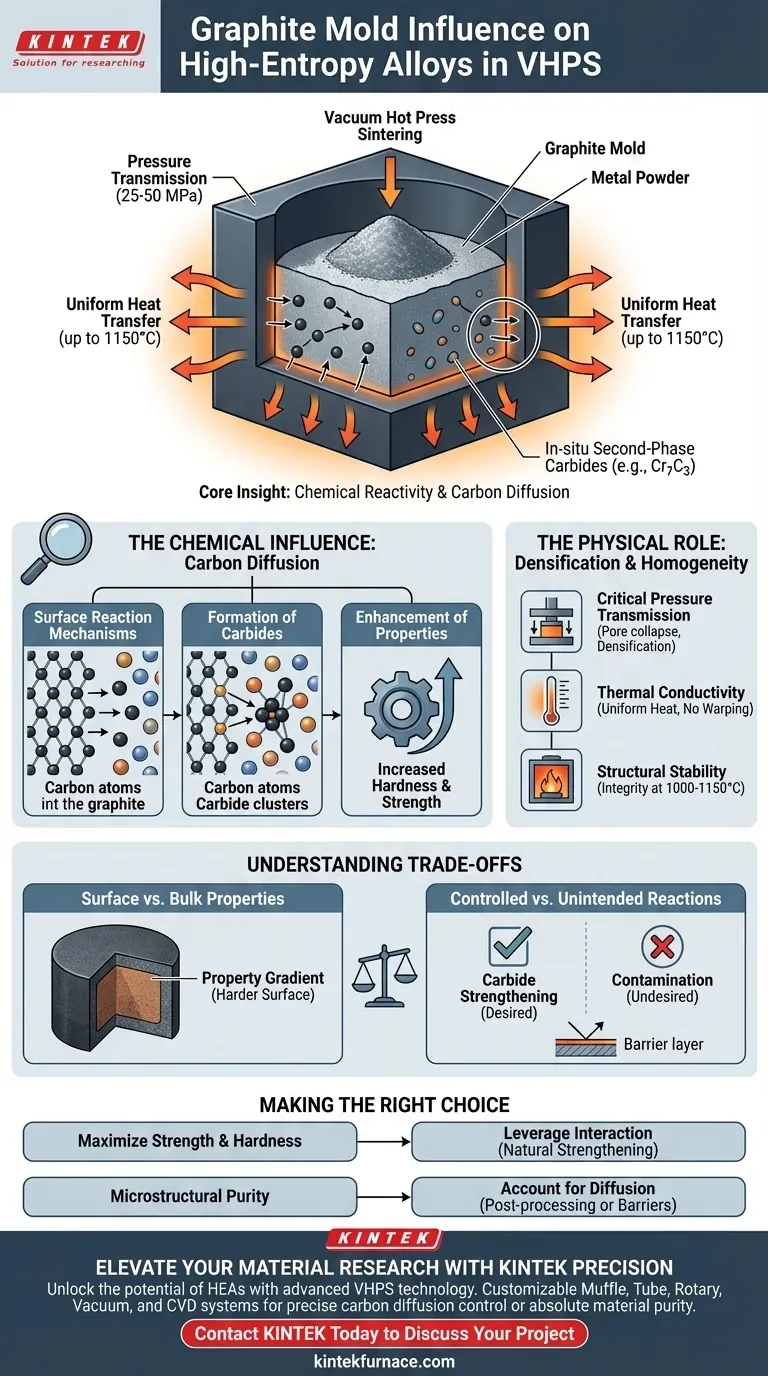
Graphite molds in Vacuum Hot Press Sintering (VHPS) act as more than passive containers; they are active participants in the alloy's microstructural evolution. While their primary function is to shape the powder and transmit pressure, the carbon from the mold can diffuse into high-entropy alloy (HEA) powders, triggering chemical reactions that fundamentally alter the material's mechanical properties.
Core Insight: While the graphite mold ensures densification through pressure transmission and thermal uniformity, its distinct influence lies in its chemical reactivity. Under high temperature and pressure, carbon diffusion from the mold can induce the formation of in-situ second-phase carbides (such as Cr7C3), which significantly enhance the hardness and strength of the final sintered alloy.

