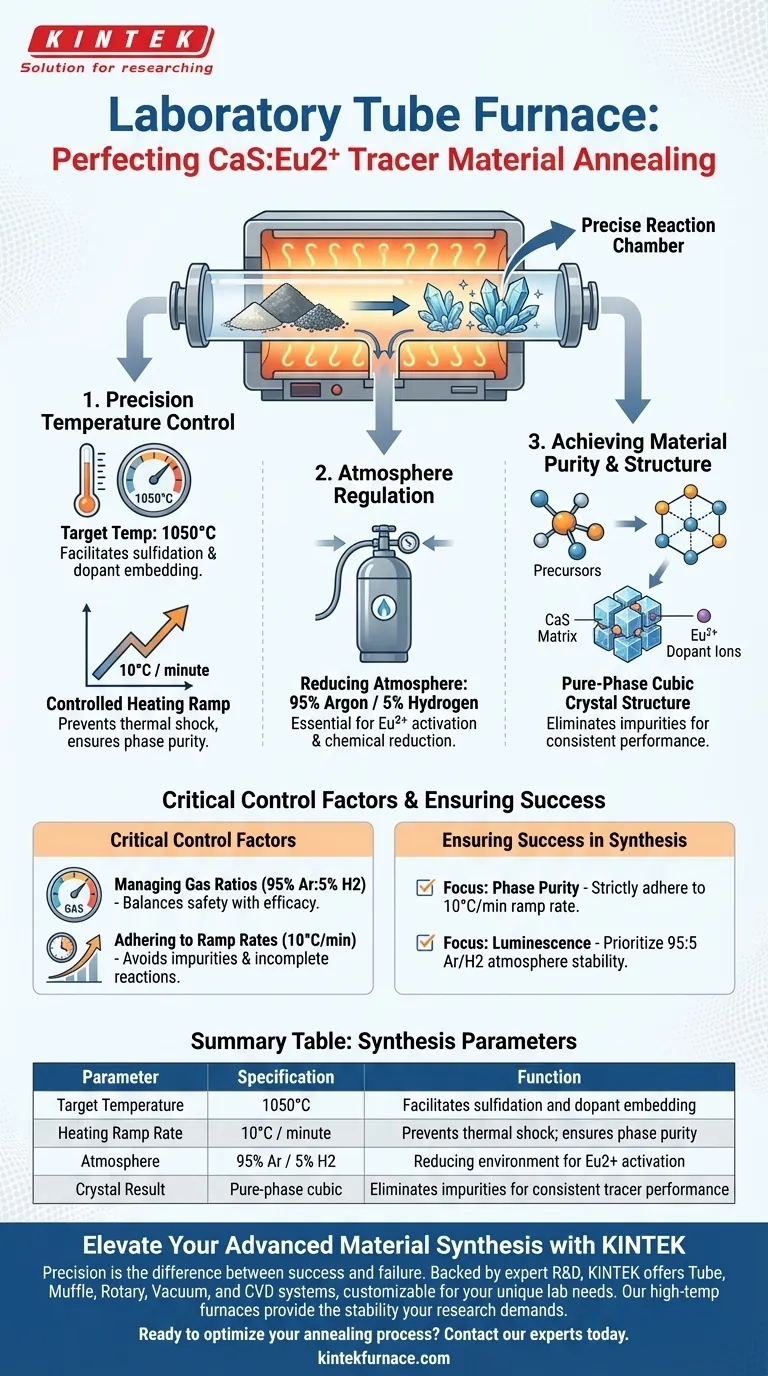
A laboratory tube furnace acts as the precise reaction chamber required to transform raw precursors into functional CaS:Eu2+ tracer materials. By maintaining a target temperature of 1050°C and a specific reducing atmosphere, the furnace ensures the material undergoes the necessary chemical changes to achieve luminescence and structural stability.
The tube furnace’s primary value lies in its ability to synchronize a controlled heating rate with a reducing gas flow. This combination is the only way to achieve a pure-phase cubic crystal structure with correctly embedded dopant ions.

