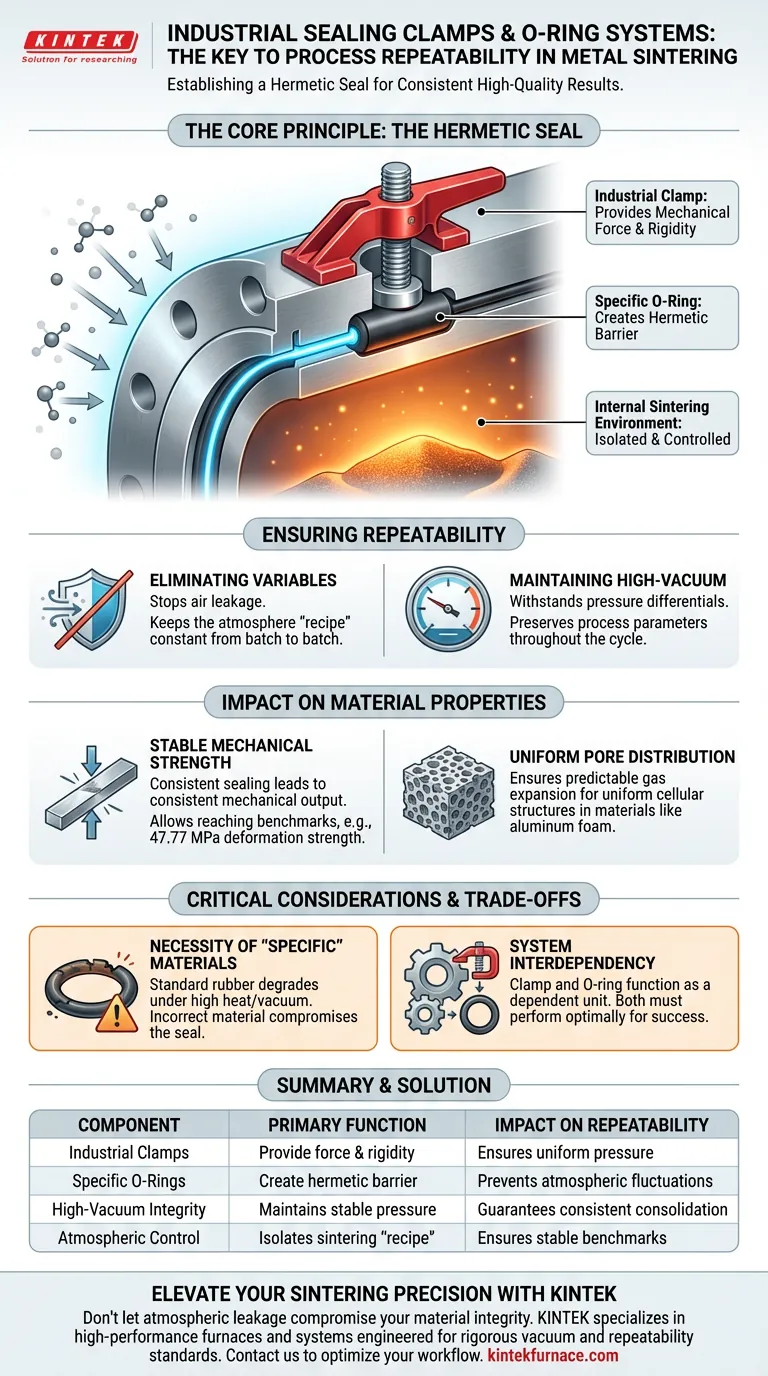
Industrial sealing clamps and O-ring systems ensure process repeatability by establishing a hermetic seal that isolates the internal sintering environment from external atmospheric fluctuations. By preventing air leakage during critical high-vacuum and high-temperature phases, these components ensure that every batch is processed under identical atmospheric conditions.
The consistency provided by high-quality sealing is the foundation of material reliability. It allows manufacturers to replicate specific mechanical benchmarks, such as a maximum deformation strength of 47.77 MPa, across multiple production cycles.
The Mechanics of Atmospheric Control
The Role of Industrial-Grade Clamps
Metal clamps provide the necessary mechanical force to secure the processing chamber.
They apply consistent pressure to the mating surfaces, ensuring the assembly remains rigid despite internal pressure changes or thermal expansion.
