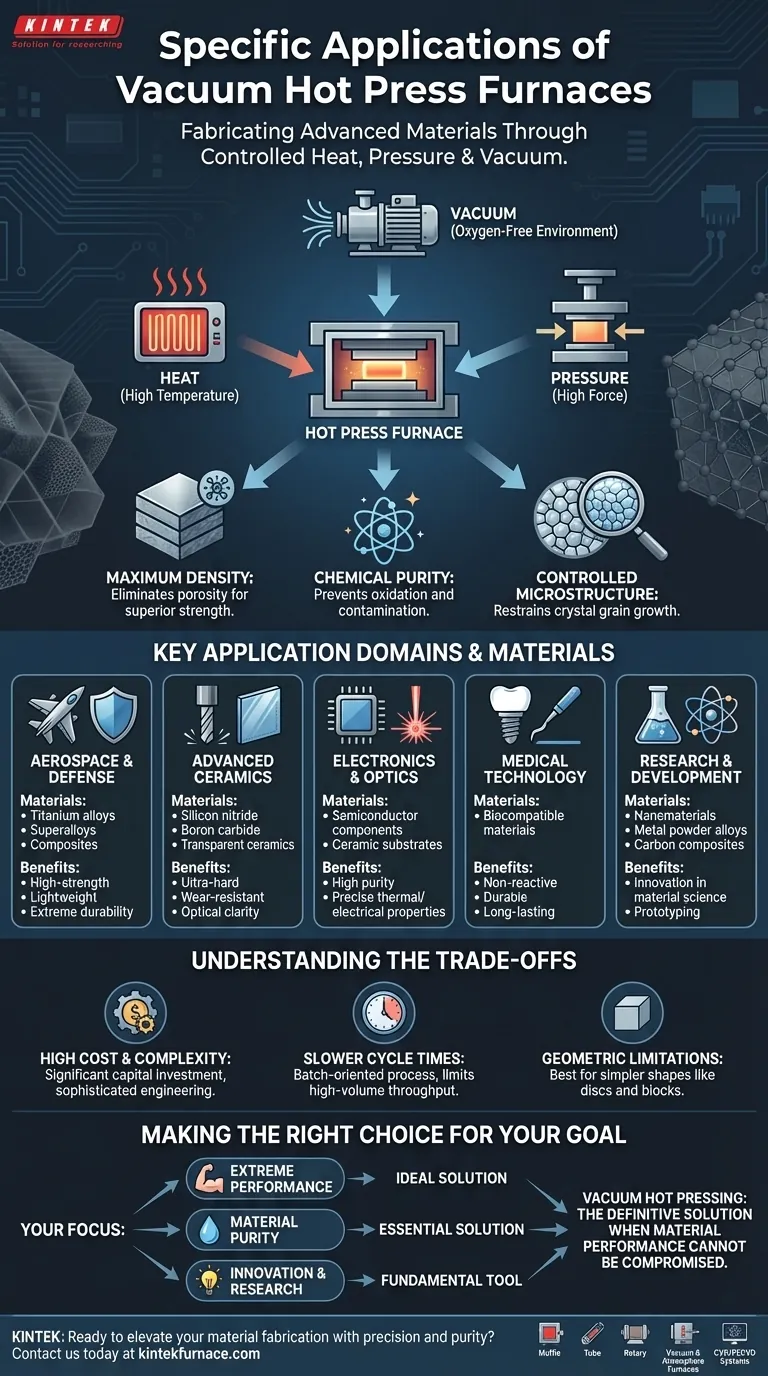
At its core, a vacuum hot press furnace is used to fabricate advanced materials that are impossible to create using conventional methods. Specific applications range from producing high-strength, lightweight components for the aerospace industry and ultra-hard cutting tools from ceramics like boron carbide, to sintering transparent ceramics for optical systems and creating biocompatible materials for medical implants.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum hot press is to simultaneously apply high temperature and high pressure in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. This unique combination allows for the creation of fully dense, highly pure materials with superior mechanical and physical properties.

The Core Principle: Why Combine Heat, Pressure, and Vacuum?
Understanding the "why" behind this technology reveals its true power. Each element—heat, pressure, and vacuum—plays a critical role in manipulating materials at a microscopic level.
Eliminating Porosity for Maximum Density
Sintering is the process of bonding material powders into a solid mass using heat. Adding high pressure during this process, known as hot pressing, physically forces the powder particles together.
