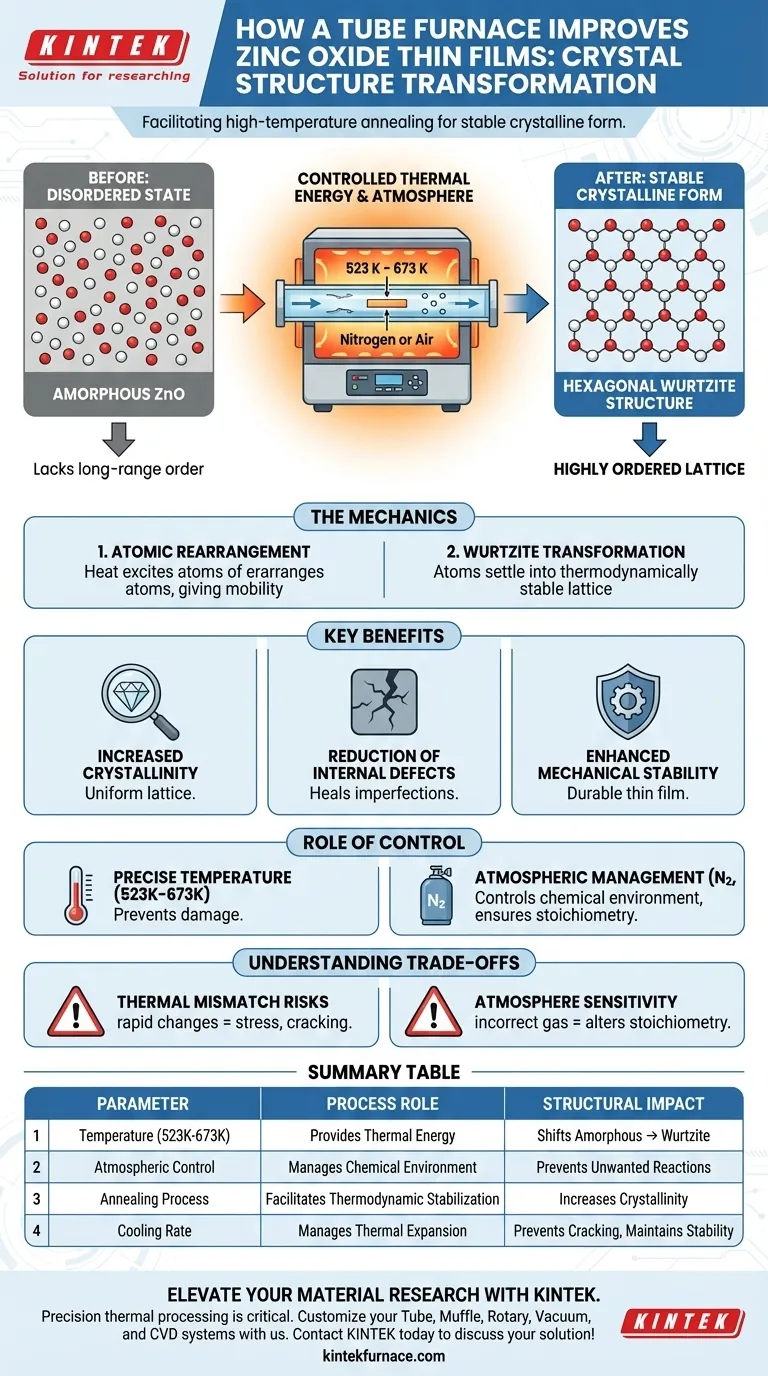
A tube furnace facilitates high-temperature annealing to transform zinc oxide thin films from a disordered state into a stable crystalline form. By applying a controlled temperature field typically between 523 K and 673 K, the furnace provides the thermal energy necessary for atomic rearrangement. This process shifts the material structure from amorphous to hexagonal wurtzite, significantly enhancing its physical properties.
The core function of the tube furnace in this application is to provide precise thermal energy in a controlled atmosphere. This drives the transition of zinc oxide from an amorphous state to a highly ordered hexagonal wurtzite structure, minimizing internal defects and maximizing mechanical stability.
