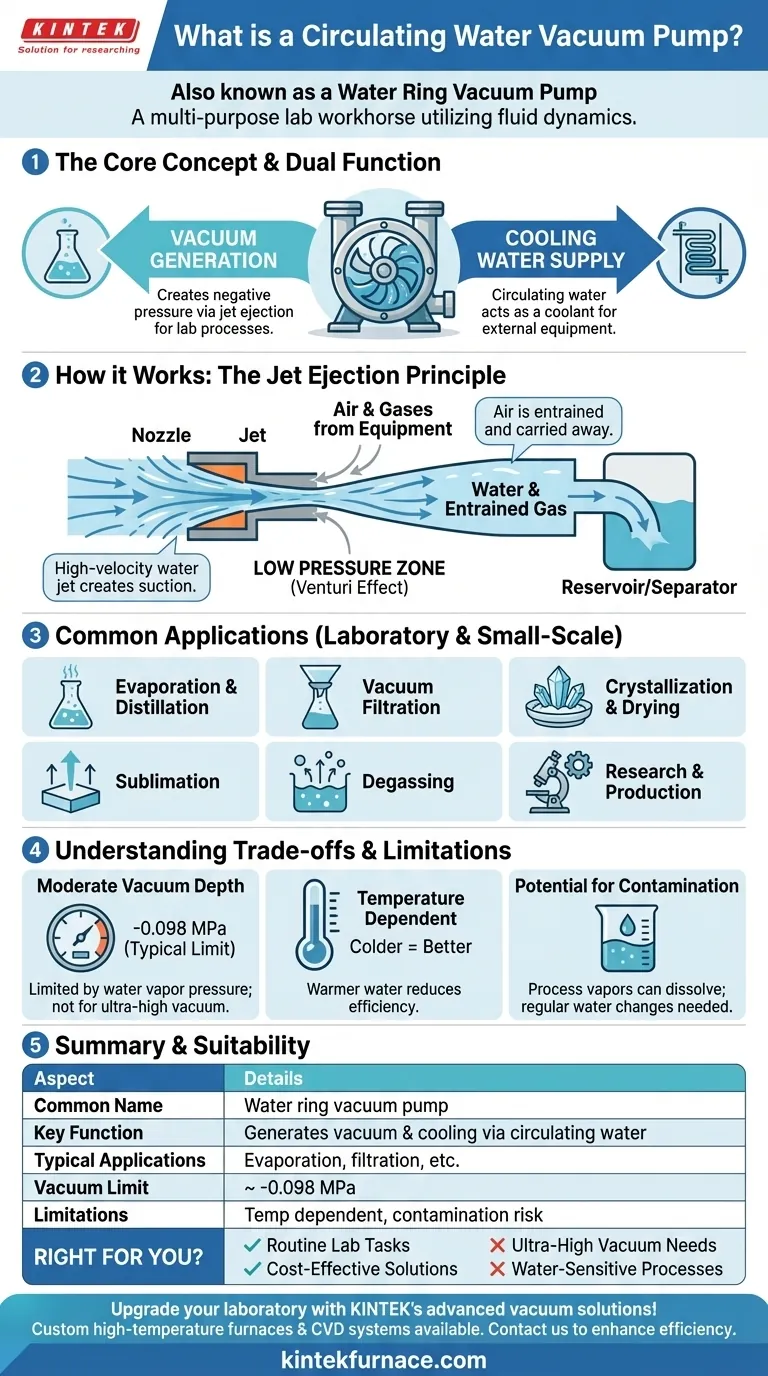
A circulating water vacuum pump is most commonly known as a water ring vacuum pump. It is a multi-purpose device that uses circulating water as its working fluid to generate negative pressure, making it a foundational piece of equipment in many laboratory and small-scale industrial settings.
At its core, a water ring pump is not just creating a vacuum; it is using the simple, reliable physics of moving fluid to enable critical scientific processes. Its value lies in its dual function of providing both vacuum and a source of circulating cooling water.

How a Water Ring Pump Creates a Vacuum
A circulating water vacuum pump's design is elegant in its simplicity. It relies on a fluid dynamic principle rather than complex mechanical compression like other pump types.
