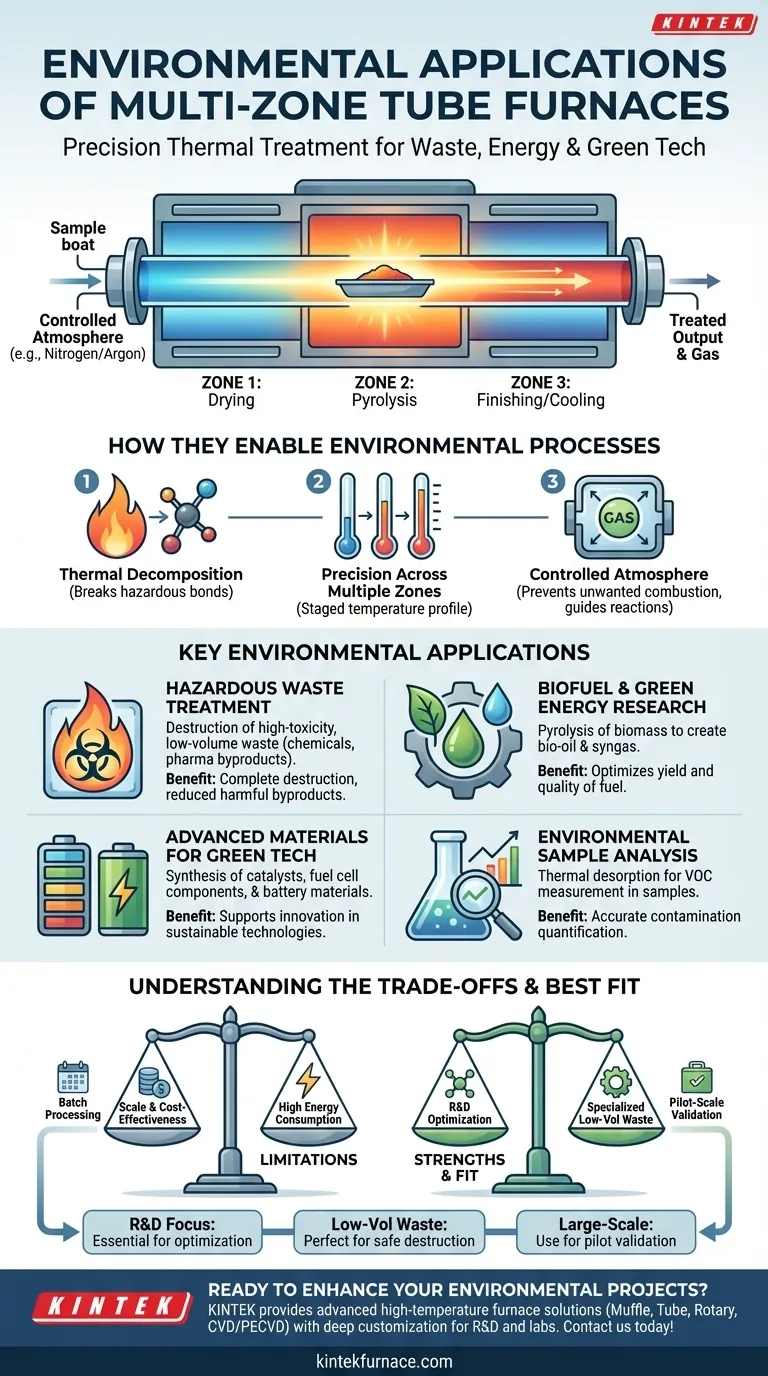
In the field of environmental protection, multi-zone tube furnaces are primarily used to process solid waste and harmful gases through high-temperature thermal treatment. By creating precise temperature profiles, they can break down hazardous substances into less toxic or inert forms, purify materials, and support the development of green technologies like biofuels and fuel cells.
The core value of a multi-zone tube furnace in environmental applications is its ability to create a staged, highly controlled thermal process. This precision allows for the selective breakdown of complex pollutants and the synthesis of advanced materials, moving far beyond the capabilities of simple, single-temperature incineration.

How Multi-Zone Furnaces Enable Environmental Processes
A multi-zone tube furnace's effectiveness stems from its ability to manage temperature and atmosphere with exceptional precision, which is critical for targeting specific chemical reactions required in environmental remediation and research.
