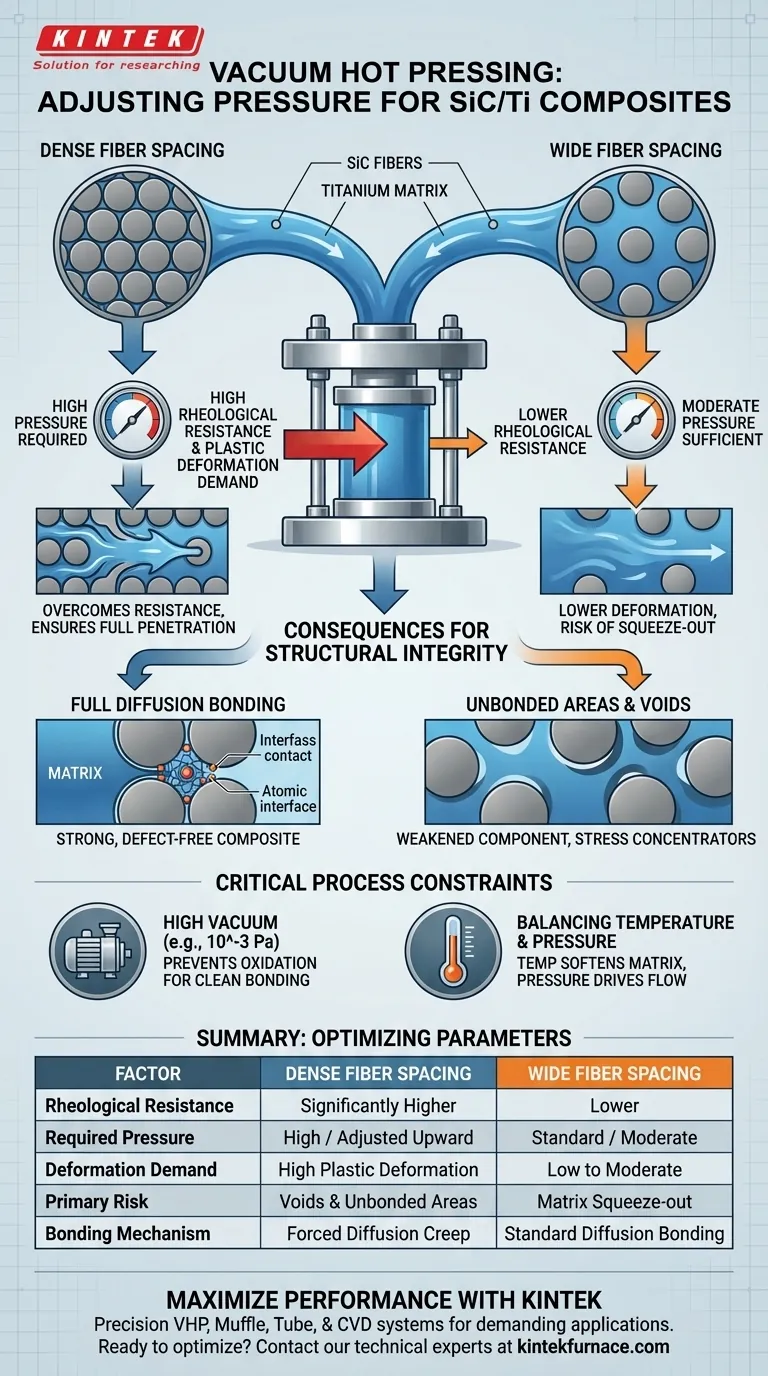
Fiber spacing directly dictates the hydraulic pressure required to achieve a defect-free SiC fiber-reinforced titanium matrix composite. As the distance between fibers decreases, the titanium matrix encounters significantly higher resistance to flow, necessitating an upward adjustment in pressure to drive the material into these tighter interstitial spaces.
Core Takeaway: Smaller fiber spacing creates narrower channels that drastically increase the rheological resistance against the titanium matrix. Higher pressure is strictly required to overcome this resistance and induce the necessary plastic deformation, ensuring the matrix fully penetrates the gaps and eliminates void formation.
The Physics of Matrix Flow and Consolidation
Overcoming Rheological Resistance
When SiC fibers are arranged densely, the spacing between them narrows. This reduction in space creates a physical barrier that restricts the movement of the matrix foil.
