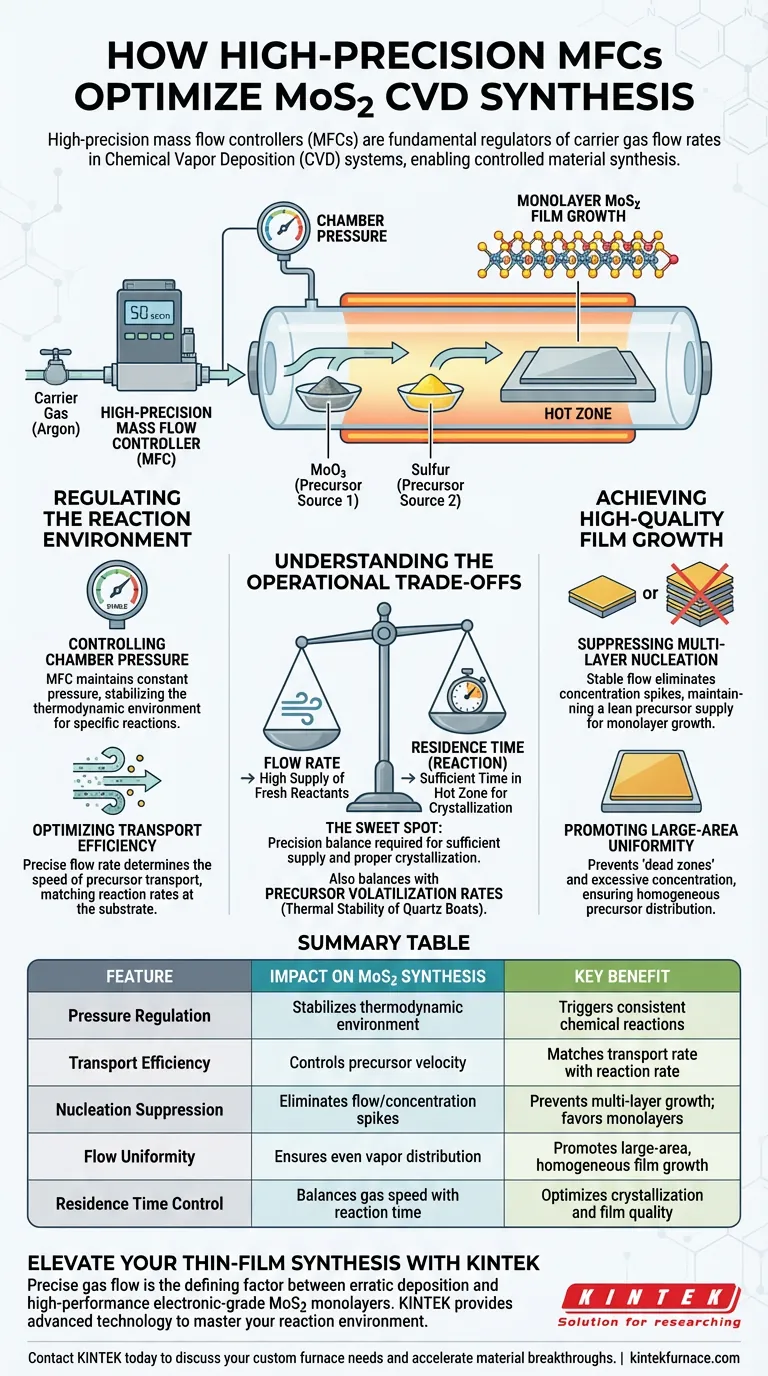
High-precision mass flow controllers (MFCs) serve as the fundamental regulators of carrier gas flow rates within a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system. They directly dictate the total pressure inside the reaction chamber and control the transport efficiency of precursor vapors, such as Argon carrying MoO3 and sulfur. This precise regulation is the primary mechanism for moving from chaotic deposition to controlled material synthesis.
Stable and repeatable flow control is essential for adjusting precursor concentration distributions to suppress multi-layer nucleation. This precision is the key to achieving the uniform growth of large-area monolayer MoS2 films.
Regulating the Reaction Environment
Controlling Chamber Pressure
The MFC is responsible for the precise admission of carrier gases, typically argon, into the system. This input flow directly determines the total pressure within the reaction chamber.