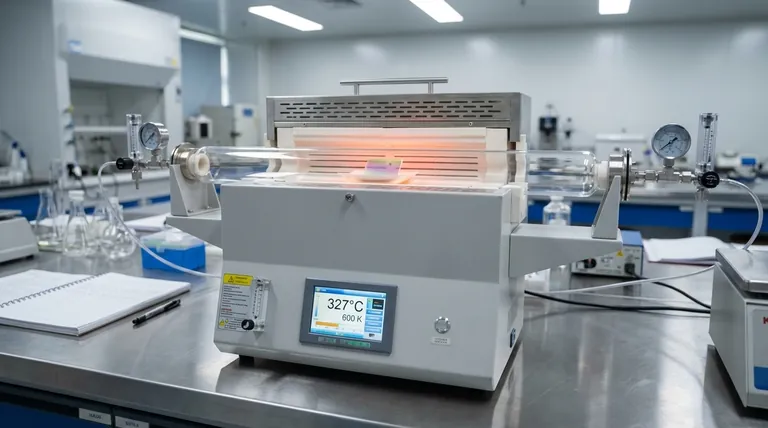

The Mechanics of Structural Transformation
Atomic Rearrangement via Thermal Energy
The primary driver of structural improvement is the application of heat. Thermal energy excites the atoms within the thin film, giving them the mobility required to break free from disordered, amorphous positions.
Achieving the Hexagonal Wurtzite Structure
As the atoms migrate, they settle into a thermodynamically stable configuration. For zinc oxide, this results in a transformation from an amorphous phase to a specific hexagonal wurtzite structure. This specific crystal lattice is crucial for the material's functional characteristics.
Key Benefits of Tube Furnace Annealing
Increased Crystallinity
The controlled thermal environment ensures a uniform crystal lattice formation. This high degree of crystallinity distinguishes high-performance films from lower-quality, disordered coatings.
Reduction of Internal Defects
The annealing process effectively "heals" imperfections within the film. By allowing atoms to align correctly, the furnace significantly reduces internal defects that would otherwise impede electron flow or structural integrity.
Enhanced Mechanical Stability
A better-structured crystal lattice naturally leads to a stronger material. The transformation into the wurtzite phase improves the overall mechanical stability of the thin film, making it more durable during subsequent handling or usage.
The Role of Environmental Control
Precise Temperature Regulation
Tube furnaces maintain specific temperature ranges, such as the 523 K to 673 K window used for zinc oxide. This precision prevents overheating, which could degrade the substrate, or under-heating, which would fail to initiate crystallization.
Atmospheric Management
The furnace allows for the introduction of specific gases to control the chemical environment. For zinc oxide, atmospheres like nitrogen or air are typically used to facilitate the annealing process without inducing unwanted reactions.
Context from Other Oxides
While zinc oxide uses these atmospheres to stabilize structure, tube furnaces are versatile tools. For example, other materials like Strontium Titanate may require a reducing atmosphere (H2 and Ar) to intentionally induce oxygen vacancies and modulate band structures. This highlights the furnace's ability to tailor the material's electronic properties through atmospheric control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Mismatch Risks
While heat improves crystal structure, rapid temperature changes can introduce stress. If the heating or cooling rates are not carefully ramped, the film may crack due to thermal expansion mismatches between the film and the substrate.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The specific atmosphere must be matched perfectly to the material's chemistry. Using an incorrect gas mix can alter the stoichiometry of the film. For instance, an overly reducing atmosphere might strip oxygen from a film where stability is the goal, rather than defect engineering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your manufacturing process, you must align the furnace parameters with your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is structural stability: Ensure your furnace maintains a steady temperature between 523 K and 673 K to maximize the formation of the hexagonal wurtzite phase.
- If your primary focus is minimizing defects: Utilize a consistent, inert (nitrogen) or oxidizing (air) atmosphere to allow for atomic rearrangement while preventing unwanted chemical reduction.
Precise thermal management is the difference between a disordered coating and a high-performance crystalline film.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Process Role | Structural Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (523K - 673K) | Provides thermal energy for atomic mobility | Shifts structure from amorphous to hexagonal wurtzite |
| Atmospheric Control | Manages chemical environment (Nitrogen/Air) | Prevents unwanted reactions and ensures stoichiometry |
| Annealing Process | Facilitates thermodynamic stabilization | Increases crystallinity and reduces internal lattice defects |
| Cooling Rate | Manages thermal expansion | Prevents film cracking and maintains mechanical stability |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision thermal processing is critical for achieving the perfect hexagonal wurtzite structure in your thin films. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific temperature and atmospheric requirements. Whether you are optimizing crystallinity or engineering specific defects, our advanced laboratory high-temp furnaces provide the uniform heat control you need.
Ready to transform your thin film production? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in g-C3N4 thin film preparation? Optimize Your Hot-Wall CVD Synthesis
- What is the purpose of using a tube resistance furnace with flowing oxygen for NMC synthesis? Achieve Pure Phase Purity
- How is heat transferred to the material inside the tube furnace? Master the Three-Stage Process for Precise Heating
- What role does a high-temperature quartz tube furnace play in CMSM production? Master Carbonization Precision
- What is the working principle of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Efficiency
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- Why is the integration of an axial rotation mechanism significant in tube furnaces? Enhance Experimental Control
- What is the specific purpose of using a laboratory tube furnace with a wet argon environment? Optimize Siloxane Curing



















