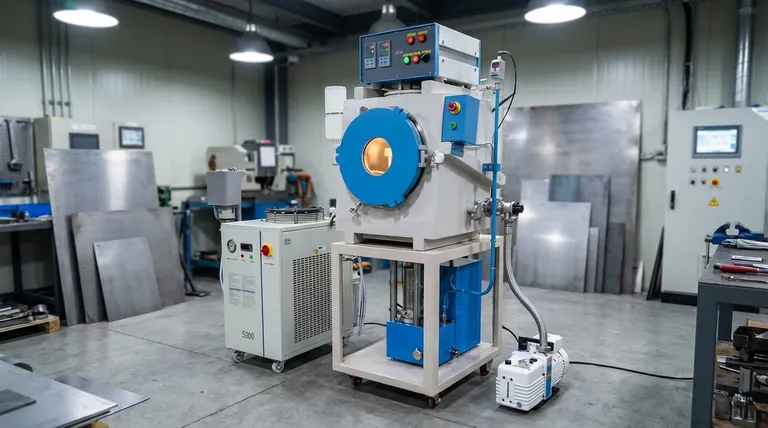
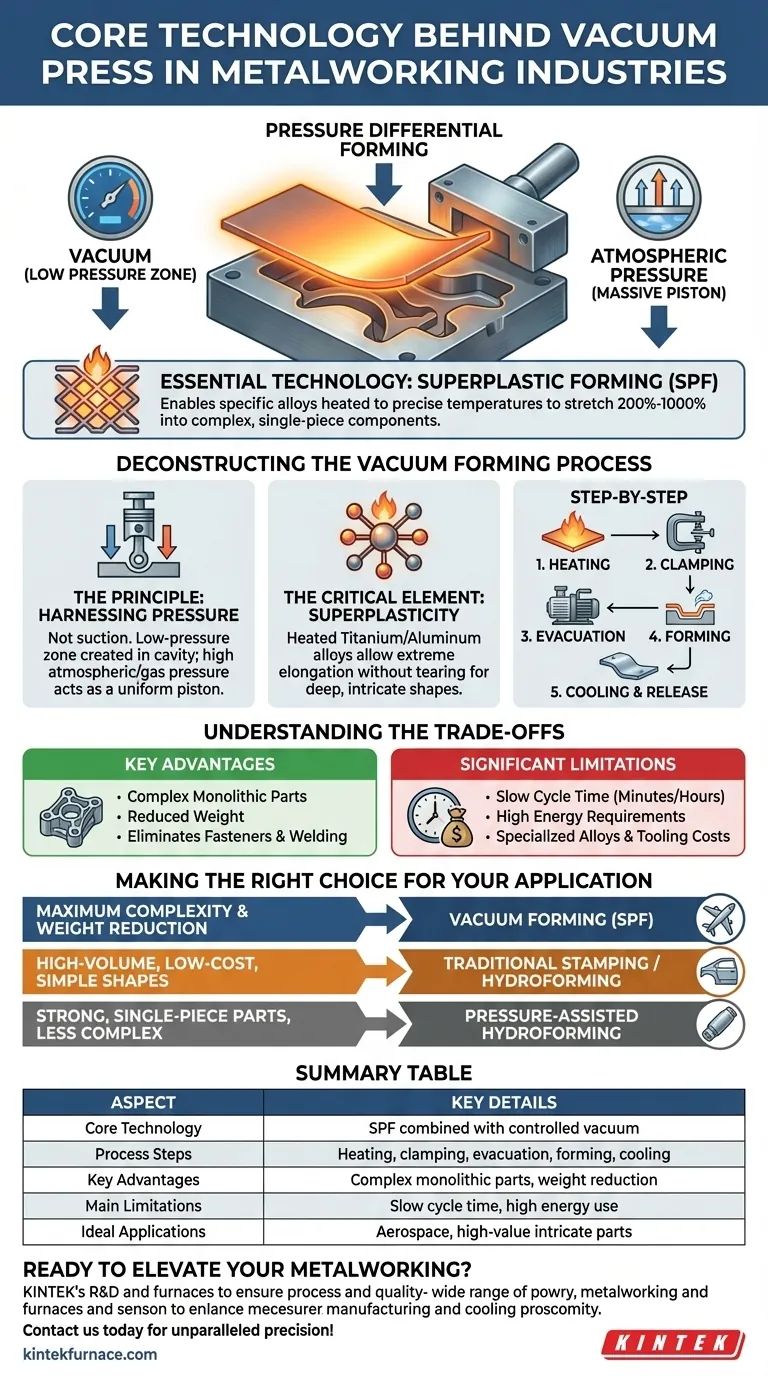
At its core, the technology behind a vacuum press in metalworking is a forming machine that uses a pressure differential to shape a heated metal sheet. By removing the air from between the metal and a mold, the machine harnesses external atmospheric pressure to force the pliable material to conform precisely to the mold's shape.
