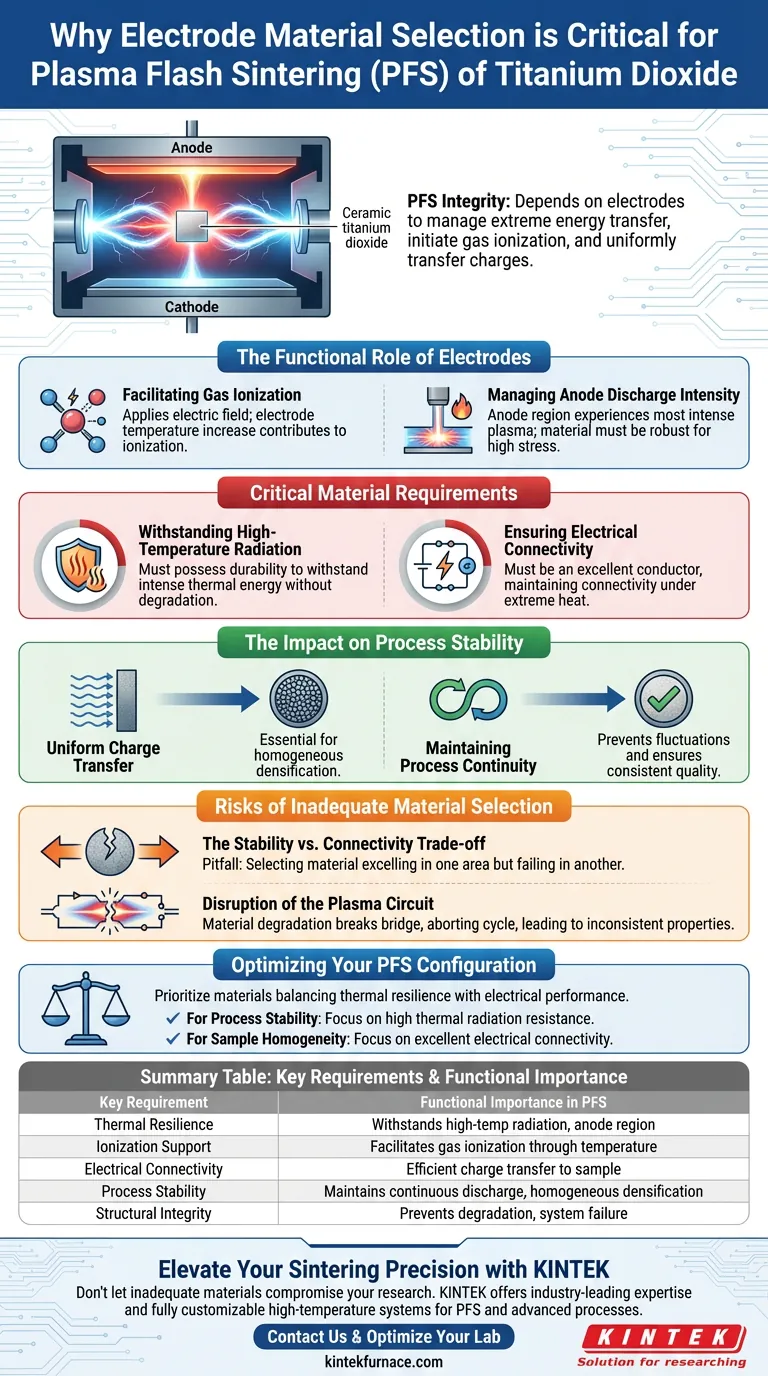
The integrity of the Plasma Flash Sintering (PFS) process hinges entirely on the capability of the electrode materials to manage extreme energy transfer. These components are not merely connectors; they are responsible for initiating gas ionization through temperature increases and transferring electrical charges uniformly from the plasma to the titanium dioxide sample.
In PFS, electrodes act as the critical interface between the power source and the ceramic body. Their ability to maintain stability under high-temperature radiation directly determines whether the plasma discharge remains continuous and effective.
The Functional Role of Electrodes
Facilitating Gas Ionization
Electrodes serve as the medium for applying the electric field necessary for the process.
Crucially, the temperature increase of the electrode material itself contributes to gas ionization. Without the right material properties to support this thermal rise, the plasma environment required for sintering cannot be effectively established.
