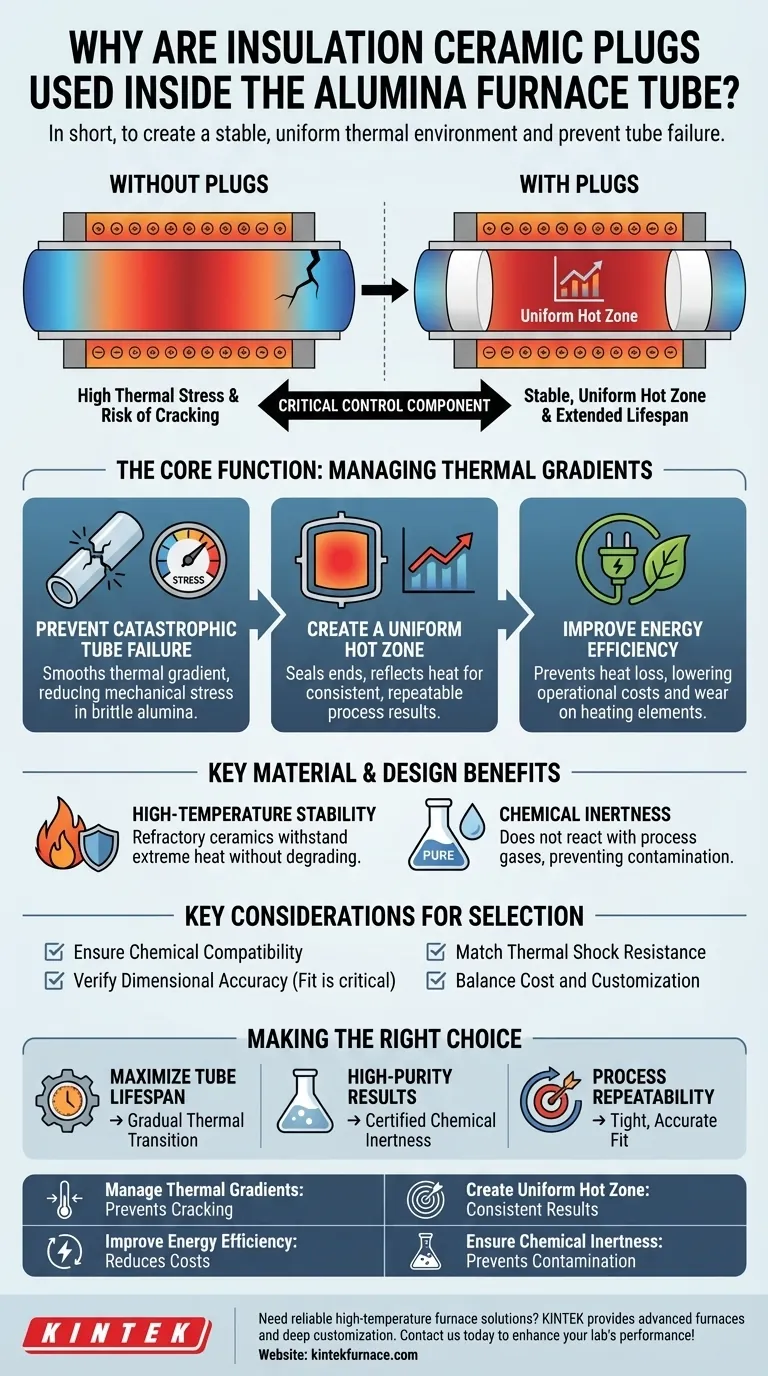
In short, insulation ceramic plugs are used inside an alumina furnace tube to create a stable and uniform thermal environment. Their primary functions are to manage steep temperature differences (thermal gradients) that can cause the tube to crack, and to define a consistent "hot zone" which is essential for achieving reliable and repeatable process results.
The core purpose of an insulation plug is not just to insulate, but to act as a critical control component. It transforms an open-ended tube with unpredictable temperature fluctuations into a contained, stable system, protecting the furnace tube from stress-induced failure while ensuring the integrity of your process.

The Core Function: Managing Thermal Gradients
The most significant challenge in a tube furnace is managing the transition from the extreme heat in the center to the ambient temperature at the ends. This temperature difference creates immense physical stress.
Preventing Catastrophic Tube Failure
Alumina, while strong at high temperatures, is a ceramic and thus brittle. When one part of the tube is significantly hotter than another, it expands at a different rate, creating a thermal gradient.
This gradient introduces mechanical stress. Without plugs, the steepest gradients occur near the ends of the furnace, making the tube highly susceptible to stress fractures and cracking. The plugs smooth this transition, drastically reducing the stress and extending the life of your furnace tube.
Creating a Uniform Hot Zone
For any scientific or industrial process, repeatability is key. Insulation plugs effectively "seal" the ends of the desired heating area.
This containment reflects heat back into the center and prevents cool air from entering, creating a much larger and more uniform hot zone. This ensures that your entire sample experiences the same temperature, leading to consistent and predictable outcomes.
Improving Energy Efficiency
By preventing heat from escaping out the ends of the tube, insulation plugs reduce the total energy required to maintain the target temperature. The furnace's heating elements don't have to work as hard, leading to lower operational costs and less wear on the system.
Key Material and Design Benefits
The effectiveness of these plugs comes from the specific properties of the materials used and their precise design.
High-Temperature Stability
Insulation plugs are typically made from high-purity alumina or other refractory ceramics. These materials are chosen for their excellent thermal stability, meaning they can withstand extreme temperatures without melting, deforming, or degrading.
Chemical Inertness
In many applications, the process atmosphere within the furnace is critical. The materials for the plugs are chemically inert, ensuring they will not react with process gases or samples. This prevents contamination and preserves the purity of your experiment or product.
Key Considerations for Selection
Choosing the wrong plug can be as bad as using no plug at all. The goal is to match the plug's properties to your specific application.
Ensuring Chemical Compatibility
You must verify that the plug material is compatible with your process environment. A standard alumina plug may not be suitable for processes involving highly reactive substances that could corrode it.
Verifying Dimensional Accuracy
The fit is critical. A plug that is too loose will fail to create an effective thermal seal, allowing heat to escape. A plug that is too tight can exert pressure on the furnace tube as it expands, creating its own stress point.
Matching Thermal Shock Resistance
The plug itself must be able to survive the heating and cooling cycles of your process. A material with poor thermal shock resistance can crack or shatter during rapid temperature changes.
Balancing Cost and Customization
High-purity, custom-machined plugs offer the best performance but come at a higher cost. For less demanding applications, a standard, lower-cost plug may be sufficient. You must weigh the need for precision against your budget.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection of an insulation plug.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tube lifespan: Prioritize plugs that create the most gradual thermal transition to minimize stress.
- If your primary focus is high-purity results: Select a plug made from a material with certified chemical inertness for your specific process atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Ensure the plugs provide a tight, accurate fit to create a highly stable and uniform hot zone.
Ultimately, selecting the right insulation plug is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and success of your high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Manage Thermal Gradients | Prevents tube cracking from stress |
| Create Uniform Hot Zone | Ensures consistent process results |
| Improve Energy Efficiency | Reduces operational costs |
| Ensure Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of samples |
Need reliable high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















