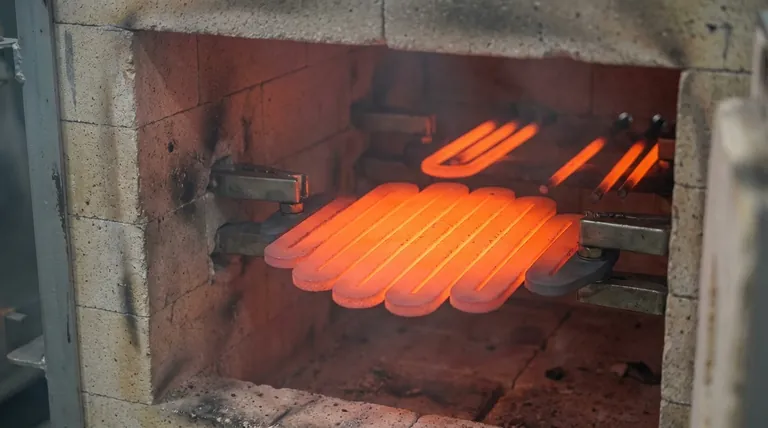
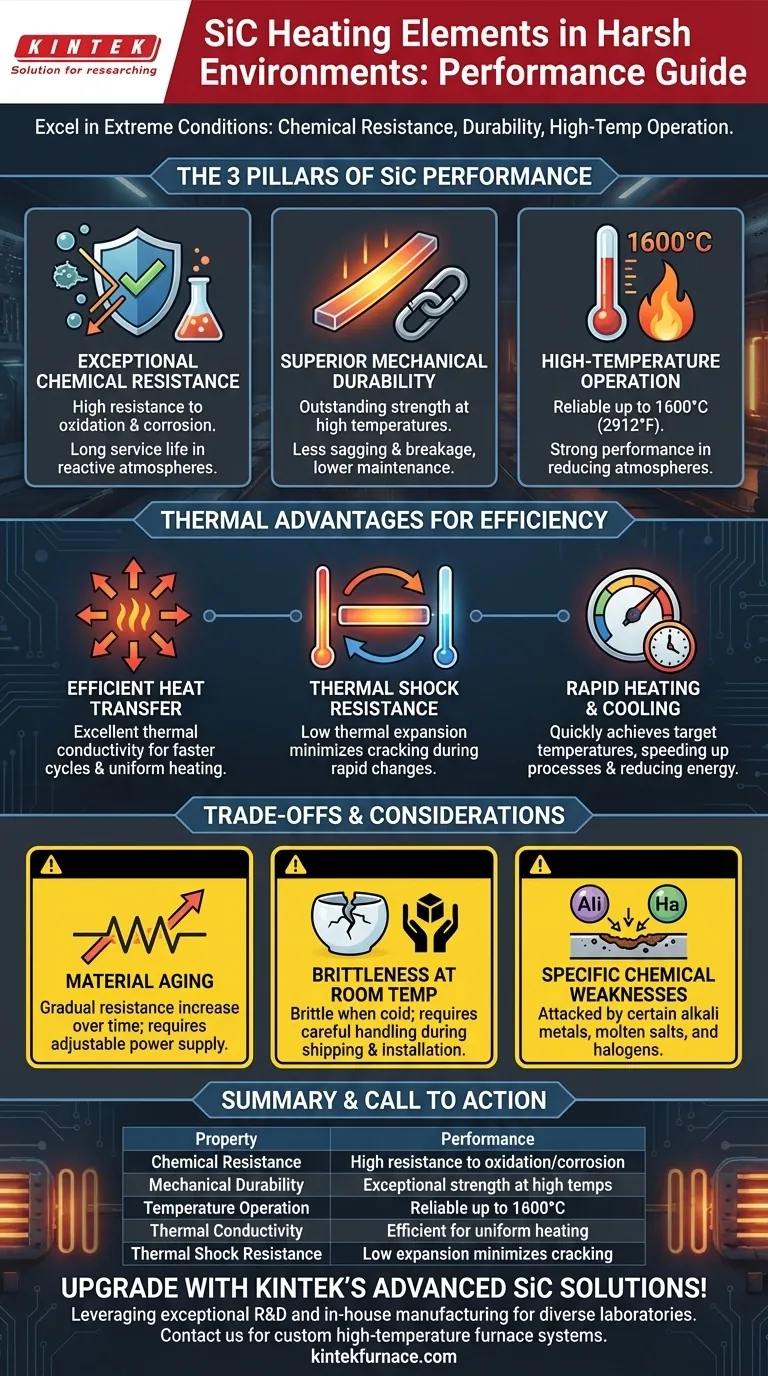
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements excel in harsh environments. Their performance is defined by a unique combination of high chemical resistance to oxidation and corrosion, exceptional mechanical strength at extreme temperatures, and the ability to operate reliably up to 1600°C, ensuring integrity where other materials would fail.