The Principle: Thermal Decomposition
At its core, the furnace uses a process of thermal decomposition (often pyrolysis in a controlled atmosphere) to break down complex, hazardous molecules. High heat severs chemical bonds, transforming harmful compounds into simpler, more stable, and often less dangerous substances.
The Advantage: Precision Across Multiple Zones
The defining feature is the multiple heating zones. Different chemical compounds break down at different temperatures. A multi-zone furnace allows an operator to create a specific temperature gradient along the length of the process tube.
This means a substance can be heated to one temperature to drive off moisture, then passed into a hotter zone for pyrolysis, and finally into another zone for a finishing reaction or controlled cooling—all in one continuous process.
The Enabler: Controlled Atmosphere
These furnaces operate with a sealed process tube, enabling full control over the internal atmosphere. By using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, unwanted combustion is prevented.
This is critical for avoiding the creation of toxic byproducts like dioxins. It also allows for the introduction of reactive gases to guide the chemical breakdown toward specific, desirable end products like syngas.
Key Environmental Applications
The unique capabilities of multi-zone tube furnaces make them suitable for a range of specialized environmental tasks, from direct waste treatment to foundational research for new green technologies.
Hazardous Waste Treatment
The most direct application is the destruction of hazardous materials. The precise thermal control is ideal for processing low-volume, high-toxicity waste streams where incomplete destruction would be unacceptable. This includes certain industrial chemical wastes, pharmaceutical byproducts, and contaminated solids.
Biofuel and Green Energy Research
Multi-zone furnaces are workhorses in the development of sustainable energy. They are used for the pyrolysis of biomass (such as agricultural waste) to create bio-oil and syngas. The ability to optimize the temperature profile is key to maximizing the yield and quality of the resulting biofuel.
Advanced Materials for Green Technology
Many environmental technologies rely on advanced materials, and tube furnaces are essential for creating them. This includes:
- Catalyst Development: Synthesizing and testing new catalysts for vehicle exhaust systems or industrial scrubbers.
- Fuel Cell Components: Sintering ceramics and other materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs).
- Battery Materials: Processing novel materials for next-generation energy storage.
Environmental Sample Analysis
In environmental testing, tube furnaces are used to prepare samples for analysis. For instance, a soil or water sample can be heated in a controlled manner (thermal desorption) to release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for measurement, helping to quantify levels of contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to applying them correctly.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
Most laboratory-scale tube furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one sample is processed at a time. This limits throughput and makes them less suitable for treating the large, continuous streams of waste generated by a municipality or large factory.
Scale and Cost-Effectiveness
While ideal for research and specialized destruction, scaling a multi-zone tube furnace process to an industrial level can be complex and expensive. For very large volumes of general waste, traditional large-scale incinerators or other reactor designs may be more cost-effective.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining high temperatures, especially across multiple zones, is an energy-intensive process. The environmental benefit of destroying a hazard must be weighed against the energy cost of the treatment itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a multi-zone tube furnace is the correct tool, you must align its capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A multi-zone tube furnace is an essential tool for optimizing pyrolysis conditions for biofuels, creating novel catalysts, or synthesizing materials for fuel cells and batteries.
- If your primary focus is specialized, low-volume waste treatment: The furnace's precise control is perfectly suited for safely destroying high-toxicity waste streams where complete and verified destruction is the top priority.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial processing: A tube furnace is best viewed as a pilot-scale instrument to validate a thermal process before investing in a larger, custom-designed continuous reactor system.
Ultimately, harnessing the precise thermal control of a multi-zone tube furnace allows you to develop highly targeted and effective solutions to complex environmental challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hazardous Waste Treatment | Thermal decomposition of toxic substances | Precise control for complete destruction, reduces harmful byproducts |
| Biofuel and Green Energy Research | Pyrolysis of biomass to produce biofuels | Optimizes yield and quality with staged temperature profiles |
| Advanced Materials Development | Synthesis of catalysts, fuel cell components, and battery materials | Supports innovation in sustainable technologies |
| Environmental Sample Analysis | Thermal desorption for VOC measurement in samples | Accurate contamination quantification in controlled atmospheres |
Ready to enhance your environmental projects with precision thermal solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories and research facilities. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs—whether for hazardous waste treatment, biofuel development, or green material synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab



















