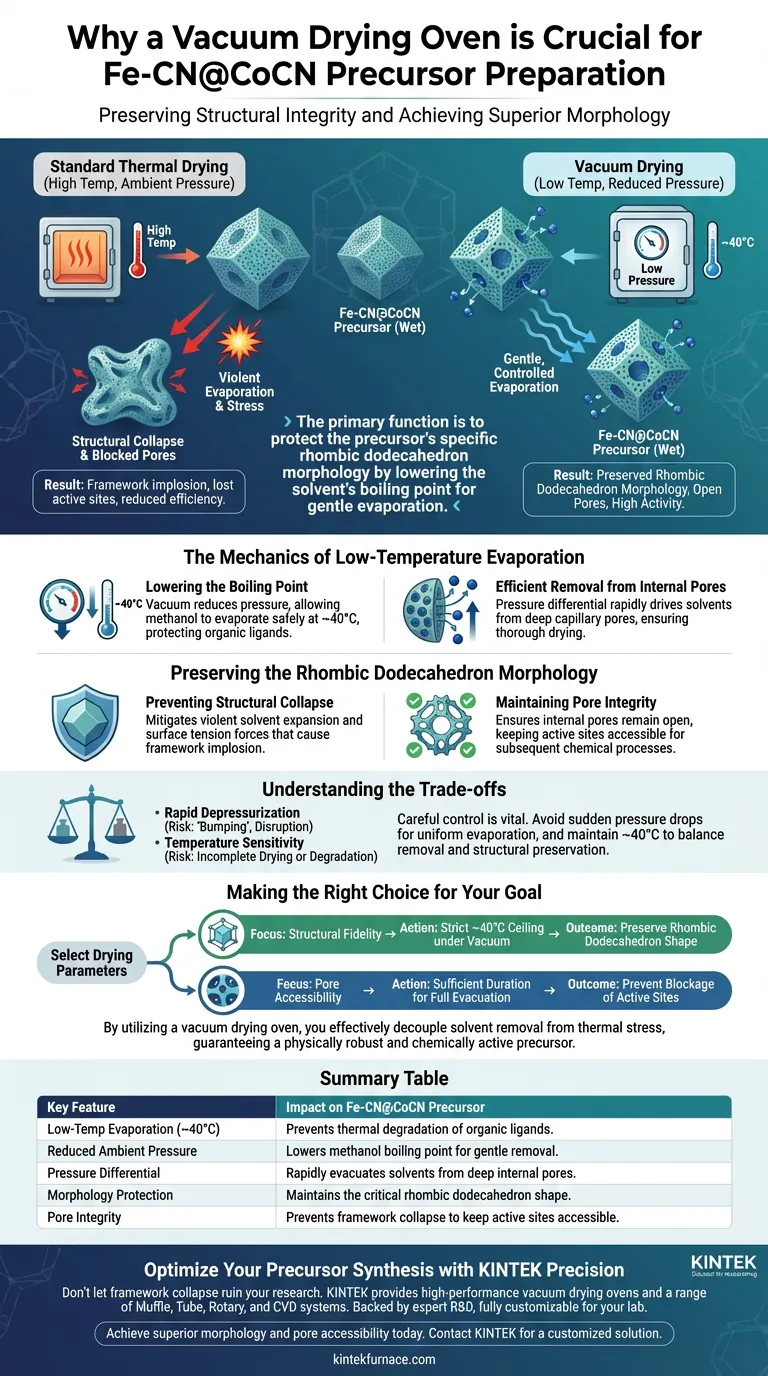
Vacuum drying is a critical step for preserving structural integrity. In the preparation of Fe-CN@CoCN precursors, this process is necessary to rapidly remove residual methanol solvent from the internal pores of Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) grains at a controlled low temperature, typically around 40°C. By significantly reducing environmental pressure, the oven allows the solvent to evaporate without the violent physical stress that causes framework collapse, thereby ensuring the final material retains its essential morphology.
The primary function of the vacuum drying oven is to protect the precursor’s specific rhombic dodecahedron morphology. It achieves this by lowering the solvent's boiling point, ensuring gentle evaporation that maintains the delicate internal pore structure.

The Mechanics of Low-Temperature Evaporation
Lowering the Boiling Point
The core challenge in drying MOF-based precursors is removing solvents trapped deep within the microstructure without applying excessive heat.