Choosing a heating element for an aggressive industrial process is a critical decision impacting uptime, cost, and safety. SiC elements are often the definitive solution because their fundamental material properties—chemical inertness, thermal efficiency, and physical durability—are purpose-built for such demanding conditions.

The Pillars of SiC Performance
To understand why SiC elements are so robust, we must look at their core material characteristics. These three pillars are what allow them to function reliably in environments that are simultaneously hot, chemically aggressive, and physically demanding.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
SiC is a ceramic material that is highly resistant to both oxidation and corrosion. This allows it to maintain its structural integrity even when exposed to harsh chemicals or oxidizing atmospheres at high temperatures.
Unlike many metallic elements that degrade quickly, SiC's inertness ensures a longer and more predictable service life, making it a superior choice for processes involving reactive gases or materials.
Superior Mechanical Durability
These elements exhibit outstanding mechanical strength, even when glowing hot. This physical toughness makes them far less prone to sagging, warping, or breaking compared to more fragile alternatives.
This durability directly translates to lower maintenance requirements and fewer costly replacements, minimizing furnace downtime and improving operational continuity.
High-Temperature Operation
SiC elements are engineered to perform at extreme temperatures, with some variants capable of operating consistently at up to 1600°C (2912°F).
They are particularly strong in reducing atmospheres, offering a clear advantage over other high-temperature elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) in specific applications.
Unpacking the Thermal Advantages
Beyond simple survivability, SiC elements offer significant thermal benefits that enhance process efficiency and control. These advantages stem from how effectively they convert electricity into usable heat and withstand thermal stress.
Efficient Heat Transfer
Silicon carbide has excellent thermal conductivity. This means it transfers the heat it generates very efficiently and evenly into the furnace chamber.
The result is uniform heating for your product and faster processing cycles, as less energy is wasted and target temperatures are reached more quickly.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
A key property of SiC is its low coefficient of thermal expansion. It does not expand or contract dramatically when its temperature changes.
This stability drastically reduces the risk of the element cracking or breaking during rapid heating and cooling cycles, a common failure point for other ceramic materials.
Rapid Heating and Cooling Rates
The combination of high conductivity and thermal stability allows SiC elements to achieve very rapid heating and cooling rates.
This capability speeds up entire industrial processes, minimizes energy consumption during ramp-up, and ultimately lowers operational costs and contributes to a more sustainable operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, no solution is without its considerations. A trusted advisor must present a complete picture. SiC elements are not universally applicable, and their properties come with certain trade-offs.
Material Aging
Over their service life, SiC elements experience a gradual increase in electrical resistance. This is a natural aging process for the material.
Operators must account for this by using a power supply, typically an SCR or multi-tapped transformer, that can increase the voltage over time to maintain the required power output.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
While strong at high temperatures, SiC elements are a ceramic and can be brittle at room temperature. They require careful handling during shipping, storage, and installation to prevent fracture.
Specific Chemical Weaknesses
Although highly resistant, SiC is not entirely immune to all chemicals. It can be attacked by certain alkali metals, molten salts, and halogens at high temperatures, requiring careful review of the process atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if SiC is the right choice, align its strengths with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process speed and efficiency: SiC's rapid heating and high thermal conductivity will significantly reduce cycle times and lower energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is reliability in a corrosive or oxidizing atmosphere: The inherent chemical resistance and mechanical strength of SiC ensure a longer service life and less production downtime.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures above 1400°C: SiC elements are one of the few reliable options that can operate consistently and effectively in this demanding range.
By understanding these core properties, you can confidently leverage Silicon Carbide to enhance the performance and reliability of your most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance in Harsh Environments |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oxidation and corrosion, ideal for reactive atmospheres |
| Mechanical Durability | Exceptional strength at high temperatures, reducing sagging and breakage |
| Temperature Operation | Reliable up to 1600°C, with strong performance in reducing atmospheres |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat transfer for uniform heating and faster cycles |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low expansion coefficient minimizes cracking during rapid temperature changes |
Upgrade your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced SiC heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability in harsh environments. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















