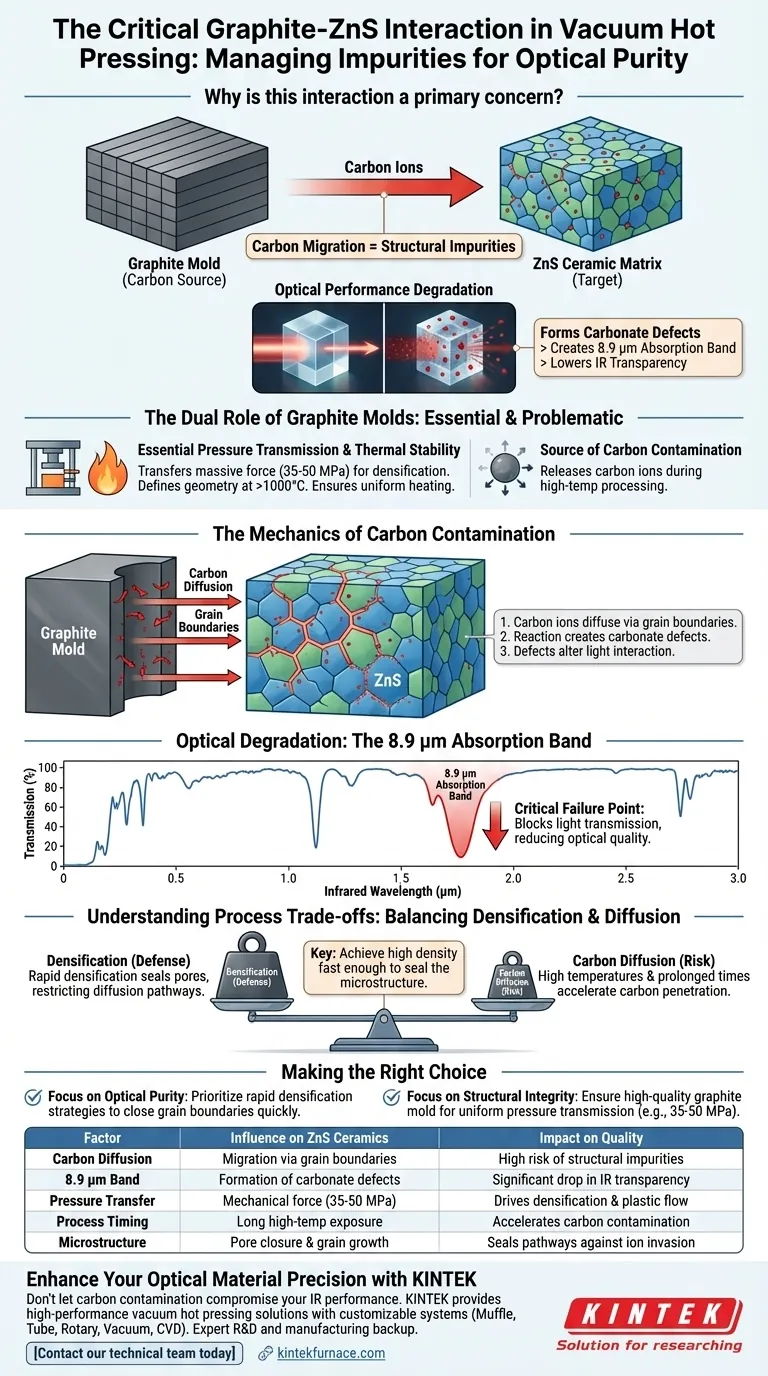
The interaction between graphite molds and Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) ceramics is a primary concern because it introduces structural impurities that degrade optical performance. During the high-temperature conditions of vacuum hot pressing, the graphite mold acts as a carbon source. Carbon ions migrate from the mold into the ceramic matrix, creating specific defects that compromise the material's transparency in the infrared spectrum.
The core issue is that carbon ions from the graphite mold diffuse into the ZnS ceramic through grain boundaries during sintering. This forms carbonate defects that create a specific infrared absorption band at 8.9 μm, directly lowering the optical quality of the final product.
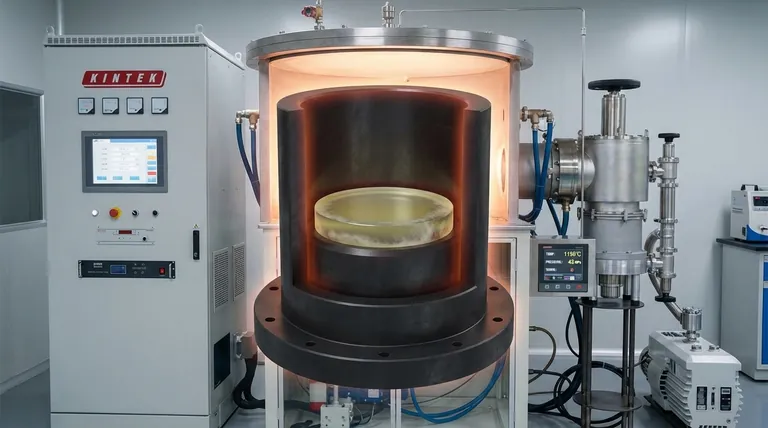

The Dual Role of Graphite Molds
To understand the risk, one must first understand why graphite is used despite the contamination potential.