The Role of Water as a Working Fluid
The pump uses water, typically stored in an integrated reservoir, as its "working fluid." This water is continuously circulated through the system, which is why it is often called a "circulating water" pump.
The Jet Ejection Principle
The core of the vacuum generation lies in the jet mechanism. The pump forces the circulating water through a nozzle, or jet, at high velocity. As this high-speed jet of water passes an opening (the suction port), it creates a region of low pressure according to the Venturi effect.
This low-pressure zone pulls air and other gases from the connected equipment (like a flask or filter), effectively creating a vacuum. The entrained gas molecules are then carried away by the water flow.
An Integrated Cooling System
A significant secondary benefit is that the circulating water can also be used as a coolant. The pump often has separate ports to supply this circulating water to an external reaction unit, such as a condenser, making it a highly efficient, dual-purpose tool.
Common Applications and Uses
The moderate but stable vacuum provided by a water ring pump is ideal for a wide range of common laboratory and light industrial tasks.
Chemical and Biological Processes
This pump is a workhorse for providing the necessary vacuum conditions for processes that require reduced pressure.
Typical applications include:
- Evaporation and Distillation
- Crystallization and Drying
- Sublimation (transitioning a solid directly to a gas)
- Vacuum Filtration and Degassing
Supporting Research and Small-Scale Production
You will find these pumps extensively used in universities, research institutes, and small-scale production facilities across various fields, including pharmaceuticals, biochemistry, food processing, and agricultural engineering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, it's important to understand the operational limitations of a water ring vacuum pump to use it effectively.
Vacuum Depth is Moderate
The ultimate vacuum a water ring pump can achieve is limited by the vapor pressure of the water being used. As the pressure in the system drops, the water itself will begin to evaporate, preventing a deeper vacuum from forming. An ultimate vacuum of -0.098 MPa is typical, which is excellent for most lab applications but insufficient for ultra-high vacuum needs.
Performance Depends on Water Temperature
The efficiency of the vacuum is directly tied to the water temperature. Colder water has a lower vapor pressure, which allows the pump to achieve a deeper and more stable vacuum. As the pump operates, the water will gradually heat up, which can slightly reduce performance over long runs.
Potential for Contamination
Since the vacuum is generated by direct contact between the process gas and the water, there is a possibility of vapors from your experiment dissolving into the circulating water. This means the water may need to be changed periodically to maintain performance and avoid cross-contamination.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Before using a water ring vacuum pump, confirm that its capabilities align with your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is routine lab filtration, distillation, or evaporation: A circulating water vacuum pump is a robust, reliable, and cost-effective solution perfectly suited for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is achieving an ultra-high vacuum for sensitive surface science or mass spectrometry: This is the wrong tool; you will need a more advanced system like a turbomolecular or ion pump.
- If your primary focus is a process sensitive to water vapor: Be aware that this pump introduces a small amount of water vapor and may not be suitable without an additional cold trap.
By understanding its simple principles and inherent limitations, you can effectively leverage this versatile pump for countless scientific applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Water ring vacuum pump |
| Key Function | Generates vacuum using circulating water and jet ejection |
| Typical Applications | Evaporation, distillation, filtration, crystallization |
| Vacuum Limit | Up to -0.098 MPa (moderate vacuum) |
| Limitations | Dependent on water temperature, potential for contamination |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced vacuum solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable equipment can enhance your experimental efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What functions do alumina crucibles and quartz tube encapsulation serve? Essential Shields for Na2In2As3 Synthesis
- Why are high-purity quartz tubes and quartz boats preferred for plastic pyrolysis? Ensure Precise, Pure Results
- What are the functions of high-purity, high-strength graphite molds in SPS? Optimize Al2O3-TiC Ceramic Sintering
- What is the primary function of high-purity graphite crucibles? Ensure Superior Purity in Aluminum Alloy Melting
- Why is a quartz reaction tube ideal for tubular carbon nanofibers? High-Purity Synthesis Solutions
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni alloy prep? Master Mechanical Alloying Efficiency
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in YBCO synthesis? Ensure Purity & Stability in Superconductor Production
- What is the significance of using high-purity quartz tubes in MoS2 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis



















