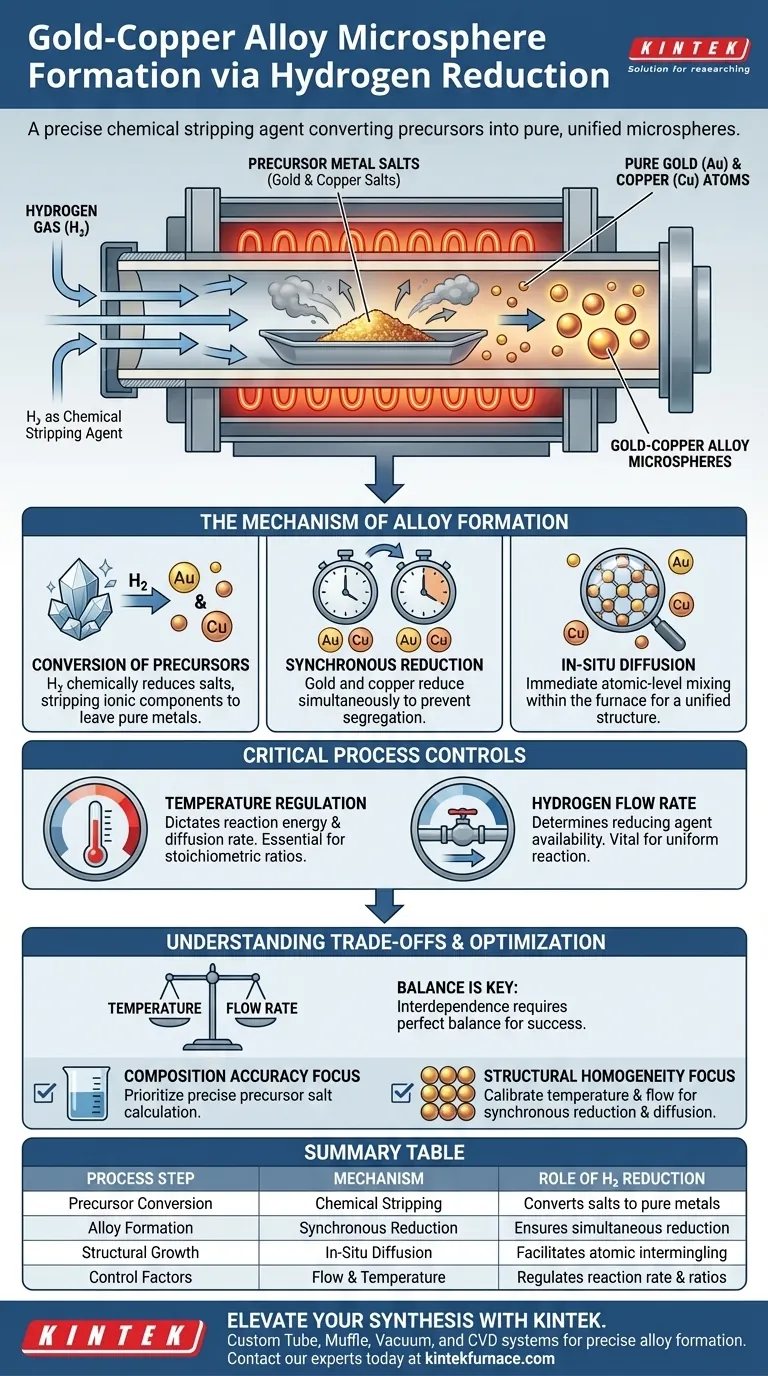
A hydrogen reduction environment functions as a precise chemical stripping agent. It facilitates the formation of gold-copper alloy microspheres by converting metal salts within a precursor directly into pure metallic elements. This environment effectively removes non-metallic components, leaving behind only the gold and copper atoms necessary for alloy formation.
By introducing hydrogen into the furnace, you convert complex metal salts into pure gold and copper. When temperature and flow rates are tuned correctly, these metals reduce simultaneously and diffuse into one another instantly, creating perfectly proportioned alloy microspheres.
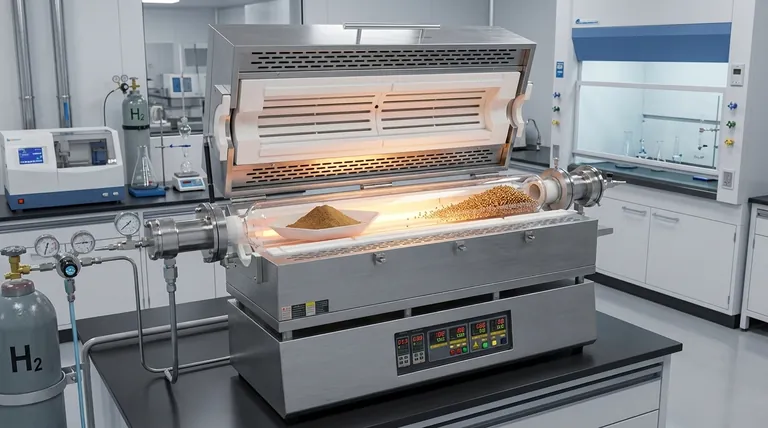

The Mechanism of Alloy Formation
Conversion of Precursors
The foundational step involves the transformation of metal salts. The hydrogen atmosphere chemically reduces these salts, stripping away the ionic components.