By maintaining a constant pressure, the MFC stabilizes the thermodynamic environment. This stability is required to trigger the specific chemical reactions necessary for MoS2 formation.
Optimizing Transport Efficiency
Beyond pressure, the MFC controls how effectively precursor vapors are moved from their source to the substrate.
The flow rate determines the speed at which volatilized materials travel. High-precision control ensures that the transport of precursors matches the reaction rate required at the substrate surface.
Achieving High-Quality Film Growth
Suppressing Multi-Layer Nucleation
One of the most critical challenges in MoS2 synthesis is limiting vertical growth to keep the material as a monolayer.
Fluctuations in gas flow can lead to spikes in precursor concentration, which triggers multi-layer nucleation. An MFC eliminates these fluctuations, maintaining a lean precursor supply that favors single-layer growth.
Promoting Large-Area Uniformity
To grow a film that covers a large area without gaps or clumps, the concentration of precursors must be distributed evenly.
Stable flow control prevents local "dead zones" or areas of excessive concentration. This results in a homogeneous distribution of reactants, allowing the MoS2 film to grow uniformly across the entire substrate.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The Balance of Flow and Temperature
While MFCs control the transport, they do not generate the vapor; that relies on the thermal stability of the quartz boats holding the precursors.
You must balance flow rate with volatilization rates. If the MFC drives gas too quickly over a quartz boat that isn't volatilizing precursors fast enough, the resulting film will be patchy or non-existent.
Residence Time vs. Supply Rate
Increasing flow rate improves the supply of fresh reactants, but it also reduces the residence time—the amount of time the gas spends in the hot zone.
If the flow is too high, precursors may be swept away before they can react and deposit. Precision is required to find the "sweet spot" where supply is sufficient but residence time allows for proper crystallization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your CVD system for MoS2 synthesis, align your flow control strategy with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is strict monolayer isolation: prioritize extremely stable, lower-range flow rates to limit precursor concentration and physically prevent multi-layer stacking.
- If your primary focus is large-scale scalability: optimize for higher transport efficiency to ensure the precursor vapor reaches the furthest edges of the substrate for uniform coverage.
Precision in gas flow is the difference between a contaminated, multi-layer sample and a pristine, electronic-grade MoS2 monolayer.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on MoS2 Synthesis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Regulation | Stabilizes the thermodynamic environment | Triggers consistent chemical reactions |
| Transport Efficiency | Controls precursor velocity from source to substrate | Matches transport rate with reaction rate |
| Nucleation Suppression | Eliminates flow fluctuations and concentration spikes | Prevents multi-layer growth; favors monolayers |
| Flow Uniformity | Ensures even distribution of reactant vapors | Promotes large-area, homogeneous film growth |
| Residence Time Control | Balances gas speed with reaction time in hot zone | Optimizes crystallization and film quality |
Elevate Your Thin-Film Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise gas flow is the defining factor between erratic deposition and high-performance electronic-grade MoS2 monolayers. KINTEK provides the advanced technology needed to master your reaction environment.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your research. Whether you are focusing on strict monolayer isolation or large-scale scalability, our high-precision systems provide the stability and control your lab requires.
Ready to optimize your MoS2 growth? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and discover how our expertise can accelerate your material breakthroughs.
Visual Guide
References
- Effects of Reaction Temperature and Catalyst Type on Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) of Crude Oil Feeds: A Microactivity Test Unit Study. DOI: 10.64589/juri/207996
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of CVD in the production of solar cells? Unlock High-Efficiency Thin-Film Layers
- How does a customized hot-wall ALD reactor contribute to 6FDA-TFDB membranes? Enhance Atomic-Level Polymer Modification
- Is PVD the same as CVD? Understanding the Physical vs. Chemical Deposition Difference
- What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and what does it produce? Discover High-Purity Thin Films and Coatings
- What are the advantages of CVD furnaces in preparing high-quality thin films? Achieve Superior Thin Films with High Purity and Uniformity
- What is a CVD system? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for High-Performance Coatings
- Can CVD furnaces be combined with other technologies? If so, how? Unlock Advanced Material Engineering
- How are CVD furnaces utilized in solar cell production? Unlock High-Efficiency Thin-Film Manufacturing



















