Carbon composite conveyor belts significantly enhance the stability and uniformity of brazing filler metal spreading. Unlike traditional metal mesh belts, carbon composite materials possess a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, which drastically minimizes mechanical vibration during furnace operation. This creates a motionless platform that allows the filler metal to flow into complex joint gaps without the disruption caused by belt movement or jitter.
The Core Insight: The quality of a brazed joint is heavily dependent on the stability of the workpiece during the wetting phase. Carbon composite belts eliminate thermal expansion-induced vibration, ensuring that capillary action is driven solely by surface tension and joint geometry, not by external mechanical agitation.
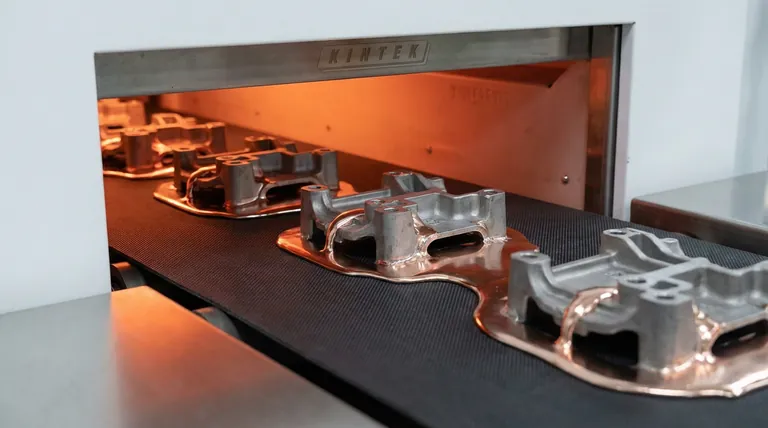

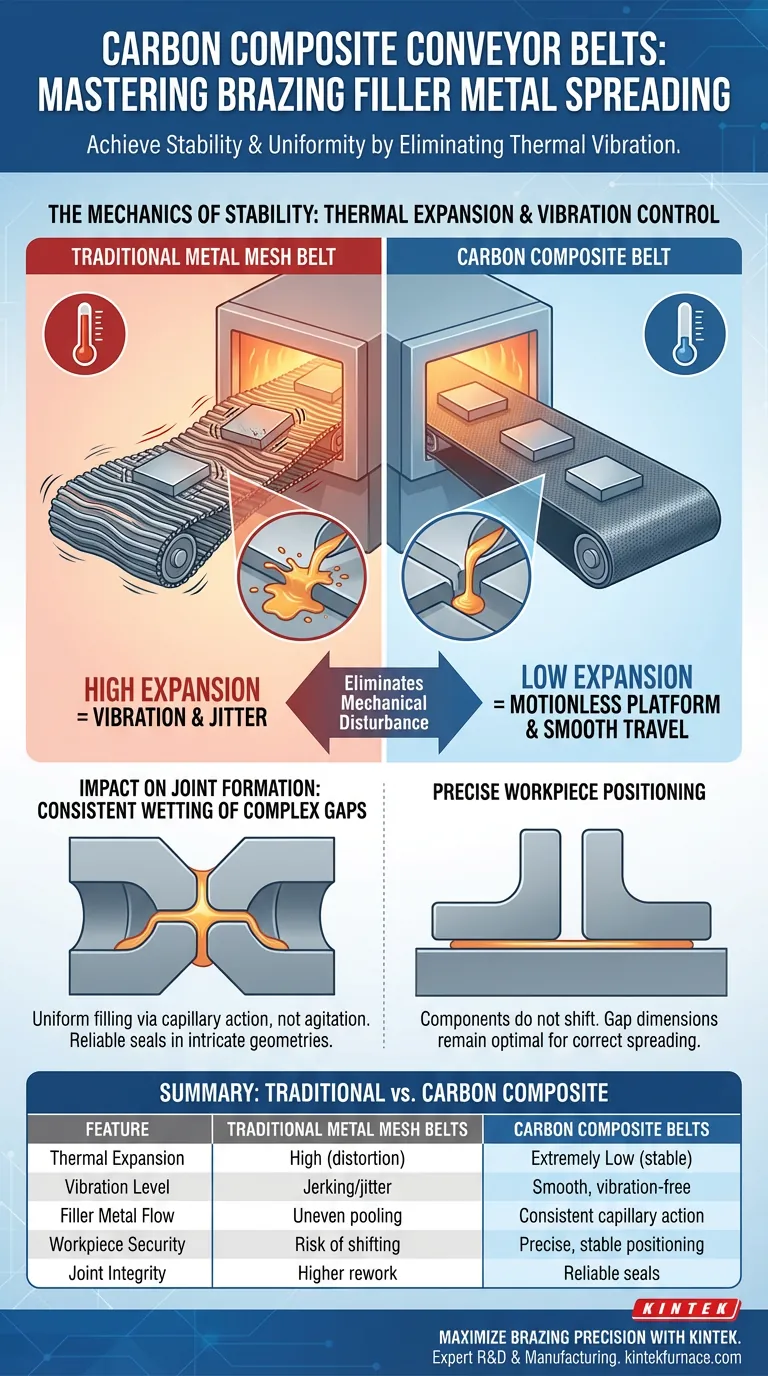
The Mechanics of Stability
Reducing Thermal Expansion
The primary driver of superior spreading behavior is the belt's low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Traditional metal belts expand and contract significantly as they cycle through heat zones. This thermal movement often translates into physical jerking or vibration as the belt moves through the furnace drive system. Carbon composite belts remain dimensionally stable, eliminating this source of kinetic energy.
