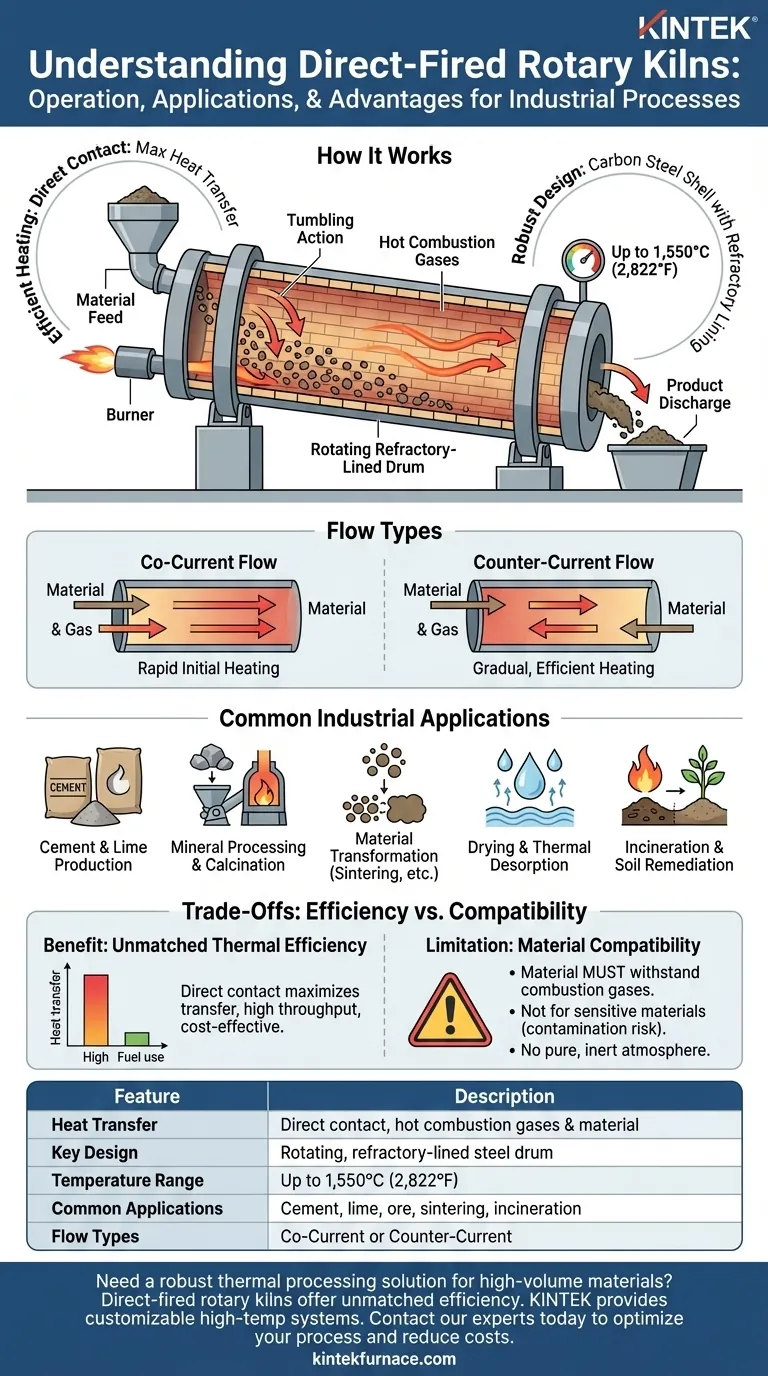
In short, a direct-fired rotary kiln operates by having hot combustion gases come into direct contact with the material being processed inside a large, rotating, refractory-lined drum. This direct exposure allows for highly efficient heat transfer, making these kilns ideal for high-temperature industrial processes where the material is not sensitive to the byproducts of combustion.
The defining characteristic of a direct-fired kiln is its method of heat transfer: fuel is burned directly within the kiln, and the resulting flame and hot gases mix with the material. This makes it a powerful and efficient tool, but only for materials that can withstand this direct exposure.
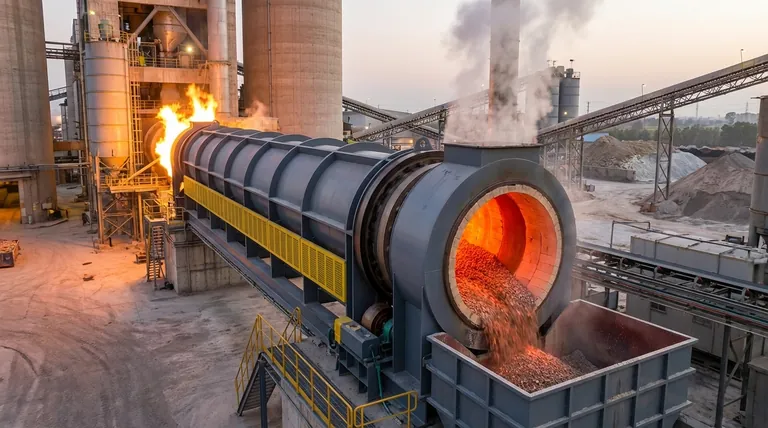

How Direct-Fired Kilns Achieve Efficient Heating
Direct-fired kilns are designed for one primary purpose: to transfer immense amounts of thermal energy to a material as efficiently as possible. This is accomplished through a few core design principles.
