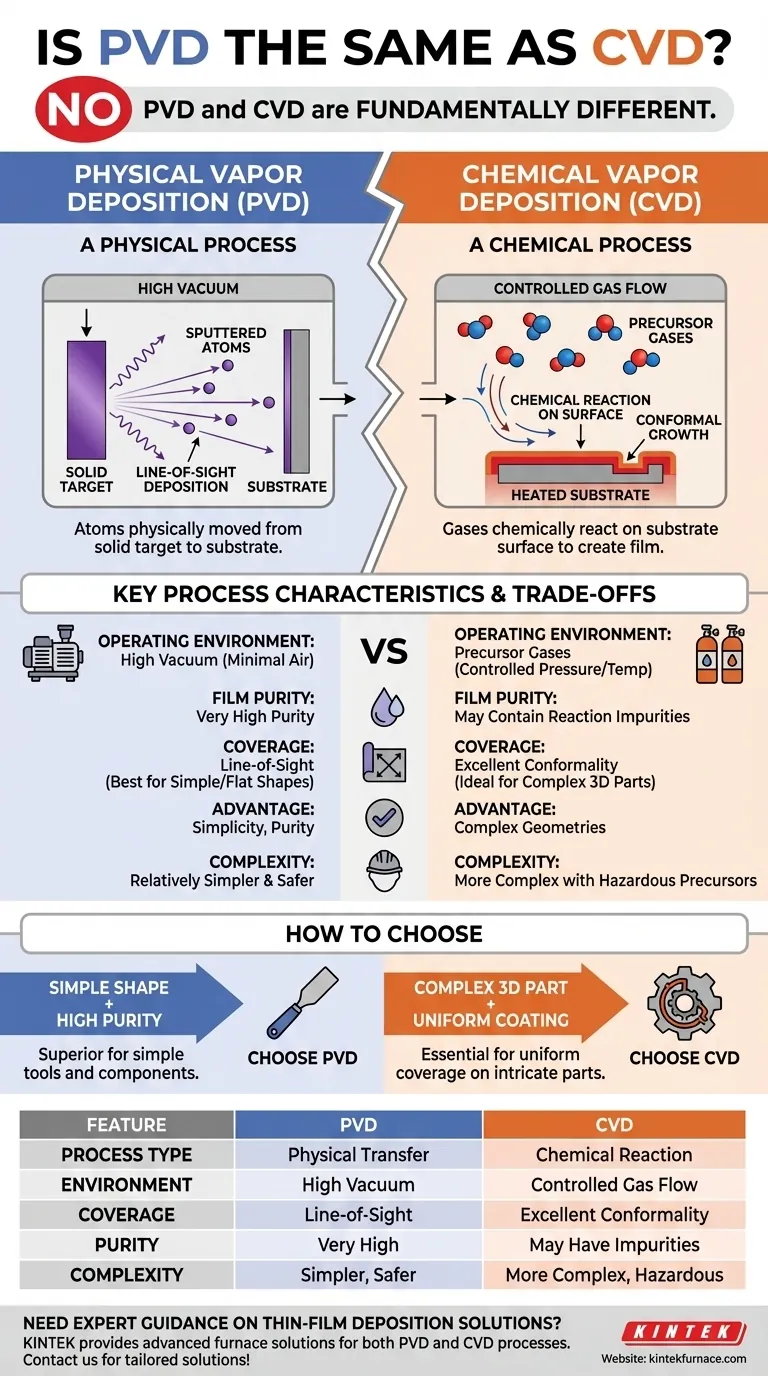
No, PVD and CVD are not the same. While both are sophisticated techniques for applying very thin films of material onto a surface, they operate on fundamentally different principles. PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a physical process, while CVD, or Chemical Vapor Deposition, is a chemical one.
The core distinction lies in how the coating material is transferred to the object. PVD physically moves atoms from a solid source to the substrate. In contrast, CVD uses precursor gases that undergo a chemical reaction on the substrate's surface to create the film.

The Fundamental Difference: Physical vs. Chemical
The names themselves provide the best clue to their function. One is a physical transfer, the other is a chemical creation.
How PVD Works: A Physical Process
Physical Vapor Deposition is a process that takes place in a high vacuum. A solid source material, known as the "target," is bombarded with energy, causing atoms to vaporize or be sputtered off its surface.
These individual atoms then travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber and condense onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin, solid film. It is conceptually similar to spray painting, but on an atomic level.
How CVD Works: A Chemical Process
Chemical Vapor Deposition introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
When these gases come into contact with the heated substrate, a chemical reaction is triggered. This reaction causes a solid material to form and deposit onto the surface, creating the desired film while by-product gases are exhausted from the chamber.
Comparing Key Process Characteristics
Understanding the operational differences helps clarify when to use one method over the other.
Operating Environment
PVD requires a high vacuum to allow atoms from the target to travel to the substrate without colliding with air molecules.
CVD operates with controlled flows of precursor gases under specific pressures and temperatures to facilitate the chemical reaction.
Film Purity and Adhesion
PVD processes generally produce films with very high purity and strong adhesion, as the source material is transferred directly with minimal contamination.
CVD films can sometimes contain impurities from the chemical reaction itself or have lower adhesion if the surface preparation is not perfect.
Conformality and Coverage
Because PVD is a "line-of-sight" process, it excels at coating flat or simple surfaces but struggles to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or internal channels.
CVD has a significant advantage in conformality. The precursor gases can flow around and into intricate geometries, resulting in a highly uniform coating even on the most complex parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between PVD and CVD involves weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each process against your application's specific needs.
Advantage PVD: Simplicity and Purity
The PVD process is mechanically simpler and involves fewer variables to control compared to CVD. It is often the preferred choice for producing extremely pure, dense, and hard coatings on tools and components where line-of-sight deposition is sufficient.
Advantage CVD: Complex Geometries
CVD's ability to "grow" a film from a gas phase makes it unmatched for applications requiring a uniform coating over complex shapes. This is critical in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where films must evenly coat microscopic structures.
Process Complexity and Safety
PVD is generally considered simpler and safer, as it primarily involves physical processes in a vacuum. The primary hazards are related to high voltage and vacuum systems.
CVD is more complex, requiring precise control over gas flows, temperatures, and pressures. It also often involves volatile, corrosive, or toxic precursor gases, which demand more robust safety protocols.
How to Choose Between PVD and CVD
Your choice depends entirely on the desired properties of the final film and the geometry of the part being coated.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-pure, hard coating on a relatively simple shape: PVD is likely the superior and more straightforward choice.
- If your primary focus is a perfectly uniform coating on a complex 3D part with internal surfaces: CVD is the only practical option to ensure complete coverage.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and avoiding hazardous chemical precursors: PVD offers a more direct and often safer manufacturing route.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between a physical transfer and a chemical reaction is the key to selecting the right technology for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer of atoms | Chemical reaction on surface |
| Operating Environment | High vacuum | Controlled gas flow, specific pressure/temperature |
| Coating Coverage | Line-of-sight (best for flat/simple shapes) | Excellent conformality (ideal for complex 3D parts) |
| Film Purity | Very high purity | May contain impurities from reaction |
| Process Complexity | Relatively simpler and safer | More complex with hazardous precursors |
Need Expert Guidance on Thin-Film Deposition Solutions?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for both PVD and CVD processes. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and manufacturing processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















