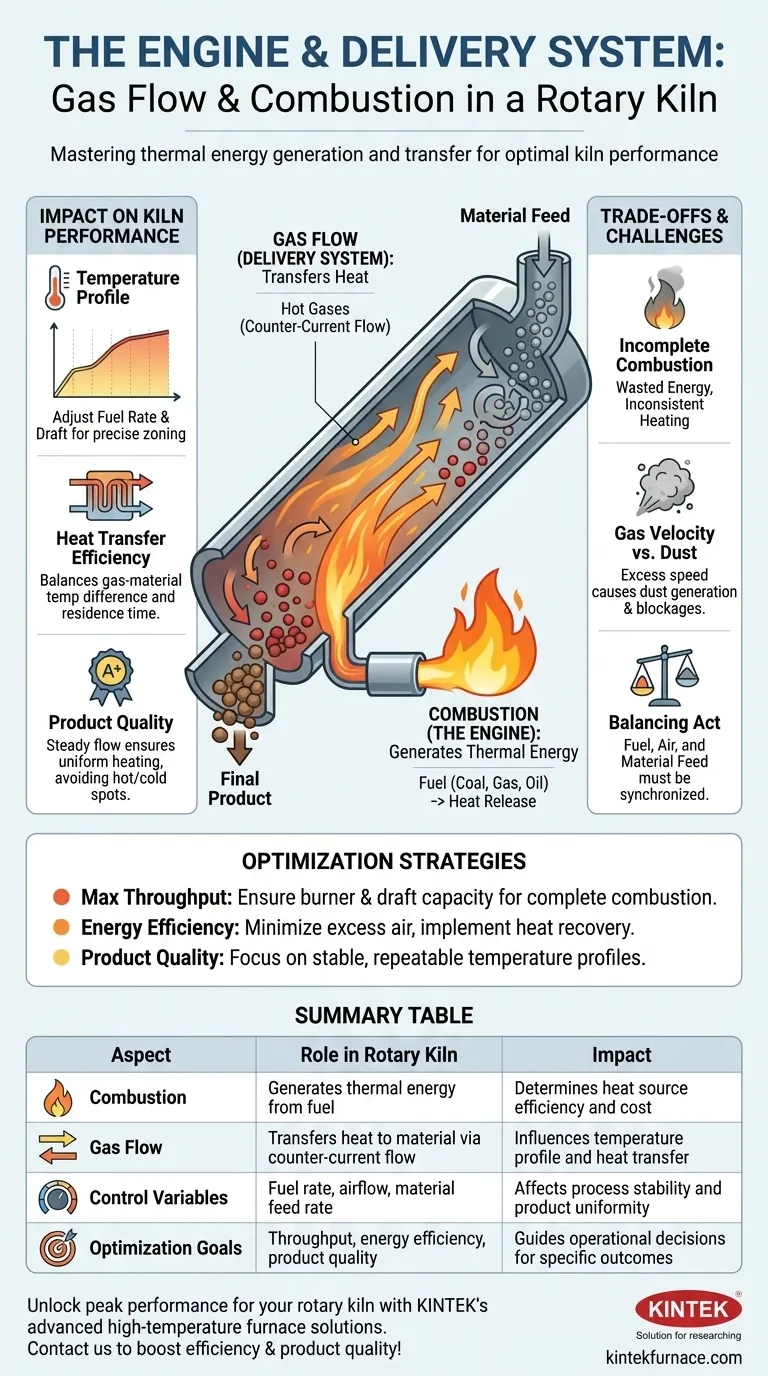
At its core, the role of combustion in a rotary kiln is to act as the engine that generates thermal energy, while the gas flow serves as the critical delivery system that transfers this energy to the material being processed. These two interconnected elements are not merely operational details; they are the primary levers for controlling the entire chemical or physical transformation occurring inside the kiln.
A rotary kiln is a dynamic heat exchanger. Mastering its performance requires understanding that combustion is the source of power, and gas flow is the mechanism for precisely applying that power to the material to achieve the desired outcome efficiently and consistently.

The Core Function: Generating and Transferring Heat
To understand the kiln, you must first see it as a system designed for a single purpose: controlled heat transfer. Combustion and gas flow are the two sides of this coin.
Combustion as the Kiln's Engine
The primary function of combustion is to release the chemical energy stored in fuel (like coal, gas, or oil) as thermal energy, or heat. This process is the kiln's sole heat source.