Under atmospheric pressure, removing methanol requires temperatures that could damage the organic ligands in the framework. A vacuum oven reduces the ambient pressure, which lowers the boiling point of the methanol. This allows the solvent to transition from liquid to gas at a safe temperature (~40°C), preserving the chemical composition of the precursor.
Efficient Removal from Internal Pores
Solvents like methanol can become tightly bound within the internal pores of the grains due to capillary action.
Standard thermal drying is often inefficient at drawing these deep-seated solvents out. The vacuum environment creates a pressure differential that rapidly drives the solvent out of the porous structure, ensuring the material is thoroughly dried rather than just superficially dried.
Preserving the Rhombic Dodecahedron Morphology
Preventing Structural Collapse
The Fe-CN@CoCN precursor relies on a specific geometric shape—the rhombic dodecahedron—to function effectively.
If the solvent is removed via high-temperature evaporation at standard pressure, the rapid expansion of gas and high surface tension forces can lead to "violent solvent evaporation." This physical stress causes the delicate MOF framework to implode or collapse. Vacuum drying mitigates this force, keeping the external and internal structure intact.
Maintaining Pore Integrity
The effectiveness of the final catalyst depends heavily on its surface area and pore accessibility.
By preventing collapse, the vacuum drying process ensures the internal pores remain open. If the structure were to collapse during drying, the active sites within the framework would be sealed off, rendering the precursor significantly less effective for subsequent chemical processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Rapid Depressurization
While vacuum drying is gentler than thermal drying, it requires careful control.
If the pressure is reduced too abruptly, the solvent may "bump" or boil explosively, which can mechanically disrupt the powder. The application of vacuum must be steady to ensure uniform evaporation rather than physical disruption.
Temperature Sensitivity
Even under vacuum, temperature control remains vital.
While the primary goal is to lower the drying temperature to 40°C, setting the temperature too low may result in incomplete solvent removal. Conversely, exceeding the recommended temperature negates the benefits of the vacuum, potentially leading to the very structural degradation the process is designed to avoid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the highest quality Fe-CN@CoCN precursor, align your drying parameters with your specific objective:
- If your primary focus is Structural Fidelity: Maintain a strict temperature ceiling of 40°C under vacuum to preserve the rhombic dodecahedron shape and prevent framework collapse.
- If your primary focus is Pore Accessibility: Ensure the drying duration is sufficient to fully evacuate residual methanol from the deep internal pores, preventing blockage of active sites.
By utilizing a vacuum drying oven, you effectively decouple solvent removal from thermal stress, guaranteeing a precursor that is physically robust and chemically active.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Impact on Fe-CN@CoCN Precursor |
|---|---|
| Low-Temp Evaporation (~40°C) | Prevents thermal degradation of organic ligands. |
| Reduced Ambient Pressure | Lowers methanol boiling point for gentle removal. |
| Pressure Differential | Rapidly evacuates solvents from deep internal pores. |
| Morphology Protection | Maintains the critical rhombic dodecahedron shape. |
| Pore Integrity | Prevents framework collapse to keep active sites accessible. |
Optimize Your Precursor Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don’t let framework collapse ruin your material research. KINTEK provides high-performance vacuum drying ovens designed to protect delicate MOF structures like Fe-CN@CoCN. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique lab requirements.
Achieve superior morphology and pore accessibility today.
Contact KINTEK for a customized solution
Visual Guide
References
- Shuning Ren, Hongyu Liang. Preparation of Metal–Organic-Framework-Derived Fe-CN@CoCN Nanocomposites and Their Microwave Absorption Performance. DOI: 10.3390/coatings14010133
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does 500°C annealing affect NiO-doped Ga2O3 thin films? Optimize Your High-Precision Thermal Treatment
- Why is a laboratory oven used for 80 °C drying before sintering NASICON membranes? Ensure Structural Integrity
- Why is precise temperature rate control in a sintering furnace vital for ceramic-sapphire composite production?
- How does microstructural observation assist in optimizing LATP sintering? Master High-Density Material Processing
- How does controlled thermal treatment affect delta-MnO2? Optimize Porosity & Surface Area for Better Battery Performance
- Why is MFI-type zeolite (S-1) selected for H-TiO2 synthesis? Master High-Efficiency Nanoparticle Templating
- What unique advantages does microwave heating equipment provide for iron-containing dust reduction? Boost Recovery Rates
- Why is a vacuum system composed of molecular and mechanical pumps essential? Ensure Purity in Magnetron Sputtering



















