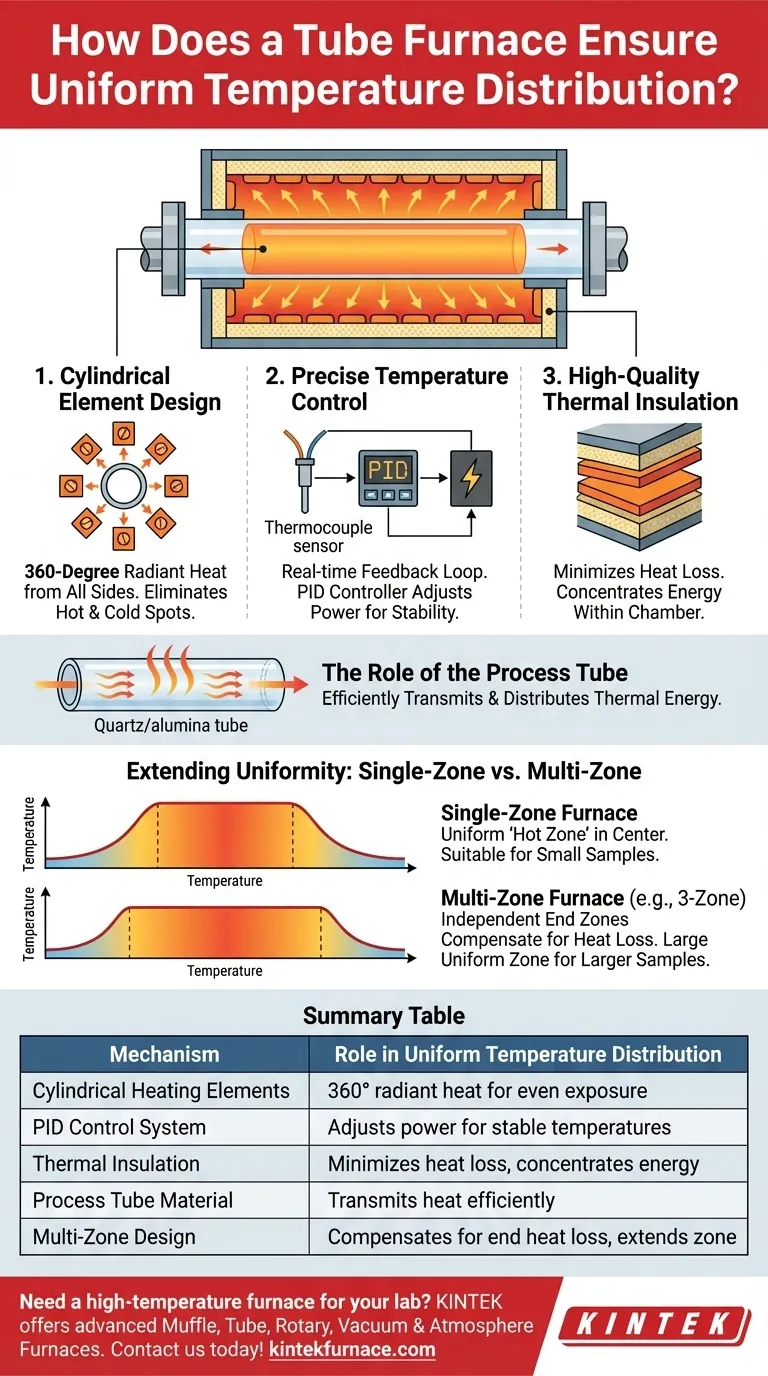
At its core, a tube furnace achieves uniform temperature distribution through three primary mechanisms working in concert: the strategic 360-degree placement of heating elements around the process tube, a precise feedback control system using thermocouples, and high-efficiency thermal insulation that minimizes heat loss. This design ensures that a sample is heated evenly from all sides, which is critical for the success of sensitive thermal processes.
The exceptional temperature uniformity of a tube furnace is not an accident; it is a direct result of its cylindrical geometry. By surrounding the sample with a consistent source of radiant heat, the furnace creates a naturally stable and uniform thermal environment that is difficult to achieve with other designs.

The Core Principles of Uniform Heating
To understand how a tube furnace delivers such consistent results, it is essential to examine its fundamental design components. Each element plays a distinct and critical role in creating and maintaining a uniform thermal zone.
