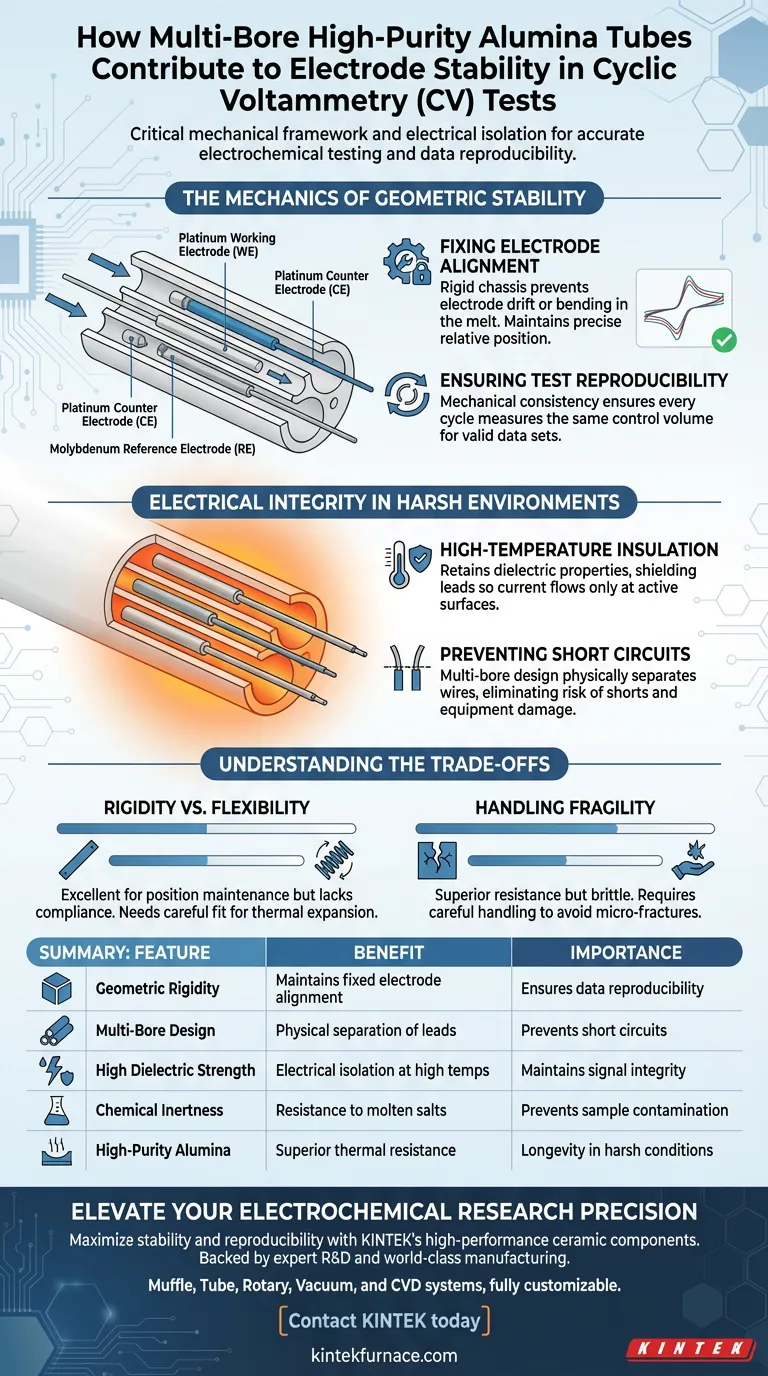
Multi-bore high-purity alumina tubes provide the critical mechanical framework and electrical isolation necessary for accurate electrochemical testing. By rigidly fixing the relative positions of the working, counter, and reference electrodes, these components eliminate geometric variables within the melt. Simultaneously, they prevent short circuits at high temperatures, ensuring that the resulting data reflects the true chemical behavior rather than mechanical instability.
The core value of these tubes is the assurance of data reproducibility. By locking electrode geometry and insulating conductive paths, they ensure that current-voltage curves remain consistent across multiple test cycles.