The essential technology is not just the vacuum itself, but the combination of a controlled vacuum with superplastic forming (SPF). This process enables specific metal alloys, heated to a precise temperature, to stretch into complex, single-piece components that would be impossible to create with traditional stamping.

Deconstructing the Vacuum Forming Process
To truly understand how this works for metals, we must look beyond the simple idea of suction and see it as a highly controlled engineering process.
The Principle: Harnessing Pressure
The term "vacuum suction" can be misleading. A vacuum press doesn't "pull" the metal onto the mold.
Instead, it creates a low-pressure zone in the sealed cavity between the metal sheet and the mold. The significantly higher atmospheric pressure (or applied gas pressure) on the other side of the sheet then acts as a massive, uniform piston, pushing the metal down and into every detail of the mold.
The Critical Element: Superplasticity
Unlike plastics, you cannot form cold metal in this way. The key is heating specific alloys—typically of titanium or aluminum—to a temperature where they exhibit superplasticity.
In this state, the metal can undergo extreme elongation (from 200% to over 1000%) without the necking, thinning, or tearing that would occur during conventional forming. This property is what allows for the creation of deep, intricate, and seamless shapes.
Step-by-Step: From Sheet to Component
The process is methodical and precise:
- Heating: A sheet of a superplastic alloy is heated to its specific forming temperature, often within the press itself using heated platens.
- Clamping: The hot sheet is securely clamped over a female die (the mold) inside a sealed press.
- Evacuation: A powerful vacuum system rapidly removes the air from the cavity between the sheet and the die.
- Forming: Atmospheric pressure pushes the material into the die. In many advanced applications, pressurized inert gas (like argon) is introduced on the top side to accelerate and control the forming process.
- Cooling & Release: Once fully formed, the part is cooled and then removed from the press.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum forming is a powerful but specialized tool. It is not a universal replacement for other metalworking methods. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses is critical for proper application.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is the ability to form complex, monolithic parts. This reduces the need for multiple smaller components, fasteners, and welding, which in turn decreases overall weight and eliminates potential points of failure. This is why it is indispensable in the aerospace industry for parts like engine nacelles, complex ducting, and fuselage panels.
Significant Limitations
The main drawback is slow cycle time. The heating, forming, and cooling process can take many minutes, or even hours, compared to the seconds required for traditional stamping.
Furthermore, the process has high energy requirements due to the sustained high temperatures. The specialized superplastic alloys and the complex tooling also contribute to a higher overall cost, making it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost consumer goods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct forming process depends entirely on your project's goals for complexity, material, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is maximum design complexity and weight reduction in high-value components: Vacuum forming with superplastic alloys is the superior, and often only, choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production of simple shapes: Traditional mechanical stamping or hydroforming will be far more economical and efficient.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, single-piece parts without the extreme complexity of SPF: Consider pressure-assisted hydroforming as a potential alternative.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum forming is a strategic decision to trade production speed for unparalleled geometric complexity and component integration.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Technology | Superplastic forming (SPF) combined with controlled vacuum |
| Process Steps | Heating, clamping, evacuation, forming, cooling & release |
| Key Advantages | Complex monolithic parts, weight reduction, no fasteners |
| Main Limitations | Slow cycle time, high energy use, specialized alloys |
| Ideal Applications | Aerospace components, high-value parts requiring intricate shapes |
Ready to elevate your metalworking with advanced vacuum press solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superplastic forming and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve unparalleled precision and efficiency in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between hot pressing and cold compacting and sintering? Optimize Your Material Manufacturing
- How does automation enhance the hot pressing process? Boost Precision, Efficiency, and Quality
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance
- What is a vacuum press and why is it important in modern manufacturing? Unlock Flawless Bonding and Precision
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density and Strength for Advanced Materials



