Cylindrical Element Design
The most significant factor is the physical arrangement of the heating elements. They are positioned cylindrically to encircle the process tube.
This 360-degree configuration subjects the material inside to constant, even radiant heat from all directions. This eliminates the hot and cold spots that can occur in furnaces where heat originates from a single plane, such as the bottom or top.
Precise Temperature Control
A tube furnace does not simply apply power; it intelligently regulates it. A thermocouple, a sensitive temperature sensor, is placed near the heating elements to provide real-time temperature data.
This data is fed to a PID controller (Proportional-Integral-Derivative), which constantly adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements. This feedback loop corrects for the smallest temperature deviations, ensuring the setpoint is held with extreme stability over time.
High-Quality Thermal Insulation
Effective insulation is crucial for preventing heat from escaping into the surrounding environment. By minimizing heat loss, the insulation concentrates the thermal energy within the heating chamber.
This concentration ensures that the energy delivered by the elements is used to heat the sample, not the lab, further contributing to a stable and uniform internal temperature.
The Role of the Process Tube
The material of the tube itself, often quartz or alumina, also aids in uniformity. Materials like quartz transmit heat radiation very efficiently and evenly, helping to distribute the thermal energy uniformly across the sample contained within it.
Extending Uniformity: Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Furnaces
For demanding applications, the standard design can be enhanced to create an even larger and more precise uniform heating zone.
The Standard Single-Zone Furnace
A basic tube furnace uses a single set of heating elements controlled as one unit. This creates a highly uniform "hot zone" in the center of the furnace.
However, the temperature naturally drops off toward the ends of the tube due to heat loss. This is perfectly acceptable for small samples placed directly in the center.
The Advanced Multi-Zone Furnace
A multi-zone furnace, typically with three independent heating zones, offers superior control. It features a central zone and two end zones, each with its own thermocouple and controller.
By setting the end zones to a slightly higher temperature, you can actively compensate for the natural heat loss at the ends. This technique dramatically flattens the temperature profile, creating a much larger and more uniform hot zone across the furnace's length. This is essential for processing larger samples or multiple samples at once.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a tube furnace's performance is governed by physical realities that are important to understand for achieving optimal results.
The "Uniform Zone" is Not the Entire Tube
It is a common misconception that the entire length of the furnace tube is at the target temperature. The specified uniform zone is a specific region, almost always in the center, where the temperature variation is within a tight tolerance (e.g., ±1°C or ±5°C).
Ramp Rates Affect Uniformity
Heating or cooling the furnace too quickly can introduce temporary temperature gradients. A slower, more controlled ramp rate allows the entire chamber and the sample to heat up more evenly, ensuring better uniformity throughout the entire process cycle.
How Tube Furnaces Differ from Other Designs
A rotary furnace also uses a tube but is designed for powders and granules, using rotation to mix materials and ensure every particle is heated evenly.
A muffle furnace heats a chamber from the outside, which provides good general uniformity but lacks the direct, 360-degree radiant heating that makes a tube furnace so precise for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is entirely dependent on the precision and scale required by your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment or material synthesis on small samples: A single-zone tube furnace is highly effective and economical, provided you place the sample in the center of the hot zone.
- If your primary focus is high-precision annealing or growing uniform thin films via CVD: A multi-zone furnace is the necessary choice to guarantee a large, flat temperature profile essential for consistent results across larger substrates.
- If your primary focus is processing powders, pellets, or other granular materials: A rotary tube furnace is the only design that ensures uniformity through both heating and mechanical mixing.
Understanding how a tube furnace masterfully controls its thermal environment empowers you to select the right tool and optimize its use to achieve your desired material properties with precision and repeatability.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Role in Uniform Temperature Distribution |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Heating Elements | Provide 360-degree radiant heat for even exposure from all sides |
| PID Control System | Uses thermocouples to adjust power and maintain stable temperatures |
| Thermal Insulation | Minimizes heat loss to concentrate energy within the chamber |
| Process Tube Material | Transmits heat efficiently for uniform sample heating |
| Multi-Zone Design | Compensates for end heat loss to extend uniform hot zones |
Need a high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform heating and reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















