gas) efficiently. If the tube were full of air, the transport agent would struggle to vaporize and circulate effectively.
Ensuring Stoichiometric Precision
Crystal quality depends on maintaining the exact ratio of elements (stoichiometry) in the final compound.
By removing foreign gases, you ensure that the internal pressure is generated solely by the transport agent and the reactants. This control allows the chemical reaction to proceed exactly as calculated, resulting in crystals with the correct chemical composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum sealing is essential, it introduces specific technical challenges that must be managed to avoid failure.
The Risk of Incomplete Evacuation
A "rough" vacuum is often insufficient for high-purity applications.
If the vacuum system does not achieve a low enough pressure, residual pockets of gas will remain. These microscopic contaminants can become trapped inclusions within the crystal, compromising its electronic or magnetic properties.
Thermal Stress and Seal Integrity
Quartz is used because it can withstand processing temperatures up to 800°C, but the seal itself is a vulnerability.
If the tube is sealed poorly while under vacuum, the thermal stress of the furnace can cause the quartz to crack or leak. A leak during the heating phase destroys the vacuum, instantly oxidizing the batch and wasting the materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The rigor of your vacuum sealing process should align with the specific requirements of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Purity: Ensure your vacuum system is capable of high-vacuum levels to remove even trace contaminants that could cause lattice defects.
- If your primary focus is Stoichiometric Control: Prioritize precise tube dimensions and seal placement to guarantee the correct internal volume for the iodine transport agent to operate.
Ultimately, the vacuum seal is the defining barrier that separates a pristine van der Waals crystal from a contaminated, unusable compound.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in NiPS3 Synthesis | Impact of Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Removal | Prevents precursor oxidation (Ni, P, S) | Contaminated samples/Oxide formation |
| Moisture Extraction | Eliminates side reactions from water vapor | Disrupted chemical balance & low purity |
| Low Pressure | Enables transport agent (Iodine) volatilization | Poor material transport & growth failure |
| Inert Headspace | Maintains precise chemical stoichiometry | Incorrect crystal lattice/Lattice defects |
| Quartz Integrity | Withstands high temperatures up to 800°C | Tube cracking or vacuum leaks |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision
Achieving the perfect van der Waals crystal requires absolute control over your thermal environment. At KINTEK, we understand the rigorous demands of Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) and high-purity synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs.
Whether you are scaling NiPS3 production or conducting delicate material research, our high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and vacuum compatibility your work deserves. Contact KINTEK today to find your custom heating solution and ensure every batch meets the highest standards of stoichiometric purity.
Visual Guide
References
- Michael F. DiScala, K. W. Plumb. Elucidating the Role of Dimensionality on the Electronic Structure of the Van der Waals Antiferromagnet NiPS<sub>3</sub>. DOI: 10.1002/apxr.202300096
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a vertical alumina tube resistance furnace applied in the hydrogen reduction of bauxite residue particles?
- How does a laboratory tube furnace contribute to the sintering process of Cu-Al2O3? Enhance Composite Density & Strength
- What are the differences between solid and split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is a vacuum tube furnace? Essential for High-Purity Material Processing
- What are the benefits of using an alumina tube furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temp Material Processing
- What are the pros and cons of vertical tube furnaces? Precision vs. Capacity for Your Lab
- What design features contribute to the durability and safety of modern lab tube furnaces? Ensuring Long-Term Reliability and Operator Protection
- What advantages do drop tube furnaces offer? Achieve Precise Control and High Efficiency



















