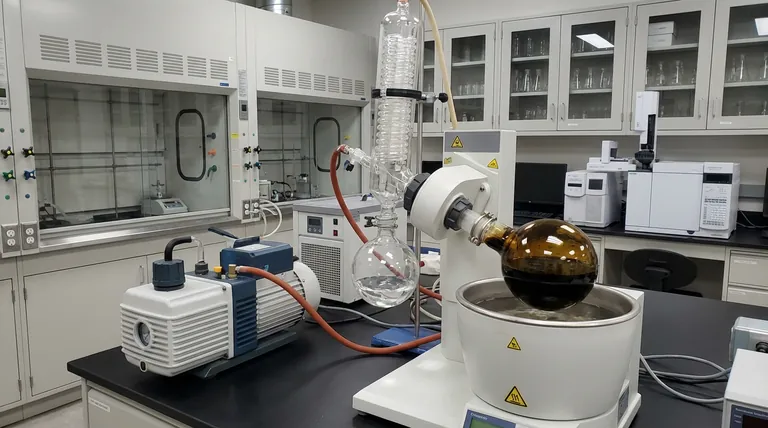
In hydrotreated coal tar analysis, a rotary evaporator serves as the critical link between chemical separation and final compositional analysis. It allows you to remove elution solvents efficiently by applying constant heat within a reduced pressure environment. This specific combination ensures that solvents are stripped away rapidly without subjecting the delicate coal tar fractions to damaging high temperatures.
Core Takeaway The rotary evaporator is indispensable because it decouples solvent removal from high heat. By lowering the boiling point via vacuum, it yields dry, high-purity samples for quantitative weighing while preserving the original chemical structure of the sub-components.

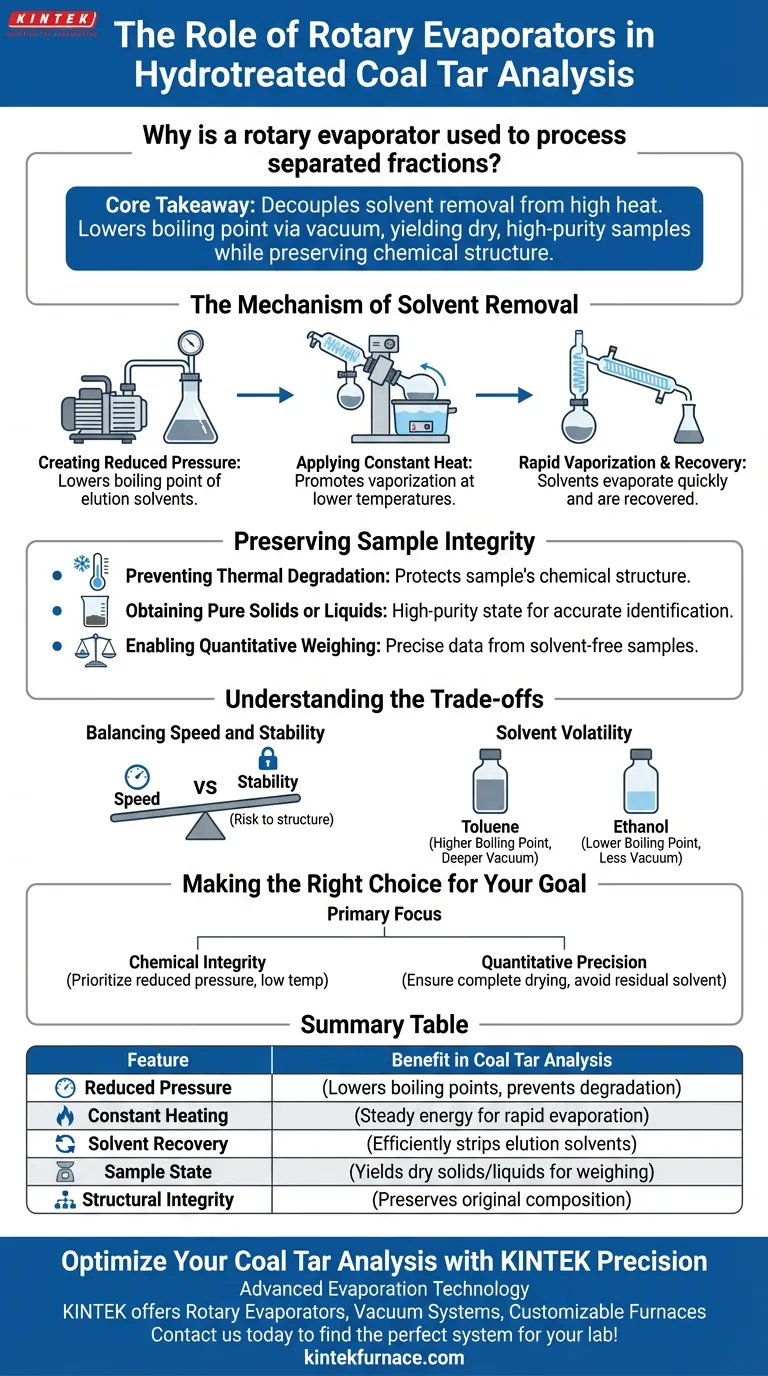
The Mechanism of Solvent Removal
Creating a Reduced Pressure Environment
The rotary evaporator operates by pulling a vacuum on the sample flask. This reduction in pressure significantly lowers the boiling point of elution solvents.