This restriction results in higher rheological resistance, meaning the material fights back against the flow. You cannot use standard pressure settings for dense arrangements because the force will be insufficient to overcome this increased friction and resistance.
Driving Plastic Deformation
To fill these narrow gaps, the titanium matrix foil must undergo significant shape changes. This process is known as plastic deformation.
The matrix must be physically squeezed from a solid foil shape into the intricate voids between fibers. Tighter spacing demands a higher degree of this deformation, which can only be achieved by applying greater mechanical pressure via the hydraulic system.
Consequences for Structural Integrity
Preventing Unbonded Areas
The primary risk of failing to adjust pressure is the creation of unbonded areas. If the pressure is too low for the specific fiber density, the matrix will bridge across the fibers without flowing all the way to the bottom of the gap.
This leaves voids or "shadows" within the composite. These voids act as stress concentrators and weaken the final component.
Facilitating Diffusion Bonding
Pressure does more than just move material; it creates the intimacy required for bonding. The Vacuum Hot Press (VHP) process relies on diffusion creep to fuse the matrix and fibers.
By increasing pressure in dense arrays, you ensure that the matrix creates full contact with the fiber surface. This contact is a prerequisite for the atomic diffusion that creates a strong physical bond between the metal and the reinforcement.
Critical Process Constraints and Trade-offs
The Role of Vacuum Environment
While pressure drives the flow, it cannot succeed without a pristine environment. The high vacuum (e.g., 10^-3 Pa) is essential to prevent the oxidation of the chemically active titanium matrix.
If the environment is not maintained at high vacuum, oxygen reacts with the titanium. Even with high pressure, oxidized surfaces will fail to bond effectively, rendering the pressure adjustment moot.
Balancing Temperature and Pressure
High pressure works synergistically with high temperature. The elevated temperatures (often between 870°C and 950°C for titanium consolidation) soften the matrix, making it easier to deform.
However, relying solely on temperature to improve flow is risky due to potential grain growth or fiber degradation. Therefore, mechanical pressure remains the primary lever for managing difficult fiber spacings.
Optimizing Process Parameters for Density
To ensure the successful consolidation of your SiC/Titanium composites, evaluate your fiber architecture before setting your VHP parameters.
- If your primary focus is a Dense Fiber Arrangement: Significantly increase hydraulic pressure to overcome high rheological resistance and force the matrix into tight interstitial gaps.
- If your primary focus is Defect Elimination: Prioritize pressure adjustments to ensure sufficient plastic deformation, preventing the formation of voids and unbonded areas.
- If your primary focus is Interfacial Quality: Maintain a high vacuum alongside your pressure adjustments to ensure diffusion bonding occurs on clean, oxide-free surfaces.
Correctly matching your pressure parameters to your fiber spacing is the single most effective method for guaranteeing a fully dense, structurally sound composite.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Dense Fiber Spacing | Wide Fiber Spacing |
|---|---|---|
| Rheological Resistance | Significantly Higher | Lower |
| Required Pressure | High / Adjusted Upward | Standard / Moderate |
| Deformation Demand | High Plastic Deformation | Low to Moderate |
| Primary Risk | Voids and Unbonded Areas | Matrix Squeeze-out |
| Bonding Mechanism | Forced Diffusion Creep | Standard Diffusion Bonding |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision is critical when handling the complex rheology of SiC-reinforced titanium. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides industry-leading Vacuum Hot Press (VHP), Muffle, Tube, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding aerospace and industrial applications. Our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific pressure and vacuum requirements, ensuring defect-free consolidation and superior structural integrity.
Ready to optimize your composite fabrication?
Contact our technical experts today to find your custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is 'final short-time pressing' important in vacuum hot pressing? Unlock Maximum Material Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace for preparing high-density carbon nanotube reinforced copper matrix composites? Achieve Maximum Density and Purity for Superior Performance
- How does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace mitigate copper sintering swelling? Solve Fe-Cu Expansion Issues
- What are the advantages of SPS over hot pressing for high-entropy alloys? Achieve Superior Density and Microstructure
- How does temperature control in a vacuum hot pressing furnace influence the interface quality of Ti-Al composites?
- What role does the mechanical pressure applied by the hot pressing mechanism play? Optimize Densification Now
- What are the advantages of industrial SPS vs traditional sintering for SiC? Superior Density and Fine-Grain Structure
- What roles do high-purity, high-strength graphite molds play in SPS? Driving Densification and Precision



















