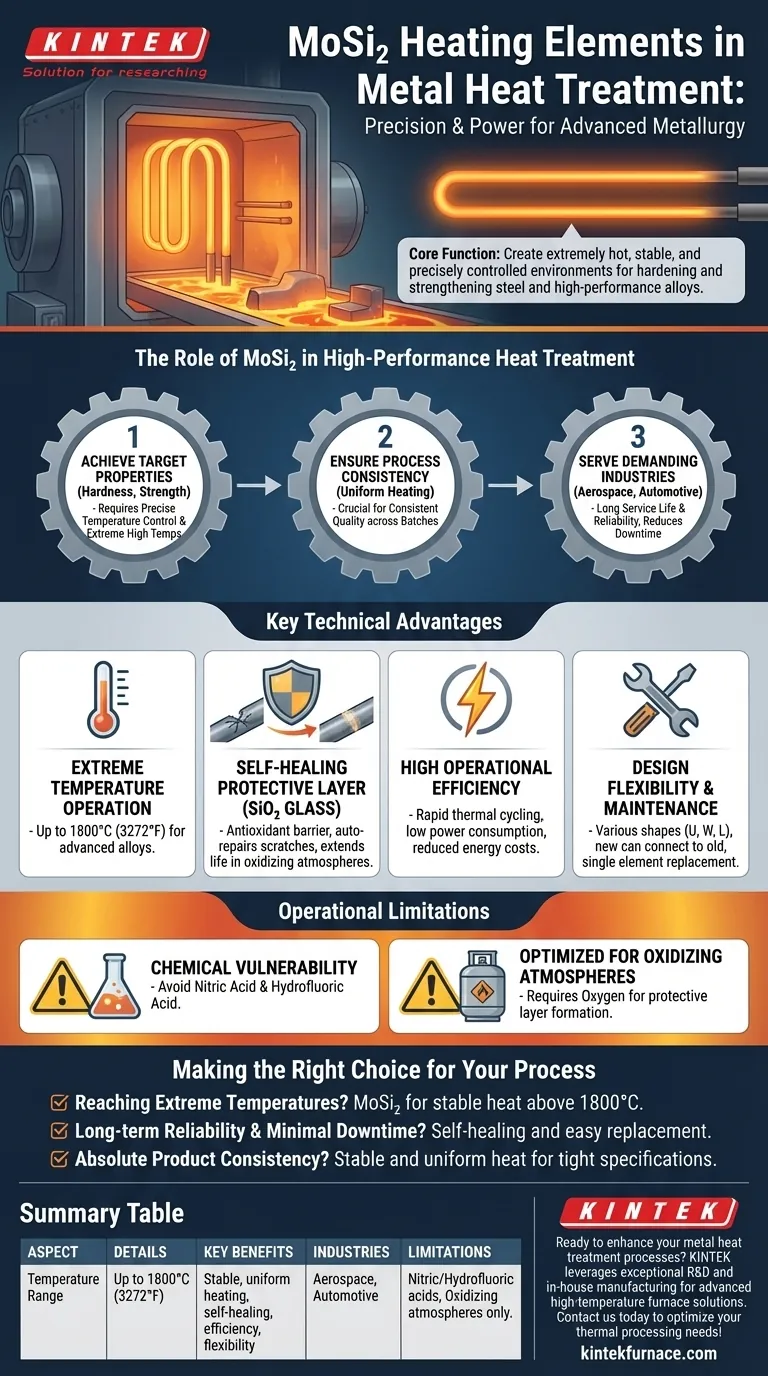
At its core, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements are used in metal heat treatment to create an extremely hot, stable, and precisely controlled furnace environment. This allows for processes like hardening and strengthening of steel and high-performance alloys, which is essential for manufacturing critical components with enhanced mechanical properties.
The true value of MoSi₂ elements in heat treatment is not just their ability to reach extreme temperatures, but their operational stability and uniformity. This combination ensures consistent, repeatable results and minimizes costly furnace downtime, which is paramount in high-stakes industries like aerospace and automotive.
The Role of MoSi₂ in High-Performance Heat Treatment
MoSi₂ elements are not just a heat source; they are a critical enabler of modern metallurgical processes. Their unique properties directly support the goals of heat treatment.
Achieving Target Material Properties
The primary goal of heat treatment is to alter a metal's microstructure to achieve specific properties like hardness and strength.
This requires precise temperature control and the ability to reach very high temperatures, which MoSi₂ elements provide reliably.
Ensuring Process Consistency
Uniform heating across the entire furnace chamber is crucial for consistent quality. Inconsistent temperatures can lead to batches of parts with varying properties or internal stresses.
MoSi₂ elements are known for providing stable and uniform heating, ensuring that every component receives the exact same thermal cycle.
Serving Demanding Industries
Industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing rely on high-strength materials and operate with very high costs associated with furnace downtime.
MoSi₂ elements are preferred in these sectors because their long service life and reliability support continuous work and reduce expensive interruptions.
Key Technical Advantages of MoSi₂ Elements
Several key characteristics make MoSi₂ the technology of choice for these demanding applications.
Extreme Temperature Operation
MoSi₂ elements can operate at furnace temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). This capability allows for the treatment of advanced alloys and specialized steels that require intense heating.
The Self-Healing Protective Layer
At high temperatures in an oxygen atmosphere, a thin, protective layer of silica (SiO₂) glass forms on the element's surface.
This layer acts as an antioxidant barrier and has a unique auto-repair function. If the element is scratched or damaged, the underlying material re-oxidizes to heal the protective film, dramatically extending its service life.
High Operational Efficiency
These elements feature a high heating rate and relatively low power consumption. This efficiency allows for rapid thermal cycling and helps reduce overall energy costs in production environments.
Design Flexibility and Maintenance
MoSi₂ elements are produced in various shapes (e.g., U, W, and L shapes) to fit different furnace designs.
Crucially, new elements can be connected to old ones in the same circuit. This simplifies maintenance, as a single failed element can be replaced without needing to replace the entire set.
Understanding the Operational Limitations
While highly effective, MoSi₂ elements have specific limitations that must be managed for optimal performance and longevity.
Chemical Vulnerability
The protective silica layer makes the elements highly resistant to most acids and alkalis.
However, they will be attacked and dissolved by nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. The furnace environment must be free of these chemicals.
Optimized for Oxidizing Atmospheres
The self-healing silica layer relies on the presence of oxygen to form. The elements are explicitly designed for continuous work in an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Using them in reducing or other specialized atmospheres may impact their performance and lifespan, as the protective layer cannot properly form or be maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine how you leverage the benefits of MoSi₂ elements.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme process temperatures: MoSi₂ elements are the definitive choice for applications requiring stable heat above the limits of metallic or silicon carbide elements.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and minimal downtime: The self-healing silica layer and the ability to mix old and new elements make MoSi₂ ideal for continuous, high-volume production.
- If your primary focus is absolute product consistency: The stable and uniform heat output of MoSi₂ ensures that every part in a batch receives the same thermal treatment, which is critical for achieving tight specifications.
By understanding these core characteristics, you can confidently specify the right heating technology for your critical thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) |
| Key Benefits | Stable, uniform heating; self-healing protective layer; high efficiency; design flexibility |
| Industries Served | Aerospace, automotive manufacturing |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to nitric and hydrofluoric acids; optimized for oxidizing atmospheres |
Ready to enhance your metal heat treatment processes with reliable, high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior performance and efficiency for industries like aerospace and automotive. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















