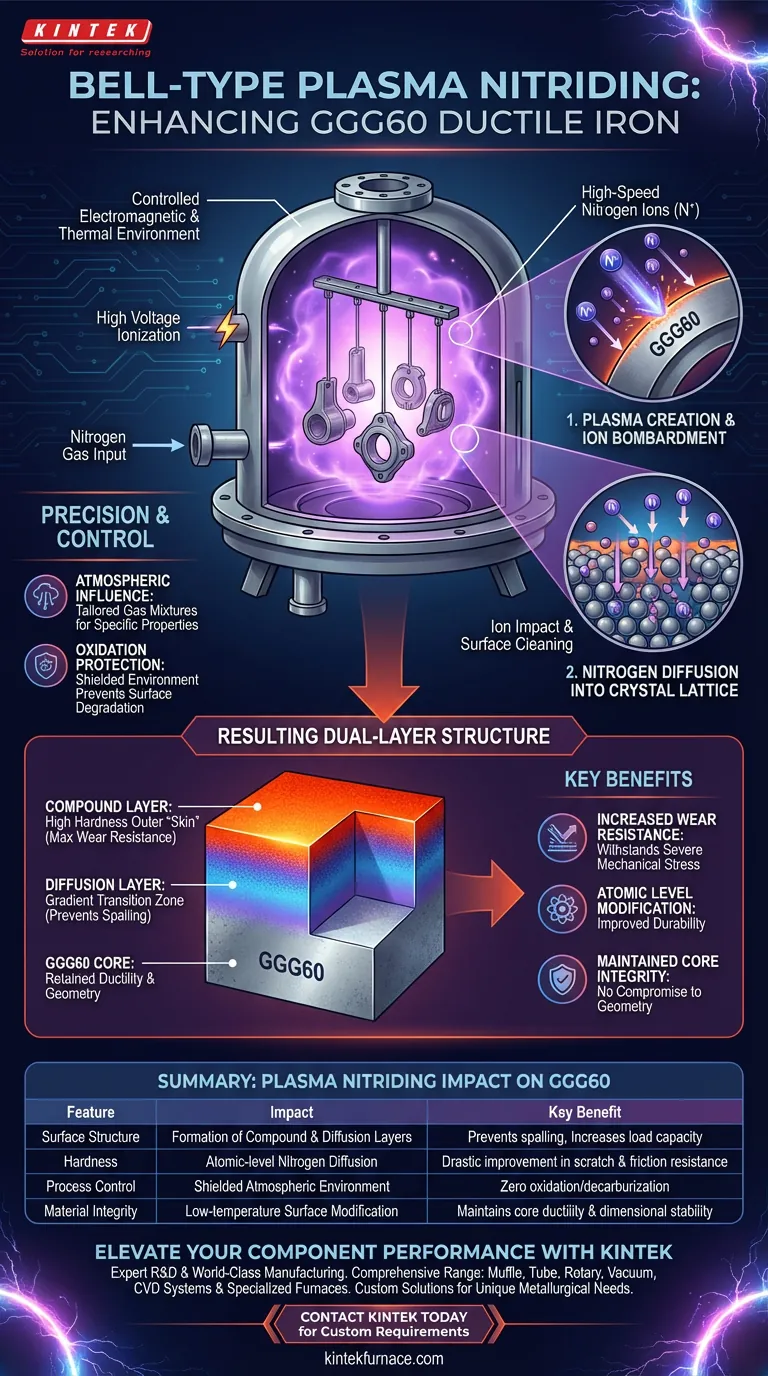
A bell-type plasma nitriding furnace enhances GGG60 ductile iron by utilizing high-voltage ionization to create a plasma environment where high-speed nitrogen ions bombard the material's surface. This process cleans the surface and forces nitrogen atoms to diffuse into the iron's crystal lattice, creating a dual-layer structure that significantly increases surface hardness and wear resistance.
Core Takeaway: The enhancement is driven by a precise electrochemical reaction that creates a hard compound layer and a supporting diffusion layer. This modification occurs at the atomic level, improving durability without compromising the core geometry of the component.

The Mechanism of Surface Modification
Creating the Plasma Environment
The furnace establishes a controlled electromagnetic and thermal environment. Inside the bell, high voltage is applied to ionize gases, transforming them into plasma.
