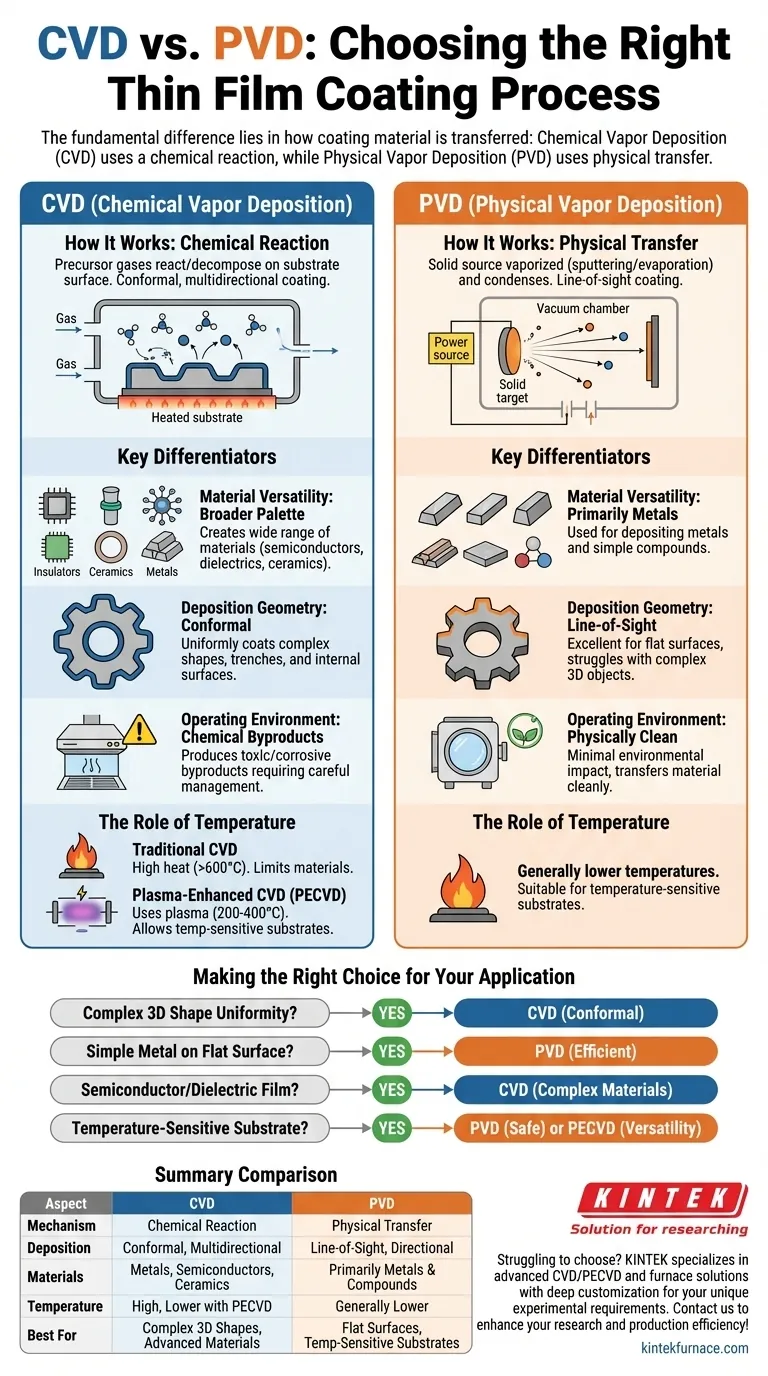
The fundamental difference between Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) lies in how the coating material is transferred to the substrate. CVD uses a chemical reaction on the surface to create the film from precursor gases. In contrast, PVD physically transfers material from a solid source to the substrate through methods like sputtering or evaporation, without any chemical change.
The choice between CVD and PVD is not a matter of which is universally "better," but a strategic decision based on your specific requirements for material type, substrate geometry, and temperature sensitivity. Understanding their core mechanisms is the key to selecting the right tool for your application.