The Mechanics of the Annealing Process
Precision Temperature Control
The synthesis of CaS:Eu2+ is highly sensitive to thermal conditions. The tube furnace provides a stable high-temperature environment, specifically holding the material at 1050°C.
Controlled Heating Ramp
Reaching the target temperature requires a measured approach rather than a sudden spike. The furnace creates a controlled ramp rate of 10°C per minute.
This gradual increase allows the precursors to react evenly. It prevents thermal shock and ensures the chemical lattice forms systematically.
Atmosphere Regulation
Standard air or inert environments are insufficient for this specific synthesis. The tube furnace allows for the introduction of a strictly controlled reducing atmosphere, typically a mixture of 95% Argon and 5% Hydrogen.
This gas flow is essential for driving the chemical reduction required to activate the Europium (Eu2+) ions within the host material.
Achieving Material Purity and Structure
Facilitating Sulfidation Reactions
The combination of heat and the reducing atmosphere within the tube drives proper sulfidation reactions. This chemical process converts the starting materials into the desired Calcium Sulfide (CaS) matrix.
Dopant Embedding
For the material to function as a tracer, the Europium dopant must be integrated correctly. The furnace environment ensures these ions are embedded deep into the crystal lattice.
Crystallization Results
The ultimate output of this strictly controlled process is a pure-phase cubic crystal structure. The tube furnace eliminates variables that could lead to impurities or structural defects, ensuring the final phosphor performs consistent tracer functions.
Critical Control Factors
Managing Gas Ratios
The 95:5 ratio of Argon to Hydrogen is not arbitrary; it balances safety with chemical efficacy. The furnace must maintain this specific balance to prevent oxidation without introducing dangerous levels of hydrogen.
Adhering to Ramp Rates
Deviating from the 10°C/minute heating rate is a common source of error. Ramping too quickly can trap impurities or result in incomplete reactions, compromising the phase purity of the final cubic structure.
Ensuring Success in Synthesis
To maximize the quality of your CaS:Eu2+ production, align your furnace settings with your specific outcome goals:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Strictly adhere to the 10°C/minute ramp rate to ensure the crystal lattice forms without defects.
- If your primary focus is Luminescence (Dopant Activation): Prioritize the stability of the 95:5 Argon/Hydrogen atmosphere to ensure full reduction of the Europium ions.
Success in this synthesis relies not just on reaching high temperatures, but on the precise orchestration of atmosphere and heating rates.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Function in Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 1050°C | Facilitates sulfidation and dopant embedding |
| Heating Ramp Rate | 10°C / minute | Prevents thermal shock; ensures phase purity |
| Atmosphere | 95% Ar / 5% H2 | Reducing environment for Eu2+ activation |
| Crystal Result | Pure-phase cubic | Eliminates impurities for consistent tracer performance |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a successful tracer material and a failed batch. At KINTEK, we understand that achieving a pure-phase cubic crystal structure requires absolute control over thermal ramps and atmospheric integrity.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are synthesizing phosphors or developing new superconductors, our high-temp furnaces provide the stability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your annealing process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Arzu Coşgun Ergene, Andrey Turshatov. High Photoluminescence Quantum Yield and Tunable Luminescence Lifetimes in the Sub‐Second Range of CaS:Eu<sup>2+</sup> Phosphors for Tracer Based Sorting. DOI: 10.1002/admt.202500353
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a dual-zone tube furnace facilitate the synthesis of CrSBr single crystals? Master the CVT Process
- What materials are used for a tube furnace heating chamber? Optimize for temperature, purity, and durability.
- What is chemical vapor transport and how is it related to tube furnaces? Master CVT for High-Quality Crystal Growth
- What is the role of an industrial tubular furnace in the thermal treatment of municipal sludge? Expert Lab Insights
- What critical environmental controls does a tubular furnace provide for CMS membranes? Optimize Pore Engineering
- How does the industrial tube furnace contribute to Fe-N-C catalyst synthesis? Master High-Temperature Carbonization
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform temperature distribution? Discover Key Mechanisms for Precise Heating
- How does a dual-temperature zone tube furnace facilitate the preparation of composite materials like ReO3–Cu2Te?



