This pressure eliminates the tiny voids or pores between particles, resulting in a final product that is almost 100% dense. This density is directly linked to superior strength, hardness, and thermal conductivity.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Heating reactive materials like titanium or certain advanced ceramics in the open air would cause them to instantly oxidize, ruining their properties. The vacuum environment removes oxygen and other reactive gases.
This ensures the material remains chemically pure throughout the high-temperature process, which is critical for applications in aerospace, electronics, and medicine where even minor impurities can lead to catastrophic failure.
Controlling Microstructure and Grain Growth
The properties of a material are heavily influenced by the size and arrangement of its microscopic crystal grains. High temperatures can cause these grains to grow, which often degrades strength.
The application of high pressure allows for sintering to occur at lower temperatures or for shorter times. This gives engineers precise control to restrain crystal grain growth, which is essential for producing high-performance nanomaterials and fine-grained ceramics.
Key Application Domains & Materials
The principles of hot pressing enable manufacturing in some of the world's most demanding industries.
Aerospace & Defense: High-Strength, Lightweight Components
This sector requires materials that are both incredibly strong and as light as possible. Vacuum hot pressing is used to fabricate parts from titanium alloys, superalloys, and advanced composites.
These materials form the backbone of jet engine components, structural airframe parts, and armor systems that must perform under extreme stress and temperature.
Advanced Ceramics: From Cutting Tools to Transparent Armor
Materials like silicon nitride and boron carbide are exceptionally hard but brittle and difficult to form. Hot pressing consolidates their powders into dense shapes for industrial cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
The process is also used to create transparent ceramics, which are as clear as glass but far more durable, for applications like scratch-proof lenses and transparent armor.
Electronics & Optics: Precision Components
The electronics industry relies on materials with specific thermal and electrical properties. Hot pressing is used to fabricate certain semiconductor components and ceramic substrates that require high purity and density.
For optical applications, the technology produces components with precise shapes and flawless internal structures, ensuring predictable light transmission.
Medical Technology: Biocompatible Implants
Materials used inside the human body must be pure, non-reactive, and extremely durable. Vacuum hot pressing is a key method for fabricating biocompatible materials for dental implants and surgical tools.
The process ensures the final product is free of contaminants and has the mechanical integrity to last for decades.
Research & Development: Prototyping Novel Materials
In scientific research, vacuum hot presses are indispensable tools for creating and testing new classes of materials.
This includes consolidating nanomaterials, developing new metal powder alloys, and experimenting with unique carbon composite structures that push the boundaries of material science.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hot pressing is a specialized process with inherent limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging these trade-offs.
High Cost and Complexity
Vacuum hot press furnaces are expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain. The combination of high vacuum, high temperature, and high pressure requires sophisticated engineering, leading to significant capital investment.
Slower Cycle Times
Compared to conventional manufacturing methods like casting or forging, hot pressing is a much slower, batch-oriented process. The time required to heat, press, and cool each part limits throughput, making it unsuitable for high-volume production.
Geometric Limitations
The need to apply uniform pressure generally restricts the process to simpler geometries, such as discs, blocks, and cylinders. Creating complex, three-dimensional shapes is often difficult or impossible, requiring extensive post-process machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum hot press depends entirely on whether the required material properties justify the cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance: This technology is unmatched for creating dense, pure materials that can withstand severe mechanical stress and high temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace, defense, and energy applications.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The vacuum environment is essential for producing biocompatible medical implants and high-purity electronic components where contamination is not an option.
- If your primary focus is innovation and research: A vacuum hot press is a fundamental tool for developing the next generation of advanced ceramics, composites, and nanomaterials.
Ultimately, vacuum hot pressing is the definitive solution when material performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Titanium alloys, superalloys, composites | High strength, lightweight, extreme durability |
| Advanced Ceramics | Silicon nitride, boron carbide, transparent ceramics | Ultra-hard, wear-resistant, optical clarity |
| Electronics & Optics | Semiconductor components, ceramic substrates | High purity, precise thermal/electrical properties |
| Medical Technology | Biocompatible materials for implants | Non-reactive, durable, long-lasting |
| Research & Development | Nanomaterials, metal powder alloys, carbon composites | Innovation in material science, prototyping |
Ready to elevate your material fabrication with precision and purity? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum hot press furnaces can deliver superior density, purity, and performance for your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?



