Ion Bombardment and Cleaning
Once the plasma is formed, high-speed nitrogen ions are accelerated toward the GGG60 ductile iron. The physical impact of these ions colliding with the material serves a dual purpose: it actively cleans the surface and prepares it for chemical modification.
Nitrogen Diffusion
Following the bombardment, nitrogen atoms penetrate the surface. These atoms diffuse directly into the crystal lattice of the iron, fundamentally altering the material's near-surface composition.
The Resulting Material Properties
Formation of the Compound Layer
The primary outcome of nitrogen diffusion is the creation of a high-hardness compound layer. This outer "skin" is the main contributor to the material's enhanced resistance against friction and abrasion.
The Diffusion Layer
Beneath the hard outer shell lies the diffusion layer. This zone serves as a gradient transition between the ultra-hard surface and the softer core, adding depth to the treatment and preventing the hard layer from spalling (peeling off) under load.
Increased Wear Resistance
The combination of these two layers results in a dramatic improvement in wear resistance. The GGG60 iron retains its ductile core properties while gaining a surface capable of withstanding severe mechanical stress.
precision and Control
Atmospheric Influence
The furnace atmosphere is not passive; it directly dictates the final properties of the material, including hardness and surface finish. By selecting specific gas mixtures, manufacturers can tailor the material's characteristics to meet precise application requirements.
Protection from Oxidation
The controlled environment acts as a shield during the heating process. Operating under a protective atmosphere prevents the surface from oxidizing or decarburizing, ensuring the chemical stability of the iron is maintained throughout the treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Complexity
While the results are superior, plasma nitriding is a complex process requiring precise control over voltage, temperature, and gas composition. Mismanagement of the electromagnetic environment can lead to inconsistent layer formation.
Surface Dependence
The effectiveness of the ion bombardment is strictly surface-dependent. Unlike induction heating which might stir the bulk molten metal to ensure uniformity, plasma nitriding acts only on the exposed geometry. Complex shapes with deep, shielded cavities may experience uneven nitriding if the plasma cannot penetrate those areas effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the benefits of bell-type plasma nitriding for your GGG60 components, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Wear Resistance: Ensure the process parameters are set to maximize the depth of the compound layer for maximum surface hardness.
- If your primary focus is Component Precision: Prioritize the control of the furnace atmosphere to prevent surface oxidation and maintain strict dimensional tolerances.
Effective plasma nitriding transforms standard ductile iron into a high-performance engineering material by engineering its surface at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma Nitriding Impact on GGG60 | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Structure | Formation of Compound & Diffusion Layers | Prevents spalling and increases load capacity |
| Hardness | Atomic-level nitrogen diffusion | Drastic improvement in scratch and friction resistance |
| Process Control | Shielded atmospheric environment | Zero oxidation or decarburization of the surface |
| Material Integrity | Low-temperature surface modification | Maintains core ductility and dimensional stability |
Elevate Your Component Performance with KINTEK
Is your GGG60 ductile iron meeting the demands of high-friction environments? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal processing solutions designed to transform standard materials into high-performance engineering assets.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized high-temp furnaces. Whether you need precise plasma nitriding or a fully customizable furnace for unique metallurgical needs, our team delivers the technical edge your lab or production line requires.
Ready to optimize your surface properties? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- İsmail Aykut Karamanlı, Okan Ünal. Study of the Wear Resistance Plasma Nitrided GGG60 by Optimization of Surface Treatment Conditions Using Response Surface Methodology. DOI: 10.1007/s40962-024-01310-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum system required for PVD of doped hydroxyapatite? Achieve High-Purity Biomedical Coatings
- What are the technical advantages of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven for processing plant materials? Preserve Nutrients
- How does heat loss occur in vacuum furnace insulation? Two Pathways Draining Efficiency
- How are vacuum furnaces used in the aerospace industry? Enhance Safety and Performance in Aviation
- What are the overall benefits of using vacuum heat treatment furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Performance
- How does a vacuum furnace improve smelting quality? Achieve Purer, Stronger Metals for Your Applications
- What role does a vacuum atmosphere play in Sn-Ag-Co TLP soldering? Optimize Bond Purity and Joint Strength
- What is the role of inert gas in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Rapid, Controlled Cooling for Superior Metallurgy



