Applying Constant Heat
While the pressure is reduced, the device applies a steady, controlled source of heat to the sample. This energy input promotes vaporization without requiring the extreme temperatures of a standard hot plate.
Rapid Vaporization
The combination of vacuum and constant heat causes solvents, such as toluene or ethanol, to evaporate quickly. This vapor is then condensed and recovered, leaving the desired fraction behind.
Preserving Sample Integrity
Preventing Thermal Degradation
The primary reason for using this method is to protect the sample's chemical structure. High temperatures can alter or destroy the sub-components of hydrotreated coal tar, rendering analysis useless.
Obtaining Pure Solids or Liquids
Once the solvent is removed, the process yields a dry solid or a highly concentrated liquid. This high-purity state is essential for accurate identification of the fraction's components.
Enabling Quantitative Weighing
To determine the composition of the coal tar accurately, you must weigh the separated fractions. The rotary evaporator ensures the sample is free of solvent weight, allowing for precise quantitative data.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Balancing Speed and Stability
While the primary reference highlights "rapid" recovery, there is a limit. Increasing heat to speed up the process poses a risk to the chemical structure you are trying to preserve.
Solvent Volatility
The efficiency of the process depends heavily on the solvent used. Solvents with naturally higher boiling points (like toluene) may require deeper vacuum levels than more volatile solvents (like ethanol) to maintain low-temperature evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the most accurate hydrotreated coal tar analysis, consider the following principles:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Integrity: Prioritize the "reduced pressure" aspect to keep the operating temperature as low as possible.
- If your primary focus is Quantitative Precision: Ensure the process runs until the sample is completely dry to prevent residual solvent from skewing weight measurements.
By utilizing the rotary evaporator correctly, you ensure that your separated fractions remain authentic to their original composition.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in Coal Tar Analysis |
|---|---|
| Reduced Pressure | Lowers boiling points to prevent thermal degradation of delicate fractions. |
| Constant Heating | Provides steady energy for rapid solvent evaporation without extreme heat. |
| Solvent Recovery | Efficiently strips elution solvents like toluene or ethanol for high-purity samples. |
| Sample State | Yields dry solids or concentrated liquids essential for quantitative weighing. |
| Structural Integrity | Preserves the original chemical composition for accurate downstream analysis. |
Optimize Your Coal Tar Analysis with KINTEK Precision
Ensure the integrity of your chemical fractions with advanced evaporation technology. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Rotary Evaporators, Vacuum systems, and customizable lab furnaces designed to meet the rigorous demands of coal tar research and material science.
Don’t compromise your quantitative data—partner with KINTEK for reliable, high-purity results. Contact us today to find the perfect system for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Analysis of Composition and Structure Characteristics of Heavy Hydrogenated Coal Tar and Its Subcomponents from Xinjiang, China. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01796
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the function of the nitrogen environment in pyrolysis? Mastering Carbonization with Laboratory Furnaces
- What are the common uses for Alumina ceramic tubes? Ideal for High-Temp, Insulation, and Corrosion Resistance
- How do a brass cap and a cooling element work together? Ensuring Reliable High-Temperature Experimental Seals
- Why is a high-performance vacuum pumping system required for DLC coatings? Achieve 3.0 x 10^-5 Pa Purity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for phosphor synthesis? Ensure Maximum Luminescence and Spectral Purity
- What is a circulating water vacuum pump also known as? Discover Its Role in Lab Efficiency
- What is the function of a condensation crystallizer in a magnesium vapor recovery system? Master Purification & Yield
- What are the key advantages of using quartz tubes in high-temperature applications? Achieve Unmatched Thermal Stability and Purity



















