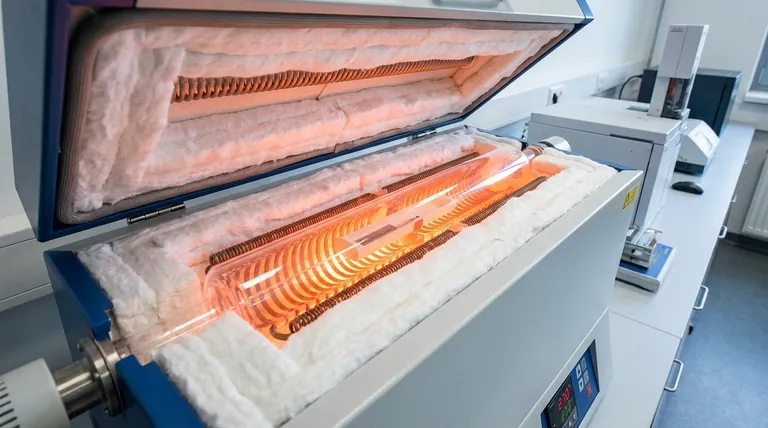
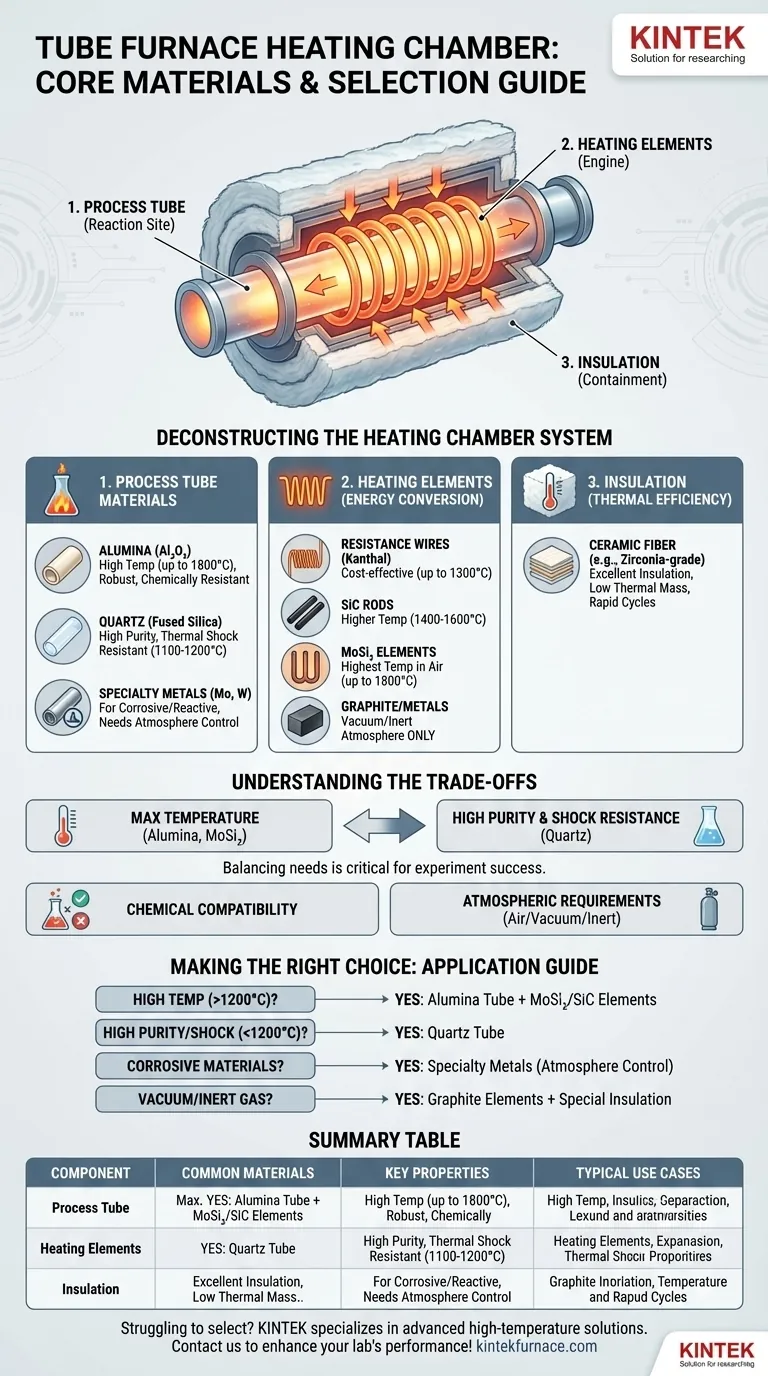
At its core, the "heating chamber" of a tube furnace is not a single component but a system of three critical parts: the process tube, the heating elements, and the insulation. The process tube, which contains the sample, is most commonly made from high-purity alumina or quartz, chosen for their exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance.