The Function of Specific Rubber O-Rings
While clamps provide the force, the rubber O-ring creates the actual barrier.
These specific O-rings compress to fill microscopic gaps between metal surfaces. This action creates a hermetic seal that stops gas flow in or out of the chamber.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
Eliminating Environmental Variables
The primary threat to repeatability in sintering is the introduction of external variables, specifically outside air.
If air leaks into the system, it alters the chemical composition of the sintering atmosphere. A hermetic seal ensures that the "recipe" of the atmosphere remains constant from batch to batch.
Maintaining High-Vacuum Integrity
Many sintering processes rely on high-vacuum states to consolidate metal powders.
The clamp and O-ring system must withstand the pressure differential. This ensures the vacuum level does not fluctuate during the cycle, preserving the process parameters.
Impact on Material Properties
Achieving Stable Mechanical Strength
Consistency in the sealing system leads directly to consistency in mechanical output.
The primary reference notes that a stable atmosphere allows materials to reach specific targets, such as a maximum deformation strength of 47.77 MPa. Without a reliable seal, this strength metric would vary wildly between batches.
Uniform Pore Distribution
For specialized materials like aluminum foam, the internal structure is as critical as the strength.
A hermetic seal ensures that the gas expansion or foaming agents act predictably. This results in a uniform pore distribution, rather than erratic or collapsed cellular structures.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of "Specific" Materials
The primary reference highlights the use of "specific" rubber O-rings. This implies that generic seals may fail.
Standard rubber may degrade under the high temperatures or vacuum conditions of sintering. Using the incorrect O-ring material can compromise the hermetic seal and destroy batch consistency.
System Interdependency
The clamp and O-ring function as a dependent unit.
Even a high-grade O-ring will fail if the clamp does not apply uniform pressure. Conversely, a strong clamp cannot compensate for a damaged or chemically incompatible O-ring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your sintered products, focus on the integrity of your vacuum interfaces.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Ensure your sealing system is rated for high-vacuum stability to consistently hit targets like 47.77 MPa deformation strength.
- If your primary focus is Structural Homogeneity: Prioritize leak-proof sealing to prevent atmospheric turbulence that disrupts uniform pore distribution in foams.
Reliable sealing is not just a safety feature; it is a quality control instrument that defines the success of your sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Impact on Repeatability |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Clamps | Provide mechanical force & rigidity | Ensures uniform pressure despite thermal expansion |
| Specific O-Rings | Create hermetic vacuum barrier | Prevents atmospheric fluctuations & air leakage |
| High-Vacuum Integrity | Maintains stable pressure levels | Guarantees consistent material consolidation |
| Atmospheric Control | Isolates sintering "recipe" | Ensures stable benchmarks like 47.77 MPa strength |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let atmospheric leakage compromise your material integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory heating solutions—from Muffle and Tube furnaces to Vacuum, Rotary, and CVD systems—all engineered to meet the most rigorous vacuum and repeatability standards.
Our expert R&D and manufacturing teams deliver customizable high-temp furnaces designed to help you achieve consistent mechanical benchmarks and uniform structural homogeneity. Contact us today to optimize your sintering workflow and discover the KINTEK advantage for your specialized lab needs.
Visual Guide
References
- María E. Hernández-Rojas, Sandro Báez–Pimiento. A Device with a Controllable Internal Atmosphere, Independent from the Heating Furnace, for Sintering Metal Particles. DOI: 10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2023-0401
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a molybdenum crucible considered an ideal choice for quartz melting? High-Purity Solutions at 2000°C
- What is the function of an alumina boat during high-temperature activation of porous carbon? Durable Lab Solutions
- What role do mass flow controllers play in gasification? Achieve Precise Atmosphere Control in Lab Furnaces
- Why are insulation ceramic plugs used inside the alumina furnace tube? Ensure Stable Heating and Prevent Tube Cracking
- How does an infrared pyrometer facilitate the precise control of temperatures during microwave-assisted metal recovery?
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles required for the cook-off method? Ensure Safety & Catalyst Purity
- Why is a heating device with magnetic stirring required for Y2O3-MgO precursors? Ensure Perfect Particle Coating
- What are the main features of a water circulating vacuum pump compared to a desktop pump? Discover Key Differences for Your Lab



