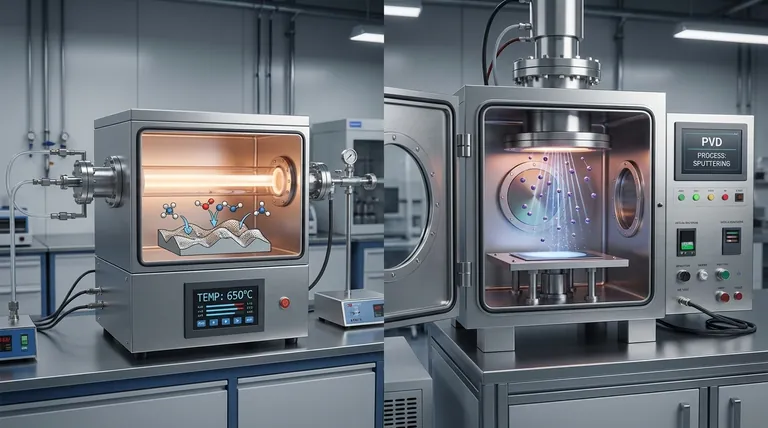
The Core Mechanism: Chemical Reaction vs. Physical Transfer
To grasp the practical differences, you must first understand how each process works at a fundamental level. One creates a new material on the surface, while the other simply moves it.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Works
CVD is a process where a substrate is placed in a reaction chamber and exposed to one or more volatile precursor gases.
When the chamber is heated, these gases react or decompose on the substrate's surface, forming a new solid material. This new material is the thin film coating.
Because this process is driven by the diffusion of gases, the deposition is conformal and multidirectional, meaning it can uniformly coat complex, non-flat surfaces.
How Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Works
PVD is a vacuum-based process that involves vaporizing a solid source material, known as a "target."
This vaporization is achieved through physical means, such as sputtering (bombarding the target with high-energy ions) or evaporation (heating the target until it becomes a gas).
The vaporized atoms then travel in a straight path—a line-of-sight trajectory—and condense onto the substrate, forming the coating. No chemical reactions are involved.
Key Differentiators and Their Implications
The fundamental difference in mechanism leads to critical distinctions in material choice, coating geometry, and environmental impact.
Material Versatility: CVD's Broader Palette
PVD is primarily used for depositing metals and other simple compounds.
CVD, however, is far more versatile. The chemical reaction process allows for the creation of a wide range of materials, including semiconductors, insulators (dielectrics), and ceramics, in addition to metals. This makes CVD essential for advanced electronics and optics.
Deposition Geometry: Conformal vs. Line-of-Sight
PVD's line-of-sight nature means it is excellent for coating flat surfaces but struggles to uniformly coat complex 3D objects, as "shadowed" areas will receive little to no material.
CVD's gas-based, multidirectional deposition excels at creating highly uniform and conformal coatings over intricate shapes, trenches, and internal surfaces.
Operating Environment and Byproducts
PVD is a physically "clean" process, as it simply transfers material from a solid source. Its environmental impact is minimal.
CVD processes, by their chemical nature, often produce toxic or corrosive gaseous byproducts that must be carefully managed and treated, requiring more specialized and complex equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is often the deciding factor, as it dictates which substrates can be safely coated. Here, the distinction between different types of CVD becomes critical.
The High-Heat Demand of Traditional CVD
Conventional CVD relies on high temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the thermal energy needed to drive the chemical reactions on the substrate surface.
This high heat requirement severely limits the types of materials that can be coated, excluding most plastics and other temperature-sensitive substrates.
The Exception: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
Plasma-Enhanced CVD is a subtype of CVD that solves the temperature problem. Instead of relying solely on heat, it uses an electric field to generate a plasma.
This plasma excites the precursor gas molecules, giving them the energy to react at much lower temperatures, typically between 200-400°C.
PECVD allows for the benefits of CVD—like material versatility—on temperature-sensitive substrates. It also often produces higher-quality films with less risk of cracking compared to some traditional CVD methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine the best approach for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D shape uniformly: CVD is the superior choice due to its conformal, gas-based deposition.
- If your primary focus is depositing a simple metal film on a flat surface: PVD is often more straightforward, faster, and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is creating a semiconductor or dielectric film: CVD is the necessary technology for these chemically complex materials.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive substrate like plastic: PVD is a safe option, but for the material versatility of CVD, you must specifically consider Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD).
By aligning the process capabilities with your project's non-negotiable constraints, you can confidently select the most effective deposition technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Chemical reaction from gases | Physical transfer from solid source |
| Deposition | Conformal, multidirectional | Line-of-sight, directional |
| Materials | Metals, semiconductors, ceramics | Primarily metals and simple compounds |
| Temperature | High (traditional), lower (PECVD) | Generally lower |
| Best For | Complex 3D shapes, advanced materials | Flat surfaces, temperature-sensitive substrates |
Struggling to choose between CVD and PVD for your lab's coating needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you need conformal coatings for complex geometries or efficient metal films on flat surfaces. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods



