The Chemical Influence: Carbon Diffusion
The most significant, often overlooked influence of the graphite mold is its potential to chemically interact with the alloy powder. This moves beyond simple containment into the realm of surface alloying.
Surface Reaction Mechanisms
Under the intense conditions of VHPS, the interface between the graphite mold and the alloy powder becomes reactive. Slight surface reactions or diffusion processes occur, introducing carbon from the mold into the metallic powder.
Formation of Second-Phase Carbides
This introduced carbon does not remain an impurity; it acts as a stabilizing agent for new phases. Specifically, it promotes the formation of second-phase carbides, such as Cr7C3, within the alloy matrix.
Enhancement of Mechanical Properties
The presence of these in-situ generated carbides has a direct, positive impact on performance. They act as reinforcing agents, significantly increasing the hardness and strength of the sintered high-entropy alloy compared to a sample sintered in an inert environment.
The Physical Role: Densification and Homogeneity
While the chemical influence changes what the material is, the physical role of the mold determines the integrity of the final part.
Critical Pressure Transmission
The mold functions as the primary vessel for transmitting force from the hydraulic system to the powder. It must sustain high pressures (typically 25 to 50 MPa) to collapse pores and drive the densification of the powder particles.
Thermal Conductivity and Uniformity
Graphite is utilized for its excellent thermal conductivity. This property ensures uniform heat transfer across the mold and sample, preventing thermal gradients that could lead to warped dimensions or uneven microstructures.
Structural Stability at Extremes
The mold must maintain strict dimensional integrity without deforming. It is required to remain stable at temperatures ranging from 1000°C to 1150°C (approx. 1373 K), ensuring the final sample matches the intended geometry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the interaction between the graphite mold and the alloy is often beneficial, it introduces variables that must be managed.
Surface vs. Bulk Properties
The diffusion of carbon is primarily a surface or interface phenomenon. This can create a gradient in properties, where the surface of the sintered part is harder and chemically different from the core.
Controlled vs. Unintended Reactions
If the formation of carbides is not desired for a specific application, the graphite mold becomes a source of contamination. Engineers must decide if the carbide strengthening aligns with the design goals or if a barrier layer is required to prevent diffusion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The influence of a graphite mold is a variable you can leverage or suppress depending on your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Strength and Hardness: Leverage the graphite-alloy interaction, as the diffusion of carbon and formation of Cr7C3 carbides will act as a natural strengthening mechanism.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Purity: You must account for carbon diffusion at the surface; post-processing (such as grinding the surface) or barrier coatings may be necessary to remove the carburized layer.
Ultimately, the graphite mold is not just a tool for shaping; it is a chemical reagent that, when engaged correctly, enhances the performance limits of high-entropy alloys.
Summary Table:
| Influence Type | Mechanism / Feature | Impact on High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Carbon Diffusion | Formation of in-situ carbides (e.g., Cr7C3) increasing hardness. |
| Mechanical | Pressure Transmission | Enables high-density sintering at 25–50 MPa. |
| Thermal | High Conductivity | Ensures uniform heat distribution and prevents microstructural gradients. |
| Structural | Thermal Stability | Maintains dimensional integrity at temperatures up to 1150°C. |
| Surface | Surface Alloying | Creates a property gradient with a harder, reinforced outer layer. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your high-entropy alloys with our advanced Vacuum Hot Press Sintering (VHPS) technology. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your exact thermal processing needs. Whether you require precise carbon diffusion control or absolute material purity, our high-temperature lab furnaces ensure superior uniformity and structural integrity for your most demanding applications.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and find the perfect high-temp solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Near-Perfect Densification for Nano-Copper
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density and Strength for Advanced Materials
- What is the primary function of a hot-pressing furnace in SiC bicrystal synthesis? Achieve Precision Atomic Bonding
- What is the working principle of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Master Dense Material Creation
- What types of advanced materials can be prepared using a vacuum press? Unlock High-Performance Fabrication
- What temperature control features do vacuum hot press furnaces have? Achieve Precision in High-Temp Material Processing



















