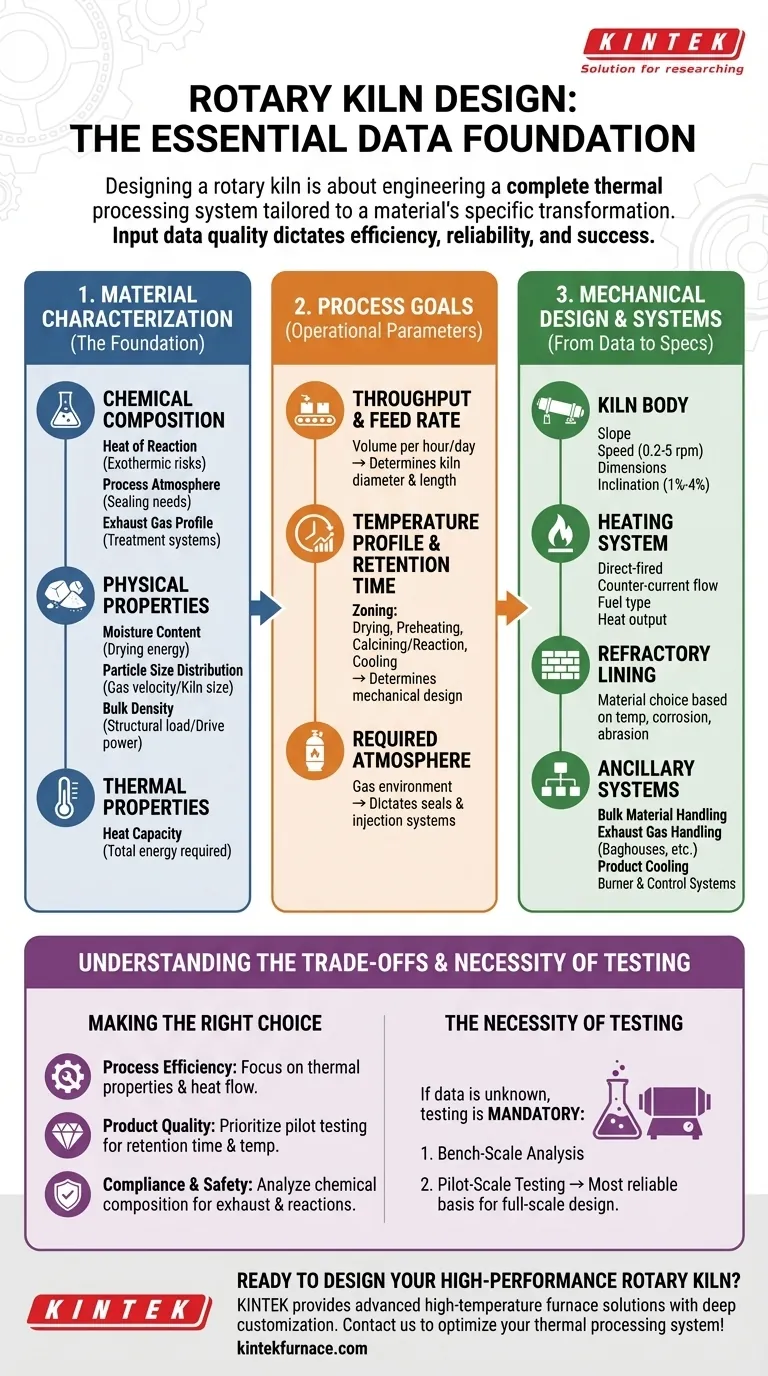
To properly design a rotary kiln, you must gather comprehensive data across three primary categories: the material's fundamental properties, the desired process requirements, and the specific operational parameters. This data includes the material's chemical composition, moisture content, particle size, and bulk density, alongside process goals like feed rate, target temperature, and the necessary retention time. Without this information, the design is based on assumption, which is a direct path to operational inefficiency and failure.
Designing a rotary kiln is not about selecting a piece of equipment; it is about engineering a complete thermal processing system tailored to a material's specific physical and chemical transformation. The quality of the input data directly dictates the efficiency, reliability, and ultimate success of the entire operation.

Material Characterization: The Foundation of Design
The material you intend to process is the single most important variable. Its characteristics dictate nearly every major design decision. Incomplete material data is the most common point of failure in kiln design.
Chemical Composition
Understanding the chemical makeup is non-negotiable. It predicts how the material will behave at high temperatures.
- Heat of Reaction: Some materials release energy (exothermic reactions) when heated. The design must account for this additional heat to prevent overheating and potential damage.
- Process Atmosphere: Certain chemical reactions require a specific atmosphere, such as an oxygen-free or carbon dioxide-rich environment. This dictates the kiln's sealing system and gas handling capabilities.