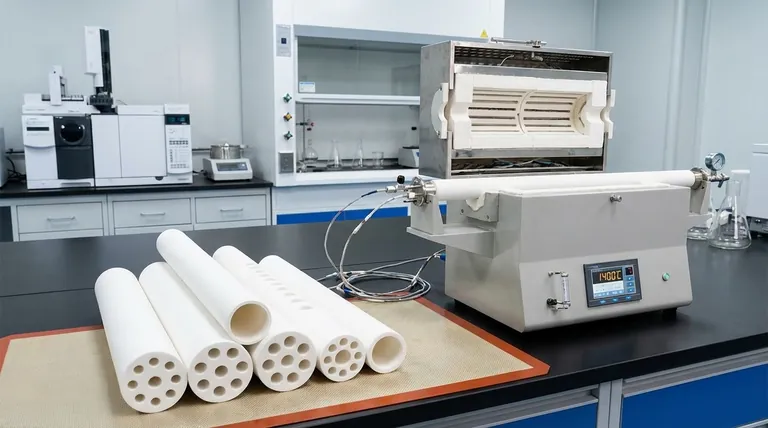

The Mechanics of Geometric Stability
Fixing Electrode Alignment
In Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), the distance between electrodes significantly influences the resistance and current flow through the electrolyte.
High-purity alumina tubes serve as a rigid chassis for Platinum (Pt) working/counter electrodes and Molybdenum (Mo) quasi-reference electrodes. This setup prevents the electrodes from drifting or bending within the melt during the experiment.
Ensuring Test Reproducibility
If the electrodes move during a test, the resulting current-voltage curves will exhibit noise or shifts unrelated to the chemical reaction.
By maintaining a precisely fixed relative position, the alumina tubes ensure that every cycle measures the same control volume. This mechanical consistency is the prerequisite for obtaining reproducible, valid data sets.
Electrical Integrity in Harsh Environments
High-Temperature Insulation
CV tests often occur in molten salts or other high-temperature environments where standard insulators degrade.
High-purity alumina retains its dielectric properties under extreme heat. These tubes shield the electrode leads, ensuring that current only flows at the active surface area of the electrode, not along the length of the wire.
Preventing Short Circuits
The "multi-bore" design allows multiple electrode wires to run through a single ceramic body while remaining physically separated.
This internal separation prevents the Platinum and Molybdenum wires from touching each other. It eliminates the risk of short circuits, which would immediately invalidate the test and potentially damage the potentiostat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Rigidity vs. Flexibility
While the rigidity of alumina is excellent for maintaining electrode position, it lacks mechanical compliance.
In setups with rapid thermal cycling, the lack of flexibility can induce stress if the thermal expansion of the metal electrodes differs significantly from the ceramic. Engineers must ensure the fit allows for slight thermal expansion without cracking the tube.
Handling Fragility
High-purity ceramics offer superior chemical and thermal resistance but are inherently brittle.
Unlike polymer or metal supports, these tubes cannot withstand significant impact or bending forces. They require careful handling during setup assembly to avoid micro-fractures that could eventually lead to mechanical failure in the melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Setup
To maximize the stability of your Cyclic Voltammetry tests, consider your specific experimental constraints:
- If your primary focus is data reproducibility: Prioritize the geometric fit of the electrodes within the bores to minimize vibration or movement within the tube itself.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature safety: Rely on the alumina's electrical insulation properties to prevent cross-talk between the working and reference electrodes in conductive melts.
The use of multi-bore alumina tubes is not just about holding wires; it is about establishing a standardized physical baseline for every electrochemical measurement you take.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit to CV Testing | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Rigidity | Maintains fixed electrode alignment | Ensures data reproducibility |
| Multi-Bore Design | Physical separation of electrode leads | Prevents short circuits |
| High Dielectric Strength | Electrical isolation at high temperatures | Maintains signal integrity |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistance to molten salt environments | Prevents sample contamination |
| High-Purity Alumina | Superior thermal resistance | Longevity in harsh conditions |
Elevate Your Electrochemical Research Precision
Maximize the stability and reproducibility of your cyclic voltammetry tests with high-performance ceramic components. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-purity multi-bore alumina tubes designed to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. All our high-temperature furnaces and accessories are fully customizable to meet your unique research requirements.
Don't let mechanical instability compromise your data. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect fit for your laboratory setup.
Visual Guide
References
- Joongseok Kim, Kyung‐Woo Yi. Investigation of Low-Temperature Molten Oxide Electrolysis of a Mixture of Hematite and Zinc Oxide. DOI: 10.3390/ma18174116
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of the constant temperature environment provided by a heating stage? Expert Lab Solutions
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity
- What functions do high-purity graphite crucibles serve in tantalum carbide synthesis? Essential Thermal & Chemical Roles
- What is the function of a high-precision mass flow controller (MFC) in CdS nanobelt vapor deposition?
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- What is the purpose of using a corundum crucible and graphite powder? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Annealing
- What are the technical advantages of using a quartz tube as a reaction chamber? Optimize g-C3N4 Thin Film CVD Processes
- Why is a gas mixing system essential for syngas annealing in copper powder production? Ensure Precise Embrittlement

