Essential Pressure Transmission
Graphite molds are not merely containers; they are active pressure transmission media. They must transfer massive hydraulic force (often up to 50 MPa) uniformly to the ZnS powder. This mechanical pressure is what drives particle rearrangement and plastic flow, which are necessary for the material to densify.
Thermal Stability and Geometry
Graphite is selected for its ability to maintain structural integrity and define the ceramic's geometry at temperatures exceeding 1000°C. Its high thermal conductivity ensures the sample is heated uniformly, which is critical for consistent material properties.
The Mechanics of Carbon Contamination
While the mold is mechanically essential, chemically it presents a significant challenge during the sintering phase.
Diffusion via Grain Boundaries
At high processing temperatures, the graphite mold releases carbon ions. These ions do not simply coat the exterior; they diffuse into the ceramic body.
The primary pathway for this invasion is along the grain boundaries of the ZnS structure. These boundaries act as "highways" for impurities to penetrate deep into the material matrix.
Formation of Carbonate Defects
Once the carbon ions migrate into the ceramic, they react chemically within the structure. This reaction results in the formation of carbonate defects. These are not inert inclusions; they alter the fundamental interaction between the material and light.
Optical Degradation and Performance Loss
The consequence of this interaction is a measurable drop in the utility of the ceramic, particularly for optical applications.
The 8.9 μm Absorption Band
The most specific and damaging result of carbon diffusion is the creation of a distinct infrared absorption band at 8.9 μm.
Reduction in Transmission
For ZnS ceramics, which are typically valued for their infrared transparency, this absorption band is a critical failure point. It blocks light transmission at that specific wavelength, reducing the overall optical performance and efficiency of the component.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
Managing this interaction requires balancing the need for densification against the risk of contamination.
The Densification Defense
Achieving a dense microstructure is the primary defense against carbon contamination. As the material densifies and pores close, the pathways (grain boundaries) available for carbon diffusion are restricted.
The Timing Dilemma
There is a delicate trade-off in process control. High temperatures and prolonged times favor better densification (removing micro-pores). However, those same conditions accelerate carbon diffusion from the mold.
Grain Growth Management
If grains grow too large or the process is uncontrolled, the grain boundaries remain accessible for longer periods, increasing the depth of carbon penetration. Process control must focus on managing grain growth to effectively suppress this diffusion effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To mitigate the risks associated with graphite-ceramic interaction, focus on the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is Optical Purity: Prioritize rapid densification strategies to close grain boundaries quickly, blocking the physical pathways for carbon diffusion.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure the graphite mold quality is high to maintain uniform pressure transmission (e.g., 35-50 MPa), which drives the plastic deformation necessary to eliminate voids.
Ultimately, success in vacuum hot pressing ZnS relies on achieving high density fast enough to seal the microstructure before carbon ions can compromise the optical lattice.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Influence on ZnS Ceramics | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Diffusion | Migration via grain boundaries | High risk of structural impurities |
| 8.9 μm Band | Formation of carbonate defects | Significant drop in IR transparency |
| Pressure Transfer | Mechanical force (35-50 MPa) | Drives densification & plastic flow |
| Process Timing | Long high-temp exposure | Accelerates carbon contamination |
| Microstructure | Pore closure & grain growth | Seals pathways against ion invasion |
Enhance Your Optical Material Precision with KINTEK
Don't let carbon contamination compromise your IR performance. KINTEK provides high-performance vacuum hot pressing solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are fully customizable to help you manage the delicate balance of temperature, pressure, and material purity.
Ready to optimize your Zinc Sulfide production? Contact our technical team today to discover how our advanced lab furnaces can meet your unique material needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of benchtop SPS/FAST for titanium R&D? Accelerate Your Microstructural Engineering
- What are the characteristics of ultrahigh pressure sintering for ceramics? Achieve Dense, Fine-Grained Ceramics
- Why are hot press furnaces important in materials research? Unlock Advanced Material Synthesis
- What is the core technology behind vacuum press in metalworking industries? Unlock Precision Metal Forming
- What are the technical advantages of a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system? Achieve Superior TiB2 Ceramic Performance
- Why is high-strength graphite selected for vacuum hot pressing of thermoelectric alloys? High-Heat Stability Expert
- What key role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in ADSC alloys? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density & Purity
- What are the benefits of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace for the preparation of SiCw/2024 aluminum matrix composites? Achieve High-Performance Aerospace Materials



