The choice of material is not a matter of preference but a critical decision dictated by your experiment's maximum temperature, chemical environment, and atmospheric requirements. Alumina is the workhorse for high temperatures, while quartz excels in applications demanding high purity and thermal shock resistance.

Deconstructing the "Heating Chamber": A System of Components
To truly understand the materials, it's essential to recognize that the heating chamber is an assembly. Each part has a distinct role and is made from materials optimized for that function.
The Process Tube: Where the Reaction Occurs
This is the central tube that holds your sample and atmosphere. Its material directly interacts with your process.
-
Alumina (Al₂O₃): This is the go-to material for high-temperature applications, typically operating up to 1700°C or even 1800°C. It offers excellent thermal and electrical insulation and is highly resistant to chemical attack, making it robust and durable.
-
Quartz (Fused Silica): Valued for its exceptional purity and superior thermal shock resistance, quartz is ideal for processes sensitive to contamination. It can handle rapid temperature changes but generally has a lower maximum operating temperature than alumina, around 1100-1200°C.
-
Specialty Metals (Molybdenum, Tungsten): For processes involving highly corrosive or specific reactive materials that would damage ceramics, refractory metal tubes are used. These are less common and require careful control of the furnace atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
The Engine of the Furnace: Heating Elements
These are the components that convert electrical energy into heat. They surround the process tube but do not typically come into direct contact with the sample.
-
Resistance Wires (e.g., Kanthal): A common and cost-effective choice for furnaces operating up to about 1300°C.
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: Used for higher temperatures, generally in the 1400°C to 1600°C range. They are durable and can operate in air.
-
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements: These are the standard for reaching the highest temperatures in air, often up to 1800°C. They form a protective silica layer during operation.
-
Graphite or Refractory Metals: Primarily used in vacuum or inert atmosphere furnaces. Graphite cannot be used in an oxidizing atmosphere (air) at high temperatures as it will burn away.
The Containment System: Insulation
The final component is the insulation, which encases the heating elements and ensures thermal energy is directed inward, providing temperature uniformity and efficiency.
- Ceramic Fiber: This is the industry standard. High-purity materials like zirconia-grade ceramic fiber are used to line the furnace casing, providing excellent thermal insulation with low thermal mass. This allows for relatively rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a tube furnace or a process tube involves balancing competing factors. An incorrect choice can lead to failed experiments or damaged equipment.
Temperature vs. Purity
The primary trade-off is between maximum temperature and purity. Alumina allows you to reach higher temperatures, while quartz offers a purer processing environment, which is critical for semiconductor or trace-element analysis.
Chemical and Atmospheric Compatibility
Your process chemistry dictates the tube material. While both alumina and quartz are highly inert, aggressive chemicals may require one over the other. More importantly, your choice of heating element must match your atmosphere; using graphite elements in air will destroy them.
Thermal Shock vs. Mechanical Durability
Quartz is superior at handling rapid temperature changes without cracking. However, alumina is generally a harder, more mechanically robust material, less prone to scratching or breaking from handling.
Cost and Lifespan
Specialty materials and higher-temperature components naturally come at a higher cost. A durable alumina tube may have a longer service life in a stable, high-temperature process, justifying its initial expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary experimental goal to guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is high temperature (above 1200°C): An alumina process tube with MoSi₂ or SiC heating elements is the standard configuration.
- If your primary focus is high purity and thermal shock resistance (below 1200°C): A quartz process tube is the ideal choice for its purity and resilience to temperature cycling.
- If you are working with highly corrosive materials: Investigate specialized metallic tubes like molybdenum, but be prepared for stricter atmospheric controls.
- If you are operating in a vacuum or inert gas: Ensure your heating elements (like graphite) and insulation are designed for this specific environment.
Understanding these core components and their material properties empowers you to select or specify a furnace that perfectly matches your scientific or industrial goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Materials | Key Properties | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Tube | Alumina, Quartz, Metals (e.g., Molybdenum) | High thermal stability, chemical resistance, purity | High-temp processes, pure environments, corrosive materials |
| Heating Elements | Kanthal, SiC, MoSi₂, Graphite | Temperature range up to 1800°C, atmosphere compatibility | Cost-effective heating, high-temp in air, vacuum/inert atmospheres |
| Insulation | Ceramic Fiber (e.g., Zirconia-grade) | Excellent thermal insulation, low thermal mass | Rapid heating/cooling, energy efficiency |
Struggling to select the right tube furnace for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your experiments. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your specific requirements for temperature, purity, and durability. Don't let material choices hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