The Role of Direct Contact
The term "direct-fired" is the key. Fuel is combusted, and the resulting hot gases flow through the same chamber as the material. This direct interaction between the heat source and the process material maximizes the rate of heat transfer.
The Rotating Drum
The kiln itself is a long, cylindrical steel shell that is slightly inclined and rotates slowly. This rotation causes the material to tumble, or "cascade," as it moves from the feed end to the discharge end. This tumbling action constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the hot gases, ensuring uniform heating.
The Refractory Lining
To protect the carbon steel shell from extreme internal temperatures, which can reach up to 1,550°C (2,822°F), the inside of the drum is lined with a thick layer of refractory brick. This insulating layer is critical for the kiln's structural integrity and longevity.
Co-Current vs. Counter-Current Flow: A Key Design Choice
The direction of the hot gas flow relative to the material flow is a critical operational decision that fundamentally changes the heating profile within the kiln.
Co-Current Flow
In a co-current (or parallel) system, the hot gas and the material enter at the same end and travel in the same direction. This means the material is hit with the hottest gas immediately upon entry, leading to a very rapid initial temperature increase.
Counter-Current Flow
In a counter-current system, the gas and material flow in opposite directions. The material enters at one end, while the burner and hot gases enter at the opposite (discharge) end. This is more thermally efficient and provides a gradual heating curve, with the material reaching its peak temperature just before it exits the kiln.
Common Industrial Applications
Direct-fired kilns are workhorses in heavy industry, used for processes that require high temperatures and can tolerate exposure to combustion gases.
High-Volume Mineral Processing
These kilns are essential for producing foundational materials like cement and lime. They are also used extensively for processing ores and minerals, such as calcining limestone or reducing iron ore.
Material Transformation
Many applications involve changing the chemical or physical properties of a material. This includes calcination (heating to drive off volatiles), sintering (heating to create a solid mass without melting), and oxidation or reduction reactions.
Drying and Thermal Desorption
Direct-fired kilns are used to produce materials like roofing granules by drying them at high temperatures. In environmental applications, they are used for incineration of waste and soil remediation to remove contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Direct Firing
While powerful, the direct-fired design is not suitable for every application. Understanding its core trade-off is essential.
The Benefit: Unmatched Thermal Efficiency
For large-scale, energy-intensive processes, direct contact is the most efficient way to transfer heat. This translates to higher throughput and lower fuel consumption per ton of product compared to other heating methods.
The Major Limitation: Material Compatibility
The primary constraint is that the material must not be negatively affected by the combustion gases. If a process requires a pure, inert atmosphere, or if the material could be contaminated by byproducts like sulfur or ash, a direct-fired kiln cannot be used.
The Versatility: Wide Operating Range
These kilns are highly versatile, with typical material residence times ranging from 15 to 180 minutes. This flexibility allows them to be tuned for a wide variety of specific thermal processes, from simple drying to complex chemical reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency for a robust material: A direct-fired kiln is almost always the superior choice for its high throughput and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination or processing sensitive materials: An indirect-fired kiln, which heats the shell from the outside, is the necessary alternative.
- If you need to control the heating profile precisely: The choice between co-current flow (for rapid initial heating) and counter-current flow (for gradual heating to a final peak temperature) becomes the most critical design decision.
Ultimately, the power of the direct-fired rotary kiln lies in its elegant simplicity, delivering massive thermal energy directly where it is needed most.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Direct contact between hot combustion gases and material |
| Key Design | Rotating, refractory-lined steel drum |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1,550°C (2,822°F) |
| Common Applications | Cement production, lime calcination, ore reduction, sintering, incineration |
| Flow Types | Co-current (rapid heating) or Counter-current (gradual, efficient heating) |
Need a robust thermal processing solution for high-volume materials like cement or minerals?
Direct-fired rotary kilns offer unmatched thermal efficiency for large-scale industrial processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable, high-temperature equipment can optimize your process, increase throughput, and reduce operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How does customization benefit the use of rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Tailored Solutions
- What data is necessary to design a rotary kiln? Essential Factors for Efficient Thermal Processing
- What types of physical and chemical transformations occur in a rotary kiln? Master Material Processing for Superior Results
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability
- What role does gas flow and combustion play in a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer for Efficiency and Quality



