This leaves behind pure metallic elements. Without this reduction, the materials would remain as salts rather than transforming into the conductive metals required for the alloy.
Synchronous Reduction
For a true alloy to form, the gold and copper must be generated at the same time. This is referred to as synchronous reduction.
If one metal reduces significantly faster than the other, the materials may segregate rather than mix. The hydrogen environment, when properly controlled, ensures both metals become metallic simultaneously.
In-Situ Diffusion
Once the atoms are reduced to their metallic state, they undergo in-situ diffusion. This means the mixing happens immediately within the furnace, rather than in a secondary processing step.
This immediate diffusion allows the gold and copper atoms to intermingle at an atomic level. This process is responsible for creating a unified alloy structure rather than separate clusters of gold and copper.
Critical Process Controls
Temperature Regulation
The furnace temperature is a primary variable in this process. It dictates the energy available for the reduction reaction and the subsequent diffusion.
Precise thermal control ensures that the reduction occurs at the correct rate. This is essential for achieving the desired stoichiometric ratios (the specific chemical proportions of gold to copper).
Hydrogen Flow Rate
The volume and speed of hydrogen gas flowing through the tube furnace are equally critical. The flow rate determines the availability of the reducing agent.
A consistent flow allows for a uniform reaction across the precursors. This uniformity is vital for the consistent formation of microspheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Balance of Process Parameters
The primary challenge in this method is the interdependence of temperature and flow rate. These two factors must be perfectly balanced to achieve success.
If the balance is off, you risk incomplete reduction or uneven diffusion. This can lead to alloys that do not meet the specific stoichiometric requirements of your project.
Sensitivity to Precursors
The process relies heavily on the quality and composition of the precursor metal salts. The hydrogen environment is efficient, but it can only act on the materials present.
Variations in the precursor mix will directly alter the final alloy. To achieve specific microsphere properties, the initial salt mixture must be calculated with high precision.
Optimizing Your Alloy Formation
To achieve the best results in your industrial tube furnace, focus on the calibration of your environmental controls.
- If your primary focus is Composition Accuracy: Prioritize the precise calculation of precursor salts to ensure the final stoichiometric ratio is correct.
- If your primary focus is Structural Homogeneity: Focus on calibrating the furnace temperature and hydrogen flow rate to guarantee synchronous reduction and uniform diffusion.
By mastering the synchronous reduction of metal salts, you ensure the production of high-quality, uniform gold-copper alloy microspheres.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Mechanism | Role of Hydrogen Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Conversion | Chemical Stripping | Converts metal salts into pure metallic elements by removing non-metallic components. |
| Alloy Formation | Synchronous Reduction | Ensures gold and copper reduce simultaneously to prevent material segregation. |
| Structural Growth | In-Situ Diffusion | Facilitates atomic-level intermingling for a unified, homogeneous alloy structure. |
| Control Factors | Flow & Temperature | Regulates the rate of reaction to achieve specific stoichiometric ratios. |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise alloy formation requires more than just high temperatures—it demands absolute control over your thermal environment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous requirements of hydrogen reduction and chemical vapor deposition.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique stoichiometric and structural needs. Whether you are producing gold-copper microspheres or pioneering new semiconductor materials, we offer the technical precision necessary for synchronous reduction and uniform diffusion.
Ready to optimize your alloy production? Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Li Zhang, Shaolong Tang. Novel Porous Gold Microspheres Anisotropic Conductive Film (PGMS‐ACF) with High Compression Ratio for Flip Chip Packaging. DOI: 10.1002/aelm.202500045
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages does a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace offer in terms of operation? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer and Uniformity
- What is the principle of tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temp Environment Control
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the initial pyrolysis of date palm leaf biomass? Key Insights
- What are the limitations of tube furnaces when handling larger samples? Overcome Size and Heat Transfer Challenges
- What environmental protection applications utilize multi zone tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Waste Treatment and Green Tech
- What is the future of zoned furnace systems? Smarter, Adaptive, and Energy-Efficient Solutions
- What safety features are typically included in vacuum tube furnaces? Essential Protection for High-Temp Labs
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in heavy metal adsorption research? Precision Thermal Simulation Guide



