Managing Anode Discharge Intensity
The interaction within the PFS chamber is not uniform across all zones.
The anode region typically experiences the most intense plasma discharge. Consequently, the material selected for the anode must be robust enough to handle higher stress levels than other components in the system.
Critical Material Requirements
Withstanding High-Temperature Radiation
Titanium dioxide sintering involves significant thermal energy.
High-quality electrodes must possess the physical durability to withstand high-temperature radiation without degrading. If the material fails under thermal stress, the physical structure of the electrode compromises the entire setup.
Ensuring Electrical Connectivity
Durability alone is insufficient; the material must also be an excellent conductor.
Electrodes must maintain excellent electrical connectivity even under extreme heat. This ensures that the electrical charges are transferred efficiently from the plasma to the ceramic body (the titanium dioxide).
The Impact on Process Stability
Uniform Charge Transfer
The goal of the electrode is to ensure the ceramic sample receives a consistent energy input.
Proper material selection ensures that electrical charges are transferred uniformly. This uniformity is essential for the homogeneous densification of the titanium dioxide sample.
Maintaining Process Continuity
Any interruption in the electrical field or plasma state can ruin the sample.
High-quality electrodes ensure process continuity and stability. They prevent fluctuations in the discharge that could lead to incomplete sintering or structural defects in the final ceramic product.
Risks of Inadequate Material Selection
The Stability vs. Connectivity Trade-off
A common pitfall in PFS is selecting a material that excels in one area but fails in another.
A material might be highly conductive but unable to withstand the radiation of the anode region. Conversely, a highly heat-resistant material might offer poor electrical connectivity, leading to an unstable plasma discharge.
Disruption of the Plasma Circuit
If the electrode material degrades, the bridge between the plasma and the ceramic breaks.
This leads to a loss of process stability, causing the sintering cycle to abort or producing a sample with inconsistent properties.
Optimizing Your PFS Configuration
To ensure successful sintering of titanium dioxide samples, you must prioritize materials that balance thermal resilience with electrical performance.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Prioritize materials with high thermal radiation resistance to survive the intense conditions of the anode region.
- If your primary focus is Sample Homogeneity: Select materials known for maintaining excellent electrical connectivity at high temperatures to ensure uniform charge transfer.
The right electrode material transforms the erratic energy of plasma into a precise, controlled tool for ceramic sintering.
Summary Table:
| Key Requirement | Functional Importance in PFS |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resilience | Withstands high-temperature radiation in the intense anode region. |
| Ionization Support | Facilitates gas ionization through controlled temperature increases. |
| Electrical Connectivity | Ensures efficient charge transfer from plasma to the ceramic sample. |
| Process Stability | Maintains continuous plasma discharge for homogeneous densification. |
| Structural Integrity | Prevents degradation and system failure under extreme energy stress. |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don't let inadequate electrode materials compromise your research or production. Achieving perfect densification in titanium dioxide requires equipment that balances thermal resilience with superior electrical performance.
KINTEK provides industry-leading expertise in high-temperature lab systems. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the unique demands of Plasma Flash Sintering and other advanced processes.
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs and see how our specialized solutions can ensure your process stability and sample homogeneity.
Visual Guide
References
- Eva Gil‐González, Luis A. Pérez‐Maqueda. Plasma‐flash sintering: Metastable phase stabilization and evidence of ionized species. DOI: 10.1111/jace.20105
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the holding time in a high-temperature furnace affect 0W Fe-C-B-Cr-W alloys? Optimize Phase Dissolution
- What role does temperature control play in biomass pyrolysis for biochar? Achieve Optimal Pore Structure & Yield
- What is the role of a high-temperature reaction furnace in flame fusion? Master Alumina Spheroidization
- Why is the ball milling step essential for NN-10ST ceramic synthesis? Unlock High-Purity Phase Formation
- What is the technical necessity of heating and stirring for K-Na alloy anodes? Ensure Peak Battery Performance
- How do high-temp furnace processes affect carbon nanofiber micro-morphology? Master Precise Structural Control
- What is the function of a high-pressure reactor in SHS? Optimize Tungsten Carbide Synthesis with Precision
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for Fe-CN@CoCN precursors? Preserve MOF Structural Integrity















