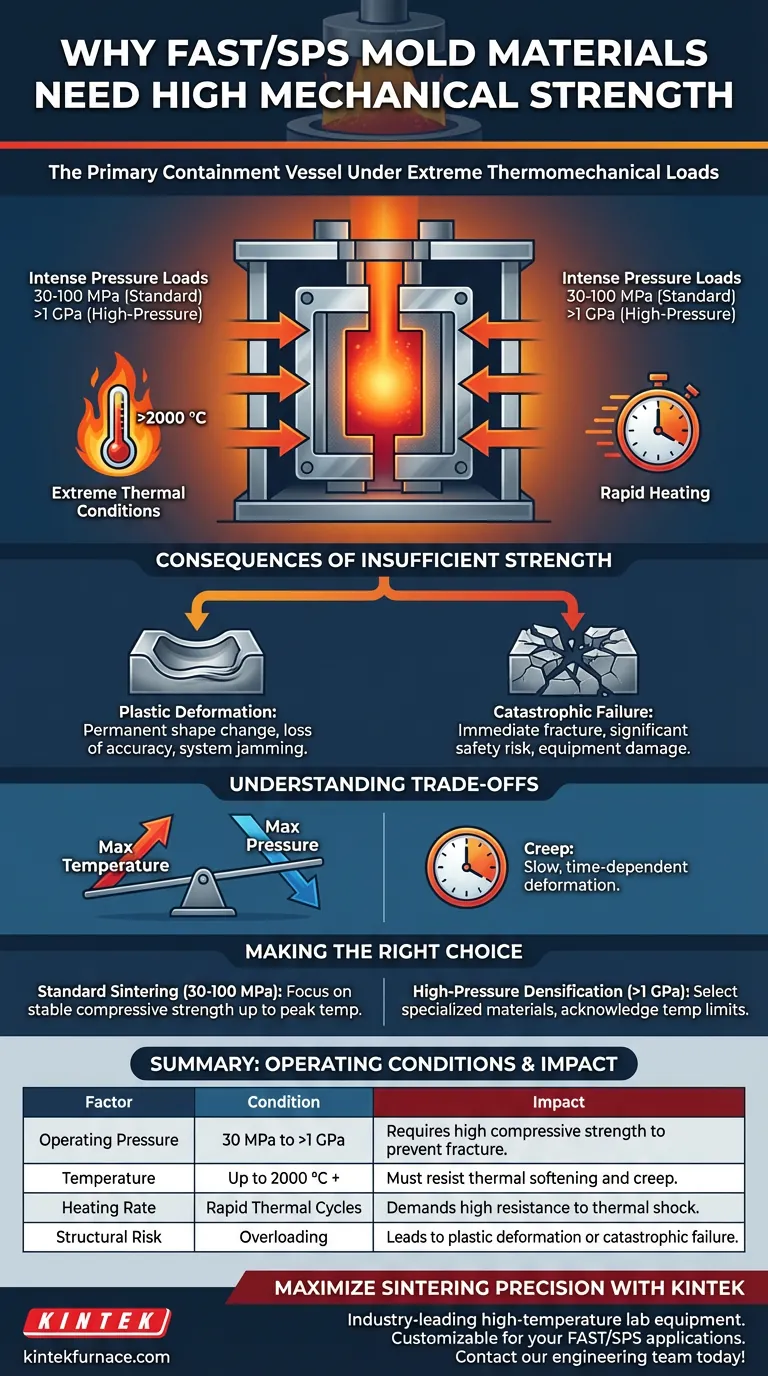
Mold materials in Field Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST) and Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems act as the primary containment vessel under severe stress. They must possess high mechanical strength to endure physical pressures that can exceed several GPa while simultaneously maintaining structural integrity at temperatures rising above 2000 °C.
The necessity for high mechanical strength is dictated by the extreme thermomechanical loads inherent to the sintering process. Without exceptional high-temperature compressive strength, the mold is liable to suffer plastic deformation or catastrophic failure during rapid heating cycles.

The Operational Environment of FAST/SPS
To understand why strength is non-negotiable, you must look at the specific forces applied during the sintering cycle.