- Exhaust Gas Profile: The chemical reactions determine the composition of the exhaust gas, which is critical for designing the legally required gas treatment systems (e.g., thermal oxidizers, baghouses).
Physical Properties
The physical form of the material dictates how it moves through the kiln and interacts with heat.
- Moisture Content: Determines the energy required for drying and influences the design of the kiln's initial "drying zone."
- Particle Size Distribution (PSD): Finer materials can be carried away by process gas, requiring lower gas velocities and potentially larger kiln diameters. Uniform, pelletized feed allows for higher gas velocities and smaller, more efficient designs.
- Bulk Density: The weight of the material directly impacts the structural load. High-density materials require a more robust shell, support system, and a more powerful drive motor.
Thermal Properties
How the material absorbs and retains heat is a core input for all thermal calculations. The heat capacity is essential for calculating the total energy required to raise the material to the target temperature.
Defining the Process Goals
Once the material is understood, you must define what you need the kiln to accomplish. These goals set the primary operational parameters for the design.
Throughput and Feed Rate
This is the amount of material you need to process per hour or day. The required feed rate is a primary factor in determining the overall volume—and therefore the diameter and length—of the kiln.
Temperature Profile and Retention Time
Retention time is the duration the material must spend in the kiln to undergo the desired transformation. This, combined with the required temperature profile, determines the kiln's core mechanical design. The kiln is often zoned to manage this process:
- Drying Zone: Removes moisture.
- Preheating Zone: Brings material up to reaction temperature.
- Calcining/Reaction Zone: The area of peak temperature where the main chemical change occurs.
- Cooling Zone: Begins to lower the product temperature.
Required Atmosphere
The specific gas environment needed for the chemical reaction dictates the design of the kiln seals and whether a system for injecting specific gases is necessary.
From Data to Mechanical Design
The material data and process goals are translated directly into the physical specifications of the kiln and its supporting systems.
The Kiln Body: Slope, Speed, and Dimensions
The combination of required retention time and material flow characteristics determines the kiln's length, diameter, rotational speed (typically 0.2 to 5 rpm), and slope (typically 1% to 4% inclination). These four variables are manipulated in the design to ensure material moves through the kiln at the correct pace.
The Heating System: Burners and Heat Flow
The process dictates the heating method. Most kilns use a direct-fired, counter-current flow system, where a burner at the discharge end heats gas that flows against the direction of the material. This is the most thermally efficient configuration. The fuel type and required heat output are calculated from the material's thermal properties and throughput.
The Refractory Lining
The inside of the steel kiln shell is protected by a refractory lining. The material for this lining (e.g., specific types of brick or castable ceramic) is chosen based on the maximum process temperature, the chemical corrosiveness of the material, and its abrasive characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and System Complexity
A common mistake is to focus solely on the kiln cylinder itself, ignoring the larger context.
It's a System, Not Just a Kiln
A rotary kiln does not operate in isolation. A complete and functional design must include the entire ancillary system:
- Bulk Material Handling: Equipment to feed material into the kiln and transport the finished product away.
- Exhaust Gas Handling: A system of baghouses, scrubbers, or thermal oxidizers to clean exhaust gases and meet environmental regulations.
- Product Cooling: Often a separate rotary cooler or other technology is needed to safely handle the hot discharged product.
- Burner and Control Systems: The complete logic and hardware to manage fuel, combustion, and temperature.
The Necessity of Testing
If key material properties are unknown, testing is mandatory. The process typically involves:
- Bench-Scale Analysis: Initial thermal and chemical analysis in a lab.
- Pilot-Scale Testing: Running the material through a smaller pilot kiln to confirm process variables like retention time and temperature in a real-world dynamic environment. The data from a pilot test is the most reliable basis for designing a full-scale commercial kiln.
Making the Right Design Choice
Your design priorities will depend on your most critical business objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Ensure you have precise data on your material's thermal properties to optimize the heat flow and minimize fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is final product quality: Prioritize pilot testing to perfectly dial in the required retention time, temperature profile, and internal atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance and safety: Invest heavily in analyzing the chemical composition to predict exhaust gases and potential exothermic reactions accurately.
Ultimately, gathering detailed and accurate data is the foundational investment that ensures your rotary kiln operates efficiently, reliably, and safely for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Data Points | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Chemical composition, moisture content, particle size, bulk density, heat capacity | Dictates kiln behavior, heating needs, and structural design |
| Process Goals | Feed rate, target temperature, retention time, required atmosphere | Sets operational parameters for throughput and transformation |
| Operational Parameters | Kiln slope, rotational speed, dimensions, refractory lining | Translates data into mechanical design for reliability and efficiency |
Ready to design a high-performance rotary kiln tailored to your needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and processing requirements. Contact us today to optimize your thermal processing system and achieve superior efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