Eliminating Mechanical Disturbance
Because the belt does not expand or distort, it travels smoothly through the furnace.
This smooth travel prevents mechanical disturbances that typically shake the workpieces. In a brazing context, even micro-vibrations can interrupt the flow of molten filler metal or cause it to pool unevenly.
Impact on Joint Formation
Consistent Wetting of Complex Gaps
The stability provided by carbon composite belts allows for uniform filling of difficult joints.
When the conveyor vibrates, the liquid filler metal can be agitated out of the gap or forced to wet the surface irregularly. A vibration-free environment ensures that the filler metal follows the intended capillary path, resulting in a reliable seal even in complex geometries.
Precise Workpiece Positioning
Stable belt movement ensures that the components being brazed do not shift relative to one another.
If parts move during the heating cycle due to belt vibration, the joint gap dimensions can change. By maintaining exact positioning, the carbon composite belt ensures the gap remains optimal for the filler metal to spread correctly.
Understanding the Constraints
The Scope of Benefit
While carbon composite belts offer superior stability, it is important to understand that they solve a specific mechanical problem: vibration caused by thermal expansion.
If your furnace has other sources of mechanical instability—such as a faulty drive motor or misaligned rollers—the belt alone may not resolve all spreading issues. The benefit of these belts is maximized in high-precision environments where the slightest movement can compromise the capillary action of the filler metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if carbon composite belts are the right solution for your brazing process, consider your specific production requirements:
- If your primary focus is brazing complex geometries: The lack of vibration is critical here; these belts ensure the filler metal penetrates intricate gaps without interruption.
- If your primary focus is reducing rework rates: The stability of the belt prevents part shifting, directly addressing common causes of incomplete wetting or misaligned joints.
By neutralizing thermal expansion, you transform the conveyor from a variable into a constant, ensuring the physics of your brazing process work exactly as intended.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Metal Mesh Belts | Carbon Composite Belts |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | High (leads to belt distortion) | Extremely Low (stable dimensions) |
| Vibration Level | Mechanical jerking/jitter | Smooth, vibration-free travel |
| Filler Metal Flow | Potential for uneven pooling | Consistent capillary action |
| Workpiece Security | Risk of shifting during heating | Precise, stable positioning |
| Joint Integrity | Higher rework on complex parts | Reliable seals in intricate gaps |
Maximize Your Brazing Precision with KINTEK
Don't let mechanical vibrations compromise your joint quality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside advanced conveyor solutions like carbon composite belts. Whether you need a standard setup or a system customizable for your unique laboratory needs, our technical team is ready to help you eliminate variables and ensure perfect wetting every time.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
References
- Yoshio Bizen, Yasuyuki Miyazawa. Brazing of Ferritic Stainless Steel with Ni-25Cr-6P-1.5Si-0.5B-1.5Mo Amorphous Brazing Foil Having a Liquidus of 1243 K with Continuous Conveyor Belt Furnace in Low-Oxygen Atmosphere. DOI: 10.2320/matertrans.mt-m2023207
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is a mechanical vacuum pump essential for Ti-50Nb-xMo melting? Ensure Purity & Prevent Alloy Embrittlement
- What is the purpose of using fused quartz tubes in high-temperature sealed reaction systems for alloy research?
- What role do high-purity graphite crucibles play in Boron Carbide sintering? Optimize Ceramic Purity and Density
- Why are high-purity alumina tubes and crucibles preferred for high-temperature smelting? Ensure Maximum Sample Purity
- How do high-precision mass flow controllers contribute to studying the oxidation behavior of lignite?
- Why is a rotary evaporator used to process separated fractions in hydrotreated coal tar analysis? Enhance Sample Purity
- How are quartz tubes used in laboratory applications? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Processes
- What advantages do platinum crucibles offer for KCdCl3 sintering? Ensure Pure, Single-Phase Sample Synthesis



