Intense Pressure Loads
Standard FAST and SPS units apply significant mechanical force to densify powders. Typical operating pressures range from 30 to 100 MPa.
In specialized high-pressure models, these loads are even more severe, reaching up to several GPa. The mold material must absorb this stress without yielding.
Extreme Thermal Conditions
Pressure is rarely applied in isolation; it is coupled with intense heat. These systems frequently operate at temperatures exceeding 2000 °C.
At these thermal extremes, the atomic structure of many materials begins to relax. The mold must maintain its rigidity despite this thermal softening effect.
The Impact of Rapid Heating
FAST and SPS technologies are defined by their speed. The process involves rapid-heating conditions, which introduce dynamic stress alongside static pressure.
The mold material must be robust enough to handle the thermal shock of rising temperatures without cracking or warping under the applied load.
Consequences of Insufficient Strength
Using a mold material that lacks the required compressive strength leads to two primary failure modes.
Plastic Deformation
If the material's yield strength is exceeded by the combination of heat and pressure, the mold will permanently change shape. This is known as plastic deformation.
A deformed mold destroys the dimensional accuracy of the sintered sample and can permanently damage the sintering system by jamming the tooling.
Catastrophic Failure
In more severe cases, insufficient strength leads to immediate fracture. Under high-pressure loads, this results in catastrophic failure of the mold assembly.
This poses a significant safety risk to the operator and risks destroying the heating elements and vacuum chamber of the device.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While maximizing strength is critical, it is important to recognize the physical limits of even the best mold materials.
The Temperature-Pressure Inverse
There is an inherent trade-off between the maximum temperature and the maximum pressure a mold can withstand. As temperature increases, compressive strength generally decreases.
You often cannot run a system at its maximum rated pressure and its maximum rated temperature simultaneously.
The Risk of Creep
Even if a mold does not fail immediately, prolonged exposure to high loads at high temperatures can cause "creep."
This is a slow, time-dependent deformation. While less dramatic than catastrophic failure, it gradually renders the mold unusable for precision applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct mold material requires balancing your specific processing parameters against the material's limits.
- If your primary focus is standard sintering (30-100 MPa): Ensure your material offers stable compressive strength up to your peak temperature to avoid gradual deformation.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure densification (>1 GPa): You must select specialized materials rated for extreme loads, acknowledging that this may limit your maximum achievable temperature.
Ultimately, the integrity of your mold dictates the safety and success of the entire sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Operating Condition | Impact on Mold Material |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | 30 MPa to >1 GPa | Requires high compressive strength to prevent fracture. |
| Temperature | Up to 2000 °C + | Material must resist thermal softening and creep. |
| Heating Rate | Rapid Thermal Cycles | Demands high resistance to thermal shock and dynamic stress. |
| Structural Risk | Overloading | Leads to plastic deformation or catastrophic assembly failure. |
Maximize Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don't let mold failure compromise your research or production. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature lab equipment, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the extreme thermomechanical demands of your unique FAST/SPS applications.
Ready to elevate your material densification process? Contact our engineering team today to discuss your high-pressure and high-temperature requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Alexander M. Laptev, Olivier Guillon. Tooling in Spark Plasma Sintering Technology: Design, Optimization, and Application. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202301391
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using SPS for protonic ceramic electrolytes? Achieve Rapid Densification
- How does vacuum hot pressing equipment enhance the matrix quality of diamond tools through improved wettability? Unlock Superior Diamond Retention
- How does the vacuum system in these furnaces work? Achieve Purity and Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- How does the hot pressing mechanism enhance TiB2-TiN density? Achieve Superior Hardness in Tool Materials
- How does temperature control precision of a vacuum hot press affect SiC fiber/TB8 matrix? Optimize Interface Quality
- What specific issue does the vacuum environment within a Vacuum Hot Press furnace address? Stop A356/SiCp Oxidation
- What is hot pressing sintering and how does vacuum hot pressing sintering improve the process? Achieve Superior Material Density and Purity
- What are some specific applications of vacuum hot press furnaces? Unlock Advanced Material Fabrication



















