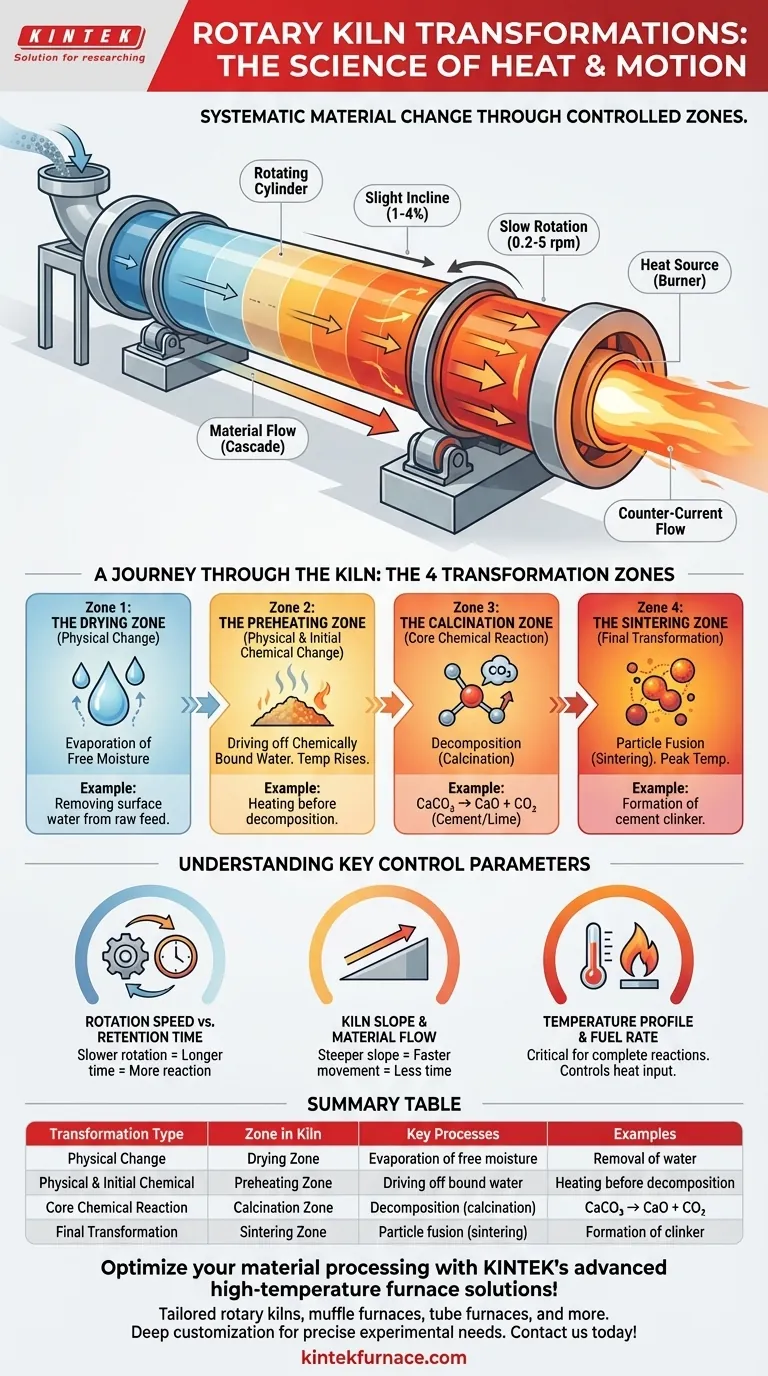
In essence, a rotary kiln systematically transforms materials through a sequence of physical and chemical changes driven by heat and motion. The primary transformations include drying to remove moisture, decomposition and calcination to break down chemical compounds, and finally sintering, where particles begin to fuse together to form a new, solid product. This controlled journey from raw feed to finished material is the fundamental purpose of the kiln.
A rotary kiln is not merely a furnace; it is a dynamic chemical reactor. Its physical design—the rotation, slope, and internal zones—is engineered specifically to guide materials through a precise sequence of temperature-driven transformations, ensuring a consistent and high-quality final product.