The goal is always complete combustion. This ensures that the maximum amount of energy is extracted from the fuel, which directly translates to higher energy efficiency and lower operational costs. Incomplete combustion not only wastes fuel but can also lead to inconsistent heating and the production of unwanted byproducts.
Gas Flow as the Heat Delivery System
Once heat is generated, it must be delivered to the material. This is the job of the hot combustion gases, which flow through the length of the kiln.
In most designs, kilns use a counter-current flow system. The solid material is fed into the higher, cooler end and slowly tumbles downward, while the hot gas from the burner at the lower end flows upward. This design is exceptionally efficient, as the hottest gases meet the most processed material, and the cooler gases preheat the fresh material entering the kiln.
How Gas Flow Dictates Kiln Performance
Controlling the flow of hot gas is just as important as creating it. The rate and characteristics of the gas flow directly influence the efficiency of the process and the quality of the final product.
Controlling the Kiln's Temperature Profile
The interaction between the hot gas and the moving material creates a temperature profile along the kiln's length. By adjusting the fuel rate (combustion intensity) and the draft (gas flow speed), operators can precisely manage this profile.
This control is essential for processes that require distinct temperature zones, such as converting limestone into cement clinker, where different chemical reactions must occur at specific temperatures and stages.
Maximizing Heat Transfer Efficiency
The effectiveness of heat transfer depends on several factors, including the temperature difference between the gas and the material, and the residence time of both.
Slower gas velocity allows more time for heat to radiate and convect to the material bed. However, the flow must be fast enough to carry heat effectively up the entire length of the kiln, ensuring the incoming material is properly preheated.
Impact on Product Quality
Inconsistent combustion or erratic gas flow leads directly to quality control problems. Unstable conditions can create "hot spots" that over-burn or sinter the material, or "cold spots" that result in an incomplete reaction.
The steady movement of gas ensures that every particle of material is exposed to the proper heat for the correct amount of time as it tumbles through the kiln, leading to a uniform and high-quality final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Optimizing a rotary kiln is a balancing act. The interplay between combustion and gas flow introduces several operational challenges that must be managed carefully.
Incomplete Combustion and Wasted Energy
Achieving complete combustion requires a precise fuel-to-air ratio. Too little air results in unburnt fuel being wasted and sent out the exhaust stack. Too much excess air simply cools the flame, reducing peak temperature and carrying valuable heat out of the system, lowering efficiency.
Gas Velocity vs. Dust Generation
A key trade-off exists with gas velocity. While a certain velocity is needed for effective heat transfer, excessively high gas speeds can act like a powerful wind.
This high velocity can pick up fine particles from the material bed and carry them out of the kiln. This not only results in a loss of valuable product but can also cause blockages and wear in downstream equipment like preheaters and filters.
Balancing Fuel, Air, and Material Feed
The three primary variables—fuel rate, airflow (draft), and material feed rate—are deeply interconnected. An increase in material feed requires a corresponding increase in fuel and air to maintain the temperature profile. Changing one without adjusting the others will disrupt the kiln's thermal balance, impacting efficiency and product quality.
Optimizing Combustion and Gas Flow for Your Goal
The right strategy depends entirely on your primary objective. Use these principles to guide your operational decisions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You must ensure your burner and draft system can deliver enough energy for complete combustion at higher material feed rates.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Prioritize maintaining complete combustion with the minimum necessary excess air and consider implementing heat recovery systems to capture energy from the exit gas.
- If your primary focus is product quality consistency: Focus on maintaining a stable and repeatable temperature profile by carefully controlling the fuel-to-air ratio and the kiln's draft (gas flow rate).
By mastering the principles of combustion and gas flow, you gain direct control over the performance and outcome of your rotary kiln process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Rotary Kiln | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Generates thermal energy from fuel | Determines heat source efficiency and cost |
| Gas Flow | Transfers heat to material via counter-current flow | Influences temperature profile and heat transfer |
| Control Variables | Fuel rate, airflow, material feed rate | Affects process stability and product uniformity |
| Optimization Goals | Throughput, energy efficiency, product quality | Guides operational decisions for specific outcomes |
Unlock peak performance for your rotary kiln with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique process needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can boost your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained



