The Fundamental Principle: Controlled Transformation
A rotary kiln operates by tumbling material through a heated, rotating cylinder that is slightly inclined. This simple mechanical action is the key to its effectiveness.
The Role of Motion
The combination of the kiln's slow rotation (typically 0.2 to 5 rpm) and its gentle slope (1% to 4%) causes the material to cascade and move steadily from the feed end to the discharge end. This constant tumbling ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat.
The Role of Heat
Heat is typically applied directly by a large burner at the discharge end of the kiln. Most industrial kilns use a counter-current flow system, where the hot combustion gases travel up the kiln in the opposite direction of the material flow. This is a highly efficient method of heat transfer.
A Journey Through the Kiln: The Four Transformation Zones
The interior of a rotary kiln is not uniform. It functions as a series of distinct zones, each responsible for a specific stage of the material's transformation.
Zone 1: The Drying Zone (Physical Change)
As raw material enters the cooler, upper end of the kiln, its first task is to shed any free moisture. The heat here is relatively low, sufficient only to evaporate water. This is a purely physical change, preparing the material for the high-temperature reactions to come.
Zone 2: The Preheating Zone (Physical & Initial Chemical Change)
As the material tumbles further down the kiln, the temperature rises significantly. Here, chemically bound water is driven off. This stage raises the material's temperature to just below the point of major chemical reactions.
Zone 3: The Calcination Zone (Core Chemical Reaction)
This is the heart of the process, where the most critical chemical transformations occur. In a process called calcination, high temperatures cause the material to decompose. For example, in cement and lime production, calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) breaks down into calcium oxide (CaO) and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas.
Zone 4: The Sintering Zone (Final Transformation)
In the hottest part of the kiln, right near the burner, the material reaches its peak temperature. Here, sintering occurs. The particles become plastic and begin to fuse together without fully melting, forming new, larger nodules with the desired chemical and physical properties, such as cement clinker.
Understanding the Key Control Parameters
Achieving the correct transformations depends on a delicate balance of several operating variables. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for process control.
Rotation Speed vs. Retention Time
The speed of the kiln's rotation directly controls retention time—the duration the material spends inside. A slower rotation increases retention time, allowing for more complete reactions, but it also reduces the overall throughput of the kiln.
Kiln Slope and Material Flow
The steepness of the kiln's incline also affects retention time. A steeper slope moves material through more quickly, while a shallower slope slows it down. This parameter is typically set during design and is not adjusted during operation.
Temperature Profile and Fuel Rate
The temperature profile across the different zones is the most critical variable. It is controlled by the fuel rate of the burner. Insufficient heat in the calcination zone will lead to incomplete reactions, while excessive heat wastes energy and can damage the kiln's protective refractory lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational focus will determine which parameters are most important for you to monitor and control.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Balance retention time (via rotation speed) with the temperature profile to ensure complete chemical reactions without wasting fuel.
- If your primary focus is product quality: The temperature and atmospheric conditions in the calcination and sintering zones are the most critical variables to master for consistent output.
- If your primary focus is equipment reliability: The refractory lining in the high-heat sintering zone is the main point of wear and requires diligent monitoring to prevent costly damage and downtime.
Ultimately, mastering a rotary kiln is about understanding it as an integrated system where mechanical motion and thermal energy work together to create profound material change.
Summary Table:
| Transformation Type | Zone in Kiln | Key Processes | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Change | Drying Zone | Evaporation of free moisture | Removal of water from raw materials |
| Physical & Initial Chemical Change | Preheating Zone | Driving off chemically bound water | Heating before decomposition |
| Core Chemical Reaction | Calcination Zone | Decomposition (e.g., calcination) | CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ in cement production |
| Final Transformation | Sintering Zone | Particle fusion (sintering) | Formation of cement clinker |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored rotary kilns, muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What data is necessary to design a rotary kiln? Essential Factors for Efficient Thermal Processing
- How does customization benefit the use of rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Tailored Solutions
- What are the primary applications of an electric rotary kiln? Achieve High-Purity Material Processing with Precision



















